Abstract
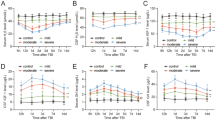
The use of methamphetamine (METH) is a growing worldwide epidemic that bears grave societal implications. METH is known to exert its neurotoxic effects on the dopaminergic and serotonergic systems of the brain. In addition to this classical studied mechanism of damage, findings from our laboratory and others have shown that acute METH treatment and mechanical injury, i.e. traumatic brain injury (TBI), share common cell injury mechanism(s). Since neuro-inflammation is a signature event in TBI, we hypothesize that certain cytokine levels might also be altered in rat brain exposed to an acute METH insult. In this study, using a cytokine antibody array chip, we evaluated the serum levels of 19 cytokines in rats 24 h after exposure to a 40 mg/kg acute regimen of METH. Data were compared to rats subjected to experimental TBI using the controlled cortical impact (CCI) injury model and saline controls. Sandwich ELISA method was used to further validate some of the findings obtained from the antibody cytokine array. We confirmed that three major inflammatory-linked cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10) were elevated in the METH and TBI groups compared to the saline group. Such finding suggests the involvement of an inflammatory process in these brain insults, indicating that METH use is, in fact, a stressor to the immune system where systemic involvement of an altered cytokine profile may play a major role in mediating chemical brain injury after METH use.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article
Change history
07 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01931-6
Abbreviations
- IL:
-
Interleukin
- METH:
-
Methamphetamine
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- TBI:
-
Traumatic brain injury
- NK:
-
Natural killers
- APC:
-
Antigen-presenting cells
References
Akbari A, Mosayebi G, Samiei AR, Ghazavi A (2019) Methadone therapy modulate the dendritic cells of heroin addicts. Int Immunopharmacol 66:330–335
Apuzzo ML, Sheikh KM, Heiden JS, Weiss MH, Kurze T (1979) Definition of cellular immune responses to brain antigens in human head trauma. J Neurosurg 51:317–322
Ares-Santos S, Granado N, Moratalla R (2013) The role of dopamine receptors in the neurotoxicity of methamphetamine. J Intern Med 273:437–453
Asanuma M, Miyazaki I, Higashi Y, Tsuji T, Ogawa N (2004) Specific gene expression and possible involvement of inflammation in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:69–75
Benveniste EN (1998) Cytokine actions in the central nervous system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 9:259–275
Borgmann K, Ghorpade A (2015) HIV-1, methamphetamine and astrocytes at neuroinflammatory Crossroads. Front Microbiol 6
Bowyer JF, Ali S (2006) High doses of methamphetamine that cause disruption of the blood-brain barrier in limbic regions produce extensive neuronal degeneration in mouse hippocampus. Synapse 60:521–532
Bowyer JF, Pogge AR, Delongchamp RR, O’Callaghan JP, Patel KM, Vrana KE, Freeman WM (2007) A threshold neurotoxic amphetamine exposure inhibits parietal cortex expression of synaptic plasticity-related genes. Neuroscience 144:66–76
Cadet JL, Jayanthi S, Deng X (2003) Speed kills: cellular and molecular bases of methamphetamine-induced nerve terminal degeneration and neuronal apoptosis. Faseb J 17:1775–1788
Cadet JL, Ordonez SV, Ordonez JV (1997) Methamphetamine induces apoptosis in immortalized neural cells: protection by the proto-oncogene, bcl-2. Synapse 25:176–184
Chiaretti A, Antonelli A, Riccardi R, Genovese O, Pezzotti P, Di Rocco C, Tortorolo L, Piedimonte G (2008) Nerve growth factor expression correlates with severity and outcome of traumatic brain injury in children. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 12:195–204
