Abstract
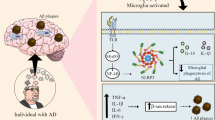
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is considered as one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorders characterized by progressive loss of mental function and ability to learn. AD is a multifactorial disorder. Various hypotheses are suggested for the pathophysiology of AD including “Aβ hypothesis,” “tau hypothesis,” and “cholinergic hypothesis.” Recently, it has been demonstrated that neuroinflammation is involved in the pathogenesis of AD. Neuroinflammation causes synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death within the brain. Excessive production of pro-inflammatory mediators induces Aβ peptide production/accumulation and hyperphosphorylated tau generating inflammatory molecules and cytokines. These inflammatory molecules disrupt blood–brain barrier integrity and increase the production of Aβ42 oligomers. Retinoids and carotenoids are potent antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents having neuroprotective properties. They are able to prevent disease progression through several mechanisms such as suppression of Aβ peptide production/accumulation, oxidative stress, and pro-inflammatory mediator’s secretion as well as improvement of cognitive performance. These observations, therefore, confirm the neuroprotective role of retinoids and carotenoids through multiple pathways. Therefore, the administration of these nutrients is considered as a promising approach to the prevention and/or treatment of AD in the future. The aim of this review is to present existing evidences regarding the beneficial effects of retinoids and carotenoids on AD’s risk and outcomes, seeking the mechanism of their action.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures (2015) Alzheimer’s & dementia: the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association 11:332–384
Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E (2006) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:41–53. doi:10.1038/nrn1824
Abdolahi M, Yavari P, Honarvar NM, Bitarafan S, Mahmoudi M, Saboor-Yaraghi AA (2015a) Molecular mechanisms of the action of vitamin A in Th17/Treg axis in multiple sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 57:605–613
Abdolahi M, Yavari P, Honarvar NM, Bitarafan S, Mahmoudi M, Saboor-Yaraghi AA (2015b) Molecular mechanisms of the action of vitamin A in Th17/Treg axis in multiple sclerosis. Journal of molecular neuroscience: MN 57:605–613. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0643-1
Ahlemeyer B, Bauerbach E, Plath M, Steuber M, Heers C, Tegtmeier F, Krieglstein J (2001) Retinoic acid reduces apoptosis and oxidative stress by preservation of SOD protein level. Free Radic Biol Med 30:1067–1077
Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J (2000) Inhibition of glutathione depletion by retinoic acid and tocopherol protects cultured neurons from staurosporine-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Neurochem Int 36:1–5
Ahmed AU (2011) An overview of inflammation: mechanism and consequences. Front Biol 6:274–281
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783–801
Al Nimer F, Beyeen AD, Lindblom R, Ström M, Aeinehband S, Lidman O, Piehl F (2011) Both MHC and non-MHC genes regulate inflammation and T-cell response after traumatic brain injury. Brain Behav Immun 25:981–990
Alcocer-Gómez E, de Miguel M, Casas-Barquero N, Núñez-Vasco J, Sánchez-Alcazar JA, Fernández-Rodríguez A, Cordero MD (2014) NLRP3 inflammasome is activated in mononuclear blood cells from patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav Immun 36:111–117
Alpsoy L, Yildirim A, Agar G (2009) The antioxidant effects of vitamin A, C, and E on aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress in human lymphocytes. Toxicol Ind Health 25:121–127
Anand R, Gill KD, Mahdi AA (2014) Therapeutics of Alzheimer’s disease: past, present and future. Neuropharmacology 76 Pt A:27–50. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.004
Anderson GD, Hauser SD, McGarity KL, Bremer ME, Isakson PC, Gregory SA (1996) Selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 reverses inflammation and expression of COX-2 and interleukin 6 in rat adjuvant arthritis. J Clin Investig 97:2672
Arunkumar E, Bhuvaneswari S, Anuradha CV (2012) An intervention study in obese mice with astaxanthin, a marine carotenoid—effects on insulin signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Food & function 3:120–126
Asadi F et al (2015) Reversal effects of crocin on amyloid β-induced memory deficit: modification of autophagy or apoptosis markers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 139:47–58
Balducci C et al (2015) The continuing failure of bexarotene in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 46:471–482
Barnes PJ (2009) Targeting the epigenome in the treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:693–696
Baune BT (2015) Inflammation and neurodegenerative disorders: is there still hope for therapeutic intervention? Current opinion in psychiatry 28:148–154
Behairi N, Belkhelfa M, Mesbah-Amroun H, Rafa H, Belarbi S, Tazir M, Touil-Boukoffa C (2015) All-trans-retinoic acid modulates nitric oxide and interleukin-17A production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimmunomodulation 22:385–393
