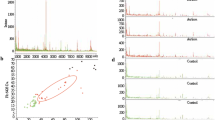
Abstract
According to WHO data, about 67 million people worldwide are affected by autism, and this number grows by 14% annually. Among the possible causes of autism are genetic modifications, organic lesions of the central nervous system, metabolic disorders, influence of viral and bacterial infections, chemical influence to the mother’s body during pregnancy, etc. The conducted research shows that research papers published until today do not name any potential protein markers that meet the requirements of the basic parameters for evaluating the efficiency of disease diagnostics, in particular high sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. Conducting proteomic research on a big scale in order to detect serologic markers of protein nature associated with development of autism spectrum disorders seems to be highly relevant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abruzzo PM, Ghezzo A, Bolotta A, Ferreri C, Minguzzi R, Vignini A, Visconti P, Marini M (2015) Perspective biological markers for autism spectrum disorders: advantages of the use of receiver operating characteristic curves in evaluating marker sensitivity and specificity. Disease Markers doi. doi:10.1155/2015/329607
Adamsen D, Meili D, Blau N, Thöny B, Ramaekers V (2011) Autism associated with low 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid in CSF and the heterozygous SLC6A4 gene Gly56Ala plus 5-HTTLPR L/L promoter variants. Mol Genet Metab 102:368–373
Anderson G, Maes M (2014) Redox regulation and the autistic spectrum: role of tryptophan catabolites, immuno-inflammation, autoimmunity and the amygdala. Curr Neuropharmacol 12:148–167. doi:10.2174/1570159X11666131120223757
Ashwood P, Krakowiak P, Hertz-Picciotto I, Hansen R, Pessah I, Van De Water J (2011) Elevated plasma cytokines in autism spectrum disorders provide evidence of immune dysfunction and are associated with impaired behavioral outcome. Brain Behav Immun 25:40–45
Bailey AR, Giunta BN, Obregon D, Nikolic WV, Tian J, Sanberg CD, Sutton DT, Tan J (2008) Peripheral biomarkers in autism: secreted amyloid precursor protein-alpha as a probable key player in early diagnosis. Int J Clin Exp Med 1:338–344
Betancur C (2011) Etiological heterogeneity in autism spectrum disorders: more than 100 genetic and genomic disorders and still counting. Brain Res 1380:42–77
Bobylova IYU, Petchatnikova IL (2013) Genetics of autistic disorder (review of foreign literature). Russian Journal of Child Neurology 8:31–45 (in Russ.). doi:10.17650/2073-8803-2013-8-3-31-45
Careaga M, Hansen RL, Hertz-Piccotto I, Van de Water J, Ashwood P (2013) Increased anti-phospholipid antibodies in autism spectrum disorders. Mediators Inflamm. doi:10.1155/2013/935608
Corbett BA, Kantor AB, Schulman H, Walker WL, Lit L, Ashwood P, Rocke DM, Sharp FR (2007) A proteomic study of serum from children with autism showing differential expression of apolipoproteins and complement proteins. Mol Psychiatry 12:292–306
Elamin NE, Al-Ayadhi LY (2014) Brain autoantibodies in autism spectrum disorder. Biomark Med 8:345–352
Filippova NV, Barylnik YB (2014) Genetic factors in etiopathogenesis of autistic spectrum disorders. Russian Society of Psychiatrists 24:96–100 (in Russ)
Folstein S, Rutter M (1977) Infantile autism: a genetic study of 21 twin pairs. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 18:297–321
Frye RE, Sequeira JM, Quadros EV, James SJ, Rossignol DA (2013) Cerebral folate receptor autoantibodies in autism spectrum disorder. Mol Psychiatry 18:369–381
Guilmatre A, Dubourg C, Mosca AL, Legallic S, Goldenberg A et al (2009) Recurrent rearrangements in synaptic and neurodevelopmental genes and shared biologic pathways in schizophrenia, autism, and mental retardation. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:947–956
Hajiyeva N, Pavlichenko AV, Kabosnidze K (2014) Advances in autistic spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (according to the proceedings of the 26st European College of Neuropsychopharmacology). Psychiatry and Psychopharmacotherapy 16(3):41–44 (in Russian)
Hashimoto K, Iwata Y, Nakamura K, Tsujii M, Tsuchiya KJ, Sekine Y, Suzuki K, Minabe Y, Takei N, Iyo M, Mori N (2006) Reduced serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adult male patients with autism. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1529–1531
Iourov IY, Vorsanova SG, Yurov YB (2013) Somatic cell genomics of brain disorders: a new opportunity to clarify genetic-environmental interactions. Cytogenet Genome Res 139:181–188
Iourov IY, Vorsanova SG, Korostelev SA, Zelenova MA, Yurov YB (2015) Long contiguous stretches of homozygosity spanning shortly the imprinted loci are associated with intellectual disability, autism and/or epilepsy. Mol Cytogenet 8:77