Connor TJ (2004) Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ’Ecstasy’): a stressor on the immune system. Immunology 111:357–367
Courtney KE, Ray LA (2014) Methamphetamine: an update on epidemiology, pharmacology, clinical phenomenology, and treatment literature. Drug Alcohol Depend 143:11–21
Csuka E, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Lenzlinger PM, Joller H, Trentz O, Kossmann T (1999) IL-10 levels in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with severe traumatic brain injury: relationship to IL-6, TNF-alpha, TGF-beta1 and blood-brain barrier function. J Neuroimmunol 101:211–221
Czigner A, Mihaly A, Farkas O, Buki A, Krisztin-Peva B, Dobo E, Barzo P (2007) Kinetics of the cellular immune response following closed head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien)
Czogalla A, Sikorski AF (2005) Spectrin and calpain: a “target” and a “sniper” in the pathology of neuronal cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:1913–1924
Dinarello CA (2014) An expanding role for interleukin-1 blockade from gout to cancer. Mol Med 20(Suppl 1):S43-58
Du SH, Qiao DF, Chen CX, Chen S, Liu C, Lin Z, Wang H, Xie WB (2017) Toll-Like Receptor 4 Mediates Methamphetamine-Induced Neuroinflammation through Caspase-11 Signaling Pathway in Astrocytes. Front Mol Neurosci 10:409
Erta M, Quintana A, Hidalgo J (2012) Interleukin-6, a major cytokine in the central nervous system. Int J Biol Sci 8:1254–1266
Eugenin EA, Greco JM, Frases S, Nosanchuk JD, Martinez LR (2013) Methamphetamine alters blood brain barrier protein expression in mice, facilitating central nervous system infection by neurotropic Cryptococcus neoformans. J Infect Dis 208:699–704
Farkas O, Polgar B, Szekeres-Bartho J, Doczi T, Povlishock JT, Büki A (2005) Spectrin breakdown products in the cerebrospinal fluid in severe head injury - preliminary observations. Acta Neurochir (wien) 147:855–861
Ginawi OT, Al-Majed AA, Al-Suwailem AK (2005) NAN-190, a possible specific antagonist for methamphetamine. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 41:122–127
Ginawi OT, Al-Majed AA, Al-Suwailem AK, El-Hadiyah TM (2004) Involvement of some 5-HT receptors in methamphetamine-induced locomotor activity in mice. J Physiol Pharmacol 55:357–369
Gonçalves J, Martins T, Ferreira R, Milhazes N, Borges F, Ribeiro CF, Malva JO, Macedo TR, Silva AP (2008) Methamphetamine-Induced Early Increase of IL-6 and TNF-α mRNA Expression in the Mouse Brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139:103–111
Gruol DL, Nelson TE (1997) Physiological and pathological roles of interleukin-6 in the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 15:307–339
Haskins WE, Kobeissy FH, Wolper RA, Ottens AK, Kitlen JW, McClung SH, O’Steen BE, Chow MM, Pineda JA, Denslow ND, Hayes RL, Wang KK (2005) Rapid discovery of putative protein biomarkers of traumatic brain injury by SDS-PAGE-capillary liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Neurotrauma 22:629–644
Hayakata T, Shiozaki T, Tasaki O, Ikegawa H, Inoue Y, Toshiyuki F, Hosotubo H, Kieko F, Yamashita T, Tanaka H, Shimazu T, Sugimoto H (2004) Changes in CSF S100B and cytokine concentrations in early-phase severe traumatic brain injury. Shock 22:102–107
Hedegaard H, Bastian BA, Trinidad JP, Spencer M, Warner M (2018) Drugs Most Frequently Involved in Drug Overdose Deaths: United States, 2011–2016. Natl Vital Stat Rep 67:1–14
Hirata H, Cadet JL (1997) p53-knockout mice are protected against the long-term effects of methamphetamine on dopaminergic terminals and cell bodies. J Neurochem 69:780–790
Ho EL, Josephson SA, Lee HS, Smith WS (2009) Cerebrovascular complications of methamphetamine abuse. Neurocrit Care 10:295–305