Ben-Dor A et al (2005) Carotenoids activate the antioxidant response element transcription system. Mol Cancer Ther 4:177–186
Bezzi P et al (2001) CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNFalpha: amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat Neurosci 4:702–710. doi:10.1038/89490
Bohn T (2008) Bioavailability of non-provitamin A carotenoids. Curr Nutr Food Sci 4:240–258
Borel P (2012) Genetic variations involved in interindividual variability in carotenoid status. Mol Nutr Food Res 56:228–240
Borrmann C, Stricker R, Reiser G (2011) Retinoic acid-induced upregulation of the metalloendopeptidase nardilysin is accelerated by co-expression of the brain-specific protein p42 IP4 (centaurin α1; ADAP1) in neuroblastoma cells. Neurochem Int 59:936–944
Bouayed J, Bohn T (2012) Dietary derived antioxidants: implications on health. INTECH Open Access Publisher
Braak H, Del Tredici K (2011) Alzheimer’s pathogenesis: is there neuron-to-neuron propagation? Acta Neuropathol 121:589–595
Britton G (1995) Structure and properties of carotenoids in relation to function. FASEB J 9:1551–1558
Cagnin A et al (2001) In-vivo measurement of activated microglia in dementia. Lancet (London, England) 358:461–467. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(01)05625-2
Carey M, Smale S (2000) Transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes. Concepts, strategies, and techniques. Cold Spring Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Chan Kc, Pen PJ, Yin Mc (2012) Anticoagulatory and antiinflammatory effects of astaxanthin in diabetic rats. J Food Sci 77(2):H76–800
Chang C-H, Chen C-Y, Chiou J-Y, Peng RY, Peng C-H (2010) Astaxanthine secured apoptotic death of PC12 cells induced by β-amyloid peptide 25–35: its molecular action targets. J Med Food 13:548–556
Chen W et al (2015) Lycopene attenuates Aβ 1–42 secretion and its toxicity in human cell and Caenorhabditis elegans models of Alzheimer disease. Neurosci Lett 608:28–33
Chew B, Wong T, Michal J, Standaert F, Heirman L (1991) Subcellular distribution of beta-carotene, retinol, and alpha-tocopherol in porcine lymphocytes after a single injection of beta-carotene. J Anim Sci 69:4892–4897
Choi W-H et al (2005) Anti-inflammatory roles of retinoic acid in rat brain astrocytes: suppression of interferon-γ-induced JAK/STAT phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 329:125–131
Ciccone MM et al (2013) Dietary intake of carotenoids and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in cardiovascular care. Mediat Inflamm 2013:782137
Corbett A et al (2012) Drug repositioning for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:833–846
Craig-Schapiro R et al (2010) YKL-40: a novel prognostic fluid biomarker for preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Psychiatry 68:903–912
Crichton GE, Bryan J, Murphy KJ (2013) Dietary antioxidants, cognitive function and dementia—a systematic review. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 68:279–292
Cunningham AJ, Murray CA, O’Neill LA, Lynch MA, O’Connor JJ (1996) Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) inhibit long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 203:17–20
Cunningham C et al (2009) Systemic inflammation induces acute behavioral and cognitive changes and accelerates neurodegenerative disease. Biol Psychiatry 65:304–312
Dai W, Yang J, Chen T, Yang Z (2014) Protective effects of bexarotene against amyloid-β25-35-induced dysfunction in hippocampal neurons through the insulin signaling pathway. Neurodegener Dis 14:77–84
Dal Pra I et al (2015) Do astrocytes collaborate with neurons in spreading the "infectious" abeta and tau drivers of Alzheimer’s disease? The Neuroscientist: a review journal bringing neurobiology, neurology and psychiatry 21:9–29. doi:10.1177/1073858414529828
Dal Prà I et al (2015) Do astrocytes collaborate with neurons in spreading the “infectious” Aβ and tau drivers of Alzheimer’s disease? Neuroscientist 21:9–29
Dawson MI, Xia Z (2012) The retinoid X receptors and their ligands. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 1821:21–56
de Oliveira BF, Veloso CA, Nogueira-Machado JA, de Moraes EN, dos Santos RR, Cintra MT, Chaves MM (2012) Ascorbic acid, alpha-tocopherol, and beta-carotene reduce oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines in mononuclear cells of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Nutr Neurosci 15:244–251. doi:10.1179/1476830512y.0000000019
De Simone R, Ajmone-Cat MA, Minghetti L (2004) Atypical antiinflammatory activation of microglia induced by apoptotic neurons: possible role of phosphatidylserine-phosphatidylserine receptor interaction. Mol Neurobiol 29:197–212. doi:10.1385/mn:29:2:197
de Vries HE, Blom-Roosemalen MC, van Oosten M, de Boer AG, van Berkel TJ, Breimer DD, Kuiper J (1996) The influence of cytokines on the integrity of the blood-brain barrier in vitro. J Neuroimmunol 64:37–43
Deane R et al (2003) RAGE mediates amyloid-β peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat Med 9:907–913
Defo MA, Pierron F, Spear PA, Bernatchez L, Campbell PG, Couture P (2012) Evidence for metabolic imbalance of vitamin A2 in wild fish chronically exposed to metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 85:88–95