Jiang YH, Wang Y, Xiu X, Choy KW, Pursley AN, Cheung SW (2014) Genetic diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders: the opportunity and challenge in the genomics era. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 51:249–262
Ramsey JM, Guest PC, Broek JA, Glennon JC, Rommelse N, Franke B, Rahmoune H, Buitelaar JK, Bahn S (2013) Identification of an age-dependent biomarker signature in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Mol Autism 4:27. doi:10.1186/2040-2392-4-27
Kaysheva AL, Kopylov AT, Yurov IY, Vorsanova SG, Yurov YB, Galiullin RA, Anashkina AS, Archakov AI, Ivanov YD (2016) Proteomic analysis of blood serum protein profiles in children with autism. Clinical Practice in Pediatrics 11:12–17 (in Russ)
Moeller S, Lau NM, Green PH, Hellberg D, Higgins JJ, Rajadhyaksha AM, Alaedini A (2013) Lack of association between autism and anti-GM1 ganglioside antibody. Neurology 81:1640–1641
Momeni N, Bergquist J, Brudin L, Behnia F, Sivberg B, Joghataei MT, Persson BL (2012) A novel blood-based biomarker for detection of autism spectrum disorders. Transl Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/tp.2012.19
Mostafa GA, AL-Ayadhi LY (2011) Increased serum levels of anti-ganglioside M1 autoantibodies in autistic children: relation to the disease severity. J Neuroinflammation. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-8-39
Mostafa GA, Al-Ayadhi LY (2013) The possible relationship between allergic manifestations and elevated serum levels of brain specific auto-antibodies in autistic children. J Neuroimmunol 261:77–81. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2013.04.003
Neale BM, Kou Y, Stevens L, Wang LS, Makarov V, Polak P (2012) Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature 485:242–245
O'Roak BJ, Vives L, Girirajan S, Karakoc E, Lee C, Smith JD et al (2012) Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature 485:246–250
Parker KJ, Garner JP, Libove RA, Hyde SA, Hornbeak KB, Carson DS, Liao CP, Phillips JM, Hallmayer JF, Hardan AY (2014) Plasma oxytocin concentrations and OXTR polymorphisms predict social impairments in children with and without autism spectrum disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:12258–12263
Rose D, Ashwood P (2014) Potential cytokine biomarkers in autism spectrum disorders. Biomark Med 8:1171–1181
Rossignol DA, Genuis SJ, Frye RE (2014) Environmental toxicants and autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Transl Psychiatry 4:e360. doi:10.1038/tp.2014.4
Singer HS, Morris CM, Williams PN, Yoon DY, Hong JJ, Zimmerman AW (2006) Antibrain antibodies in children with autism and their unaffected siblings. J Neuroimmunol 178:149–155
Singh VK, Rivas WH (2004) Prevalence of serum antibodies to caudate nucleus in autistic children. Neurosci Lett 355:53–56
Suzuki K, Matsuzaki H, Iwata K, Kameno Y, Shimmura C, Kawai S, Yoshihara Y, Wakuda T, Takebayashi K, Takagai S, Matsumoto K, Tsuchiya KJ, Iwata Y, Nakamura K, Tsujii M, Sugiyama T, Mori N (2011) Plasma cytokine profiles in subjects with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020470
Taurines R, Dudley E, Conner AC, Grassl J, Jans T, Guderian F, Mehler-Wex C, Warnke A, Gerlach M, Thome J (2010) Serum protein profiling and proteomics in autistic spectrum disorder using magnetic bead-assisted mass spectrometry. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 260:249–255
Voineagu I, Yoo HJ (2013) Current progress and challenges in the search for autism biomarkers. Dis Markers 35:55–65
Vorsanova SG, Voinova VY, Yurov IY, Kurinnaya OS, Demidova IA, Yurov YB (2010) Cytogenetic, molecular-cytogenetic, and clinical-genealogical studies of the mothers of children with autism: a search for familial genetic markers for autistic disorders. Neurosci Behav Physiol 40:745–756
Yeh E, Weiss LA (2016) If genetic variation could talk: what genomic data may teach us about the importance of gene expression regulation in the genetics of autism. Mol Cell Probes. doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2016.10.007
Yurov IY, Vorsanova SG, Korostelev SA, Vasin KS, Zelenova MA, Kurinnaya OS, Yurov YB (2016) Structural variations of the genome in autistic spectrum disorders with intellectual disability. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova 116(7):50–54 (in Russian)
Acknowledgments
The study was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation (grant no. 14-25-00132).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khramova, T.V., Kaysheva, A.L., Ivanov, Y.D. et al. Serologic Markers of Autism Spectrum Disorder. J Mol Neurosci 62, 420–429 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0950-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-017-0950-9