House RV, Thomas PT, Bhargava HN (1994) Comparison of immune functional parameters following in vitro exposure to natural and synthetic amphetamines. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 16:1–21
Ikeda T, Xia XY, Xia YX, Ikenoue T, Han B, Choi BH (2000) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemia/hypoxia-induced brain injury in neonatal rat. Acta Neuropathol 100:161–167
Itzhak Y, Ali SF (1996) The neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, 7-nitroindazole, protects against methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in vivo. J Neurochem 67:1770–1773
Jimenez A, Jorda EG, Verdaguer E, Pubill D, Sureda FX, Canudas AM, Escubedo E, Camarasa J, Camins A, Pallas M (2004) Neurotoxicity of amphetamine derivatives is mediated by caspase pathway activation in rat cerebellar granule cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 196:223–234
Kamm K, Vanderkolk W, Lawrence C, Jonker M, Davis AT (2006) The effect of traumatic brain injury upon the concentration and expression of interleukin-1beta and interleukin-10 in the rat. J Trauma 60:152–157
Kobeissy FH, Ottens AK, Zhang Z, Liu MC, Denslow ND, Dave JR, Tortella FC, Hayes RL, Wang KK (2006) Novel differential neuroproteomics analysis of traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:1887–1898
Kousik SM, Napier TC, Carvey PM (2012) The effects of psychostimulant drugs on blood brain barrier function and neuroinflammation. Front Pharmacol 3:121
Krueger J, Ray A, Tamm I, Sehgal PB (1991) Expression and function of interleukin-6 in epithelial cells. J Cell Biochem 45:327–334
Kuhn DM, Francescutti-Verbeem DM, Thomas DM (2006) Dopamine quinones activate microglia and induce a neurotoxic gene expression profile: relationship to methamphetamine-induced nerve ending damage. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1074:31–41
Ladenheim B, Krasnova IN, Deng X, Oyler JM, Polettini A, Moran TH, Huestis MA, Cadet JL (2000) Methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity is attenuated in transgenic mice with a null mutation for interleukin-6. Mol Pharmacol 58:1247–1256
Lai KSP, Liu CS, Rau A, Lanctôt KL, Köhler CA, Pakosh M, Carvalho AF, Herrmann N (2017) Peripheral inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 175 studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 88:876–882
Lan KC, Lin YF, Yu FC, Lin CS, Chu P (1998) Clinical manifestations and prognostic features of acute methamphetamine intoxication. J Formos Med Assoc 97:528–533
Lauw FN, Pajkrt D, Hack CE, Kurimoto M, van Deventer SJ, van der Poll T (2000) Proinflammatory effects of IL-10 during human endotoxemia. J Immunol 165:2783–2789
Liu HM, Sturner WQ (1988) Extravasation of plasma proteins in brain trauma. Forensic Sci Int 38:285–295
Liu X, Silverstein PS, Singh V, Shah A, Qureshi N, Kumar A (2012) Methamphetamine increases LPS-mediated expression of IL-8, TNF-α and IL-1β in human macrophages through common signaling pathways. PLoS One 7:e33822
Loftis JM, Janowsky A (2014) Neuroimmune basis of methamphetamine toxicity. Int Rev Neurobiol 118:165–197
Lotan M, Schwartz M (1994) Cross talk between the immune system and the nervous system in response to injury: implications for regeneration. Faseb J 8:1026–1033
Lotocki G, Alonso OF, Frydel B, Dietrich WD, Keane RW (2003) Monoubiquitination and cellular distribution of XIAP in neurons after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:1129–1136
Lwin T, Yang JL, Ngampramuan S, Viwatpinyo K, Chancharoen P, Veschsanit N, Pinyomahakul J, Govitrapong P, Mukda S (2020) Melatonin ameliorates methamphetamine-induced cognitive impairments by inhibiting neuroinflammation via suppression of the TLR4/MyD88/NFκB signaling pathway in the mouse hippocampus. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 110109