Dheen ST, Jun Y, Yan Z, Tay SS, Ang Ling E (2005) Retinoic acid inhibits expression of TNF-α and iNOS in activated rat microglia. Glia 50:21–31
Dias IH et al (2014) Plasma levels of HDL and carotenoids are lower in dementia patients with vascular comorbidities. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 40:399
Dilger RN, Johnson RW (2008) Aging, microglial cell priming, and the discordant central inflammatory response to signals from the peripheral immune system. J Leukoc Biol 84:932–939
Ding Y et al (2008a) Retinoic acid attenuates β-amyloid deposition and rescues memory deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mouse model. J Neurosci 28:11622–11634
Ding Y et al (2008b) Retinoic acid attenuates beta-amyloid deposition and rescues memory deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mouse model. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 28:11622–11634. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3153-08.2008
Dong Y, Benveniste EN (2001) Immune function of astrocytes. Glia 36:180–190
Dorosty-Motlagh AR, Honarvar NM, Sedighiyan M, Abdolahi M (2016) The molecular mechanisms of vitamin A deficiency in multiple sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 60:82–90
Dowlati Y, Herrmann N, Swardfager W, Liu H, Sham L, Reim EK, Lanctôt KL (2010) A meta-analysis of cytokines in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 67:446–457
Eisele YS et al (2010) Peripherally applied Aβ-containing inoculates induce cerebral β-amyloidosis. Science 330:980–982
El-Agamey A, McGarvey DJ (2008) Carotenoid radicals and radical ions. In: Carotenoids. Springer, p 119–154
Endres K et al (2014) Increased CSF APPs-α levels in patients with Alzheimer disease treated with acitretin. Neurology 83:1930–1935
Engelhardt B (2010) T cell migration into the central nervous system during health and disease: different molecular keys allow access to different central nervous system compartments. Clinical and Experimental Neuroimmunology 1:79–93
Feart C et al. (2015) Plasma carotenoids are inversely associated with dementia risk in an elderly French cohort. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci glv135
Fiala M, Liu Q, Sayre J, Pop V, Brahmandam V, Graves M, Vinters H (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2-positive macrophages infiltrate the Alzheimer’s disease brain and damage the blood–brain barrier. Eur J Clin Investig 32:360–371
Filteau SM, Rollins NC, Coutsoudis A, Sullivan KR, Willumsen JF, Tomkins AM (2001) The effect of antenatal vitamin A and β-carotene supplementation on gut integrity of infants of HIV-infected South African women. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 32:464–470
Fitz NF, Cronican AA, Lefterov I, Koldamova R (2013) Comment on "ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models". Science 340:924-c. doi:10.1126/science.1235809
Foy C, Passmore A, Vahidassr M, Young I, Lawson J (1999) Plasma chain-breaking antioxidants in Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia and Parkinson’s disease. QJM 92:39–45
Franceschelli S et al. (2014) Astaxanthin treatment confers protection against oxidative stress in U937 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide reducing O2− production
Frank MG, Baratta MV, Sprunger DB, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2007) Microglia serve as a neuroimmune substrate for stress-induced potentiation of CNS pro-inflammatory cytokine responses. Brain Behav Immun 21:47–59
Fukasawa H et al (2012) Tamibarotene: a candidate retinoid drug for Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Pharm Bull 35:1206–1212
Fung A, Vizcaychipi M, Lloyd D, Wan Y, Ma D (2012) Central nervous system inflammation in disease related conditions: mechanistic prospects. Brain Res 1446:144–155
Gabbita SP et al (2012) Early intervention with a small molecule inhibitor for tumor necrosis factor-alpha prevents cognitive deficits in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 9:99
Galimberti D, Ghezzi L, Scarpini E (2013a) Immunotherapy against amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 333:50–54. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2012.12.013
Germain P et al (2006) International Union of Pharmacology. LXIII. Retinoid X receptors. Pharmacol Rev 58:760–772
Ghahghaei A, Bathaie S, Kheirkhah H, Bahraminejad E (2013) The protective effect of crocin on the amyloid fibril formation of aβ42 peptide in vitro. Cell Mol Biol Lett 18:328–339
Godbout JP et al (2008) Aging exacerbates depressive-like behavior in mice in response to activation of the peripheral innate immune system. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2341–2351
Goncalves MB, Clarke E, Hobbs C, Malmqvist T, Deacon R, Jack J, Corcoran J (2013) Amyloid β inhibits retinoic acid synthesis exacerbating Alzheimer disease pathology which can be attenuated by an retinoic acid receptor α agonist. Eur J Neurosci 37:1182–1192
Goodman AB (2006) Retinoid receptors, transporters, and metabolizers as therapeutic targets in late onset Alzheimer disease. J Cell Physiol 209:598–603
Gutierrez EG, Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1993) Murine tumor necrosis factor alpha is transported from blood to brain in the mouse. J Neuroimmunol 47:169–176
Hadad N, Levy R (2012) The synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of lycopene, lutein, β-carotene, and carnosic acid combinations via redox-based inhibition of NF-κB signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 53:1381–1391
Hampel H (2012) Current insights into the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease: selecting targets for early therapeutic intervention. Int Psychogeriatr 24:S10–S17
Hannestad J, Della Gioia N, Bloch M (2011) The effect of antidepressant medication treatment on serum levels of inflammatory cytokines: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:2452–2459
Hardy J (2009) The amyloid hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: a critical reappraisal. J Neurochem 110:1129–1134
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297:353–356
Harrirchian MH et al (2014) The effect of vitamin A supplementation on disease progression, cytokine levels and gene expression in multiple sclerotic patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Acta medica Iranica 52:94–100
Havaux M (1998) Carotenoids as membrane stabilizers in chloroplasts. Trends Plant Sci 3:147–151
Heneka MT, O’Banion MK, Terwel D, Kummer MP (2010) Neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 117:919–947
Hirsch EC, Vyas S, Hunot S (2012) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18:S210–S212
Holmes C et al (2009) Systemic inflammation and disease progression in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 73:768–774
Honarvar NM et al (2013a) The effect of vitamin a supplementation on retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γt (RORγt) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) gene expression in avonex-treated multiple sclerotic patients. J Mol Neurosci 51:749–753
Honarvar NM et al (2013b) In vitro effect of human serum and fetal calf serum on CD4+ T cells proliferation in response to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) in correlation with RBP/TTR ratio in multiple sclerotic patients. Journal of molecular neuroscience: MN 50:571–576. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-9999-2
Horton JW, White DJ, Maass DL, Hybki DP, Haudek S, Giroir B (2001) Antioxidant vitamin therapy alters burn trauma-mediated cardiac NF-κB activation and cardiomyocyte cytokine secretion. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 50:397–408
Howren MB, Lamkin DM, Suls J (2009) Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med 71:171–186
Huang Y, Henry C, Dantzer R, Johnson R, Godbout J (2008) Exaggerated sickness behavior and brain proinflammatory cytokine expression in aged mice in response to intracerebroventricular lipopolysaccharide. Neurobiol Aging 29:1744–1753
Husson M, Enderlin V, Delacourte A, Ghenimi N, Alfos S, Pallet V, Higueret P (2006) Retinoic acid normalizes nuclear receptor mediated hypo-expression of proteins involved in β-amyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of vitamin A deprived rats. Neurobiol Dis 23:1–10
Jaeger LB et al (2009) Lipopolysaccharide alters the blood–brain barrier transport of amyloid β protein: a mechanism for inflammation in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav Immun 23:507–517
Jana M, Palencia CA, Pahan K (2008) Fibrillar amyloid-β peptides activate microglia via TLR2: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Immunol 181:7254–7262
Jarvis C et al (2010) Retinoic acid receptor-α signalling antagonizes both intracellular and extracellular amyloid-β production and prevents neuronal cell death caused by amyloid-β. Eur J Neurosci 32:1246–1255
Jiménez-Jiménez FJ et al (1999) Serum levels of β-carotene, α-carotene and vitamin A in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol 6:495–497
Jung YD et al (2002) Role of P38 MAPK, AP-1, and NF-kappaB in interleukin-1beta-induced IL-8 expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Cytokine 18:206–213
Kagechika H et al (1997) Inhibition of IL-1-induced IL-6 production by synthetic retinoids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 231:243–248
Kamenetz F et al (2003) APP processing and synaptic function. Neuron 37:925–937
Kampmann E, Johann S, Van Neerven S, Beyer C, Mey J (2008) Anti-inflammatory effect of retinoic acid on prostaglandin synthesis in cultured cortical astrocytes. J Neurochem 106:320–332
Kang SG, Lim HW, Andrisani OM, Broxmeyer HE, Kim CH (2007) Vitamin A metabolites induce gut-homing FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol 179:3724–3733
Kapoor A, Wang B-J, Hsu W-M, Chang M-Y, Liang S-M, Liao Y-F (2013) Retinoic acid-elicited RARα/RXRα signaling attenuates Aβ production by directly inhibiting γ-secretase-mediated cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. ACS Chem Neurosci 4:1093–1100
Katayama S, Ogawa H, Nakamura S (2011) Apricot carotenoids possess potent anti-amyloidogenic activity in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 59:12691–12696
Katsuki H et al (2009) Retinoic acid receptor stimulation protects midbrain dopaminergic neurons from inflammatory degeneration via BDNF-mediated signaling. J Neurochem 110:707–718
Kaulmann A, Bohn T (2014) Carotenoids, inflammation, and oxidative stress—implications of cellular signaling pathways and relation to chronic disease prevention. Nutr Res 34:907–929
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Dheen S, Ling E (2006) Insulin-like growth factor I and II expression and modulation in amoeboid microglial cells by lipopolysaccharide and retinoic acid. Neuroscience 138:1233–1244
Kawahara K et al (2009) Oral administration of synthetic retinoid Am80 (Tamibarotene) decreases brain beta-amyloid peptides in APP23 mice. Biol Pharm Bull 32:1307–1309
Kawahara K et al (2013) Cooperative therapeutic action of retinoic acid receptor and retinoid x receptor agonists in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 42:587–605
Khalili M, Hamzeh F (2010) Effects of active constituents of Crocus sativus L., crocin on streptozocin-induced model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in male rats. Iran Biomed J 14:59
Kiko T, Nakagawa K, Satoh A, Tsuduki T, Furukawa K, Arai H, Miyazawa T (2012a) Amyloid beta levels in human red blood cells. PLoS One 7:e49620. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0049620
Kiko T, Nakagawa K, Satoh A, Tsuduki T, Furukawa K, Arai H, Miyazawa T (2012b) Amyloid β levels in human red blood cells
Kiko T, Nakagawa K, Tsuduki T, Suzuki T, Arai H, Miyazawa T (2011) Significance of lutein in red blood cells of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 28:593–600
Kim CH (2010) Retinoic acid, immunity, and inflammation. Vitam Horm 86:83–101
Kim JE, Clark RM, Park Y, Lee J, Fernandez ML (2012) Lutein decreases oxidative stress and inflammation in liver and eyes of guinea pigs fed a hypercholesterolemic diet. Nutrition research and practice 6:113–119
Kipp M et al (2008) Brain-region-specific astroglial responses in vitro after LPS exposure. Journal of molecular neuroscience: MN 35:235–243. doi:10.1007/s12031-008-9057-7
Kitazawa M, Oddo S, Yamasaki TR, Green KN, LaFerla FM (2005) Lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation exacerbates tau pathology by a cyclin-dependent kinase 5-mediated pathway in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 25:8843–8853. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2868-05.2005
Kong Y et al (2014) The protective effects of crocetin on abeta(1)(−)(4)(2)-induced toxicity in Ht22 cells. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets 13:1627–1632
Koryakina A, Aeberhard J, Kiefer S, Hamburger M, Küenzi P (2009) Regulation of secretases by all-trans-retinoic acid. FEBS J 276:2645–2655
Kotilinek LA et al (2008) Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition improves amyloid-β-mediated suppression of memory and synaptic plasticity. Brain 131:651–664
Krishnaraj RN, Kumari SS, Mukhopadhyay SS (2015) Antagonistic molecular interactions of photosynthetic pigments with molecular disease targets: a new approach to treat AD and ALS. J Recept Signal Transduct 1–5
Kumar A, Dogra S (2008) Neuropathology and therapeutic management of Alzheimer’s disease—an update. Drugs Future 33:433–446
Kumar A, Singh A (2015) A review on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: an update. Pharmacol Rep 67:195–203
Kurz A, Perneczky R (2011a) Novel insights for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:373–379. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.07.018
LaClair KD, Manaye KF, Lee DL, Allard JS, Savonenko AV, Troncoso JC, Wong PC (2013) Treatment with bexarotene, a compound that increases apolipoprotein-E, provides no cognitive benefit in mutant APP/PS1 mice. Mol Neurodegener 8:18
Lacroix S, Rivest S (1998) Effect of acute systemic inflammatory response and cytokines on the transcription of the genes encoding cyclooxygenase enzymes (COX-1 and COX-2) in the rat brain. J Neurochem 70:452–466
Laflamme N, Lacroix S, Rivest S (1999) An essential role of interleukin-1beta in mediating NF-kappaB activity and COX-2 transcription in cells of the blood-brain barrier in response to a systemic and localized inflammation but not during endotoxemia. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 19:10923–10930
Landrum JT (2009) Carotenoids: physical, chemical, and biological functions and properties. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Lane MA, Bailey SJ (2005) Role of retinoid signalling in the adult brain. Prog Neurobiol 75:275–293
Lee H-P et al. (2009a) All-trans retinoic acid as a novel therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease
Lee S-A, Belyaeva OV, Kedishvili NY (2009b) Biochemical characterization of human epidermal retinol dehydrogenase 2. Chem Biol Interact 178:182–187
Lerner AJ, Gustaw-Rothenberg K, Smyth S, Casadesus G (2012) Retinoids for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Biofactors 38:84–89
Li F-J, Shen L, Ji H-F (2011) Dietary intakes of vitamin E, vitamin C, and β-carotene and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 31:253–258
Liaane-Jensen S, Lutnees BF (2008) Structure and properties of carotenoid cations. In: Carotenoids. Springer, pp 155–166
Liu B, Hong JS (2003) Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:1–7. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.035048
Liu X, Wu Z, Hayashi Y, Nakanishi H (2012) Age-dependent neuroinflammatory responses and deficits in long-term potentiation in the hippocampus during systemic inflammation. Neuroscience 216:133–142. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.04.050
Lu C-C, Yen G-C (2015) Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory activity of functional foods. Current Opinion in Food Science 2:1–8
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101:13–30
Lyman M, Lloyd DG, Ji X, Vizcaychipi MP, Ma D (2014) Neuroinflammation: the role and consequences. Neurosci Res 79:1–12
Maes M, Bosmans E, De Jongh R, Kenis G, Vandoolaeghe E, Neels H (1997) Increased serum IL-6 and IL-1 receptor antagonist concentrations in major depression and treatment resistant depression. Cytokine 9:853–858
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1291
Mecocci P et al (2002) Lymphocyte oxidative DNA damage and plasma antioxidants in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 59:794–798
Medzhitov R (2008) Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454:428–435
Medzhitov R (2010) Inflammation 2010: new adventures of an old flame. Cell 140:771–776
Melino G, Draoui M, Bernardini S, Bellincampi L, Reichert U, Cohen P (1996) Regulation by retinoic acid of insulin-degrading enzyme and of a related endoprotease in human neuroblastoma cell lines. Cell growth & differentiation: the molecular biology journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 7:787–796
Micheau O, Tschopp J (2003) Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 114:181–190
Min J-y, Min K-b (2014) Serum lycopene, lutein and zeaxanthin, and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease mortality in older adults. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 37:246–256
Mirza B, Hadberg H, Thomsen P, Moos T (2000) The absence of reactive astrocytosis is indicative of a unique inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 95:425–432
Mohammadzadeh Honarvar NM et al (2013) The effect of vitamin A supplementation on retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gammat (RORgammat) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) gene expression in Avonex-treated multiple sclerotic patients. Journal of molecular neuroscience: MN 51:749–753. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-0058-9
Monczak Y, Trudel M, Lamph WW, Miller WH Jr (1997) Induction of apoptosis without differentiation by retinoic acid in PLB-985 cells requires the activation of both RAR and RXR. Blood 90:3345–3355
Moylan S, Maes M, Wray N, Berk M (2013) The neuroprogressive nature of major depressive disorder: pathways to disease evolution and resistance, and therapeutic implications. Mol Psychiatry 18:595–606
Mrak RE, Griffin WST (2005) Glia and their cytokines in progression of neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging 26:349–354
Mueller L, Boehm V (2011) Antioxidant activity of β-carotene compounds in different in vitro assays. Molecules 16:1055–1069
Nakagawa K, Kiko T, Miyazawa T, Sookwong P, Tsuduki T, Satoh A, Miyazawa T (2011) Amyloid β-induced erythrocytic damage and its attenuation by carotenoids. FEBS Lett 585:1249–1254
Nalivaeva NN, Beckett C, Belyaev ND, Turner AJ (2012) Are amyloid-degrading enzymes viable therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease? J Neurochem 120:167–185
Nolan JM et al (2015) The impact of supplemental macular carotenoids in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized clinical trial. J Alzheimers Dis 44:1157–1169. doi:10.3233/jad-142265
Nolan JM et al (2014) Macular pigment, visual function, and macular disease among subjects with Alzheimer’s disease: an exploratory study. J Alzheimers Dis 42:1191–1202
Nolana JM et al (2015) The impact of supplemental macular carotenoids in Alzheimer’s disease: a randomized clinical trial. Methods 17:18
Nozaki Y, Yamagata T, Sugiyama M, Ikoma S, Kinoshita K, Funauchi M (2006) Anti-inflammatory effect of all-trans-retinoic acid in inflammatory arthritis. Clin Immunol 119:272–279
Obulesu M, Dowlathabad MR, Bramhachari P (2011) Carotenoids and Alzheimer’s disease: an insight into therapeutic role of retinoids in animal models. Neurochem Int 59:535–541
Ono K, Yoshiike Y, Takashima A, Hasegawa K, Naiki H, Yamada M (2004) Vitamin A exhibits potent antiamyloidogenic and fibril-destabilizing effects in vitro. Exp Neurol 189:380–392
Palozza P et al (2003) Beta-carotene regulates NF-kappaB DNA-binding activity by a redox mechanism in human leukemia and colon adenocarcinoma cells. J Nutr 133:381–388
Pereira AA, van Hattum B, Brouwer A (2012) Hepatic retinoid levels in seven fish species (teleosts) from a tropical coastal lagoon receiving effluents from iron-ore mining and processing. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:408–416
Pflanzner T et al. (2011) LRP1 mediates bidirectional transcytosis of amyloid-β across the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiology of aging 32:2323. e2321–2323. e2311
Polidori MC, Mecocci P (2002) Plasma susceptibility to free radical-induced antioxidant consumption and lipid peroxidation is increased in very old subjects with Alzheimer disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 4:517–522
Price AR, Xu G, Siemienski ZB, Smithson LA, Borchelt DR, Golde TE, Felsenstein KM (2013) Comment on "ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models". Science 340:924-d doi:10.1126/science.1234089
Qu M et al (2011) Protective effects of lycopene against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 505:286–290
R Carratu M, Marasco C, Signorile A, Scuderi C, Steardo L (2012) Are retinoids a promise for Alzheimer’s disease management? Curr Med Chem 19:6119–6125
Rafii MS, Aisen PS (2009) Recent developments in Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. BMC medicine 7:7
Ramirez-Bermudez J (2012) Alzheimer’s disease: critical notes on the history of a medical concept. Arch Med Res 43:595–599. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.11.008
Reitz C (2012) Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid cascade hypothesis: a critical review. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012:369808. doi:10.1155/2012/369808
Ricoy UM, Mao P, Manczak M, Reddy PH, Frerking ME (2011) A transgenic mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease has impaired synaptic gain but normal synaptic dynamics. Neurosci Lett 500:212–215
Ringheim GE, Szczepanik AM, Petko W, Burgher KL, Zu Zhu S, Chao CC (1998) Enhancement of beta-amyloid precursor protein transcription and expression by the soluble interleukin-6 receptor/interleukin-6 complex. Mol Brain Res 55:35–44
Roth AD, Ramírez G, Alarcón R, Von Bernhardi R (2005) Oligodendrocytes damage in Alzheimer’s disease: beta amyloid toxicity and inflammation. Biol Res 38:381–387
Rozovsky I, Finch C, Morgan T (1998) Age-related activation of microglia and astrocytes: in vitro studies show persistent phenotypes of aging, increased proliferation, and resistance to down-regulation. Neurobiol Aging 19:97–103
Saboor-Yaraghi AA et al (2015) The effect of vitamin a supplementation on FoxP3 and TGF-beta Gene expression in Avonex-treated multiple sclerosis patients. Journal of molecular neuroscience: MN 56:608–612. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0549-y
Sachdeva AK, Chopra K (2015) Lycopene abrogates Aβ (1–42)-mediated neuroinflammatory cascade in an experimental model of Alzheimer’s disease. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry
Saez TE, Pehar M, Vargas M, Barbeito L, Maccioni RB (2004) Astrocytic nitric oxide triggers tau hyperphosphorylation in hippocampal neurons. In vivo 18:275–280
Sahin M, Karaüzüm SB, Perry G, Smith MA, Alicigüzel Y (2005) Retinoic acid isomers protect hippocampal neurons from amyloid-β induced neurodegeneration. Neurotox Res 7:243–250
Salomone S, Caraci F, Leggio GM, Fedotova J, Drago F (2012) New pharmacological strategies for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: focus on disease modifying drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 73:504–517
Santos SD, Cahú TB, Firmino GO, de Castro CC, Carvalho LB Jr, Bezerra RS, José Filho LL (2012) Shrimp waste extract and astaxanthin: rat alveolar macrophage, oxidative stress and inflammation. J Food Sci 77:H141–H146
Sarrafchi A, Bahmani M, Shirzad H, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2015) Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease: new hopes in treatment with herbal antioxidants. Current pharmaceutical design
Sato M, Shudo K, Hiragun A (1988) Functional studies of newly synthesized benzoic acid derivatives: identification of highly potent retinoid-like activity. J Cell Physiol 135:179–188. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041350205
Saurer L, McCullough KC, Summerfield A (2007) In vitro induction of mucosa-type dendritic cells by all-trans retinoic acid. J Immunol 179:3504–3514
Schwaninger M, Sallmann S, Petersen N, Schneider A, Prinz S, Libermann TA, Spranger M (1999) Bradykinin induces interleukin-6 expression in astrocytes through activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. J Neurochem 73:1461–1466
Sedjo RL, Ranger-Moore J, Foote J, Craft NE, Alberts DS, Xu M-J, Giuliano AR (2004) Circulating endogenous retinoic acid concentrations among participants enrolled in a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of retinyl palmitate. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 13:1687–1692
Sen R, Baltimore D (1986) Inducibility of κ immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein NF-κB by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell 47:921–928
Shaw LM et al (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker signature in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative subjects. Ann Neurol 65:403–413
Shudo K, Fukasawa H, Nakagomi M, Yamagata N (2009) Towards retinoid therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 6:302
Sodhi RK, Singh N (2014) Retinoids as potential targets for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 120:117–123
Stahl W, Junghans A, de Boer B, Driomina ES, Briviba K, Sies H (1998) Carotenoid mixtures protect multilamellar liposomes against oxidative damage: synergistic effects of lycopene and lutein. FEBS Lett 427:305–308
Stahl W, Sies H (2003) Antioxidant activity of carotenoids. Mol Asp Med 24:345–351
Stalder AK et al (2005) Invasion of hematopoietic cells into the brain of amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J Neurosci 25:11125–11132
Streit WJ (2005) Microglia and neuroprotection: implications for Alzheimer’s disease brain research. Brain Res Rev 48:234–239. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.12.013
Subasinghe S, Unabia S, Barrow CJ, Mok SS, Aguilar MI, Small DH (2003) Cholesterol is necessary both for the toxic effect of Aβ peptides on vascular smooth muscle cells and for Aβ binding to vascular smooth muscle cell membranes. J Neurochem 84:471–479
Sugama S et al (2003) Age-related microglial activation in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration in C57BL/6 mice. Brain Res 964:288–294
Sugaya K et al (1996) Molecular indices of neuronal and glial plasticity in the hippocampal formation in a rodent model of age-induced spatial learning impairment. J Neurosci 16:3427–3443
Takasaki J et al (2010) Vitamin A has anti-oligomerization effects on amyloid-β in vitro. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 27:271–280
Tan Z et al (2007) Inflammatory markers and the risk of Alzheimer disease: the Framingham Study. Neurology 68:1902–1908
Teismann P et al (2003a) Cyclooxygenase-2 is instrumental in Parkinson’s disease neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:5473–5478. doi:10.1073/pnas.0837397100
Teismann P et al (2003b) Pathogenic role of glial cells in Parkinson’s disease. Movement disorders: official journal of the Movement Disorder Society 18:121–129. doi:10.1002/mds.10332
Terrando N et al (2011) Resolving postoperative neuroinflammation and cognitive decline. Ann Neurol 70:986–995
Tesseur I et al. (2013) Comment on "ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models". Science 340:924-e doi:10.1126/science.1233937
Tuppo EE, Arias HR (2005) The role of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:289–305
van Neerven S et al (2010) Inflammatory cytokine release of astrocytes in vitro is reduced by all-trans retinoic acid. J Neuroimmunol 229:169–179
Veeraraghavalu K et al. (2013) Comment on "ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear beta-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models". Science 340:924-f doi:10.1126/science.1235505
Vertuani S, Angusti A, Manfredini S (2004) The antioxidants and pro-antioxidants network: an overview. Curr Pharm Des 10:1677–1694
Vukic V et al (2009) Expression of inflammatory genes induced by beta-amyloid peptides in human brain endothelial cells and in Alzheimer’s brain is mediated by the JNK-AP1 signaling pathway. Neurobiol Dis 34:95–106
Wang R et al (2015) All-trans-retinoic acid reduces BACE1 expression under inflammatory conditions via modulation of nuclear factor κB (NFκB) signaling. J Biol Chem 290:22532–22542
Wang W, Shinto L, Connor WE, Quinn JF (2008) Nutritional biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease: the association between carotenoids, n-3 fatty acids, and dementia severity. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD 13:31–38
Waris G, Ahsan H (2006) Reactive oxygen species: role in the development of cancer and various chronic conditions. Journal of carcinogenesis 5:14
Wen X et al (2015) Neuroprotective effect of astaxanthin against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in HT22 cells: involvement of the Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Neuroscience 303:558–568
Wong D, Dorovini-Zis K, Vincent SR (2004) Cytokines, nitric oxide, and cGMP modulate the permeability of an in vitro model of the human blood–brain barrier. Exp Neurol 190:446–455
Woodall AA, Lee SW-M, Weesie RJ, Jackson MJ, Britton G (1997) Oxidation of carotenoids by free radicals: relationship between structure and reactivity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects 1336:33–42
Xing B, Bachstetter AD, Van Eldik LJ (2011) Microglial p38alpha MAPK is critical for LPS-induced neuron degeneration, through a mechanism involving TNFalpha. Mol Neurodegener 6:84. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-6-84
Yasojima K, McGeer E, McGeer P (2001) Relationship between beta amyloid peptide generating molecules and neprilysin in Alzheimer disease and normal brain. Brain Res 919:115–121
Yeum K-J, Aldini G, Russell RM, Krinsky NI (2009) Antioxidant/pro-oxidant actions of carotenoids. In: Carotenoids. Springer, pp 235–268
You X et al (2009) Retinoid X receptor-α mediates (R)-flurbiprofen’s effect on the levels of Alzheimer’s β-amyloid. J Neurochem 111:142–149
Zhang H, Gong B, Liu S, Fa M, Ninan I, Staniszewski A, Arancio O (2005) Synaptic fatigue is more pronounced in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2:137–140
Zhang X-S et al (2014a) Astaxanthin offers neuroprotection and reduces neuroinflammation in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Surg Res 192:206–213
Zhang Y et al (2014b) Involvement of inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced mice depressive-like behaviors. CNS neuroscience & therapeutics 20:119–124
Zhao J et al (2014) Retinoic acid isomers facilitate apolipoprotein E production and lipidation in astrocytes through the retinoid X receptor/retinoic acid receptor pathway. J Biol Chem 289:11282–11292
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance received by Mrs. Margaret Clarke from the School of Medicine, Western Sydney University who kindly edited of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadzadeh Honarvar, N., Saedisomeolia, A., Abdolahi, M. et al. Molecular Anti-inflammatory Mechanisms of Retinoids and Carotenoids in Alzheimer’s Disease: a Review of Current Evidence. J Mol Neurosci 61, 289–304 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0857-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0857-x