Mahajan SD, Aalinkeel R, Sykes DE, Reynolds JL, Bindukumar B, Adal A, Qi M, Toh J, Xu G, Prasad PN, Schwartz SA (2008) Methamphetamine alters blood brain barrier permeability via the modulation of tight junction expression: Implication for HIV-1 neuropathogenesis in the context of drug abuse. Brain Res 1203:133–148
Maier B, Schwerdtfeger K, Mautes A, Holanda M, Muller M, Steudel WI, Marzi I (2001) Differential release of interleukines 6, 8, and 10 in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma after traumatic brain injury. Shock 15:421–426
Marciano PG, Eberwine JH, Ragupathi R, Saatman KE, Meaney DF, McIntosh TK (2002) Expression profiling following traumatic brain injury: a review. Neurochem Res 27:1147–1155
Miyazaki M, Noda Y, Mouri A, Kobayashi K, Mishina M, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2013) Role of convergent activation of glutamatergic and dopaminergic systems in the nucleus accumbens in the development of methamphetamine psychosis and dependence. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:1341–1350
Mizoguchi H, Yamada K, Mouri A, Niwa M, Mizuno T, Noda Y, Nitta A, Itohara S, Banno Y, Nabeshima T (2007) Role of matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of MMP in methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization and reward: implications for dopamine receptor down-regulation and dopamine release. J Neurochem 102:1548–1560
Mizoguchi H, Yamada K, Nabeshima T (2008) Neuropsychotoxicity of abused drugs: involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization and reward in rodents. J Pharmacol Sci 106:9–14
Mizoguchi H, Yamada K, Nabeshima T (2011) Matrix metalloproteinases contribute to neuronal dysfunction in animal models of drug dependence, Alzheimer's disease, and epilepsy. Biochem Res Int 2011:681385
Mocellin S, Panelli MC, Wang E, Nagorsen D, Marincola FM (2003) The dual role of IL-10. Trends Immunol 24:36–43
Muller M, Schwerdtfeger K, Maier B, Mautes A, Schiedat T, Bianchi O, Marzi I (2001) Cerebral blood flow velocity and inflammatory response after severe traumatic brain injury. Eur J Ultrasound 12:203–208
Najera JA, Bustamante EA, Bortell N, Morsey B, Fox HS, Ravasi T, Marcondes MC (2016) Methamphetamine abuse affects gene expression in brain-derived microglia of SIV-infected macaques to enhance inflammation and promote virus targets. BMC Immunol 17:7
NSDUH-Report (2006) Methamphetamine Use, Abuse, and Dependence: 2002, 2003, and 2004. National Survey on Drug Use and Health
Park M, Kim HJ, Lim B, Wylegala A, Toborek M (2013) Methamphetamine-induced occludin endocytosis is mediated by the Arp2/3 complex-regulated actin rearrangement. J Biol Chem 288:33324–33334
Patel D, Desai GM, Frases S, Cordero RJ, DeLeon-Rodriguez CM, Eugenin EA, Nosanchuk JD, Martinez LR (2013) Methamphetamine enhances Cryptococcus neoformans pulmonary infection and dissemination to the brain. mBio 4
Perez JA Jr, Arsura EL, Strategos S (1999) Methamphetamine-related stroke: four cases. J Emerg Med 17:469–471
Pike BR, Flint J, Dutta S, Johnson E, Wang KK, Hayes RL (2001) Accumulation of non-erythroid alpha II-spectrin and calpain-cleaved alpha II-spectrin breakdown products in cerebrospinal fluid after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurochem 78:1297–1306
Pike BR, Zhao X, Newcomb JK, Posmantur RM, Wang KK, Hayes RL (1998) Regional calpain and caspase-3 proteolysis of alpha-spectrin after traumatic brain injury. NeuroReport 9:2437–2442
Pineda JA, Wang KK, Hayes RL (2004) Biomarkers of proteolytic damage following traumatic brain injury. Brain Pathol 14:202–209
Pu C, Broening HW, Vorhees CV (1996) Effect of methamphetamine on glutamate-positive neurons in the adult and developing rat somatosensory cortex. Synapse 23:328–334
Ramirez SH, Potula R, Fan S, Eidem T, Papugani A, Reichenbach N, Dykstra H, Weksler BB, Romero IA, Couraud PO, Persidsky Y (2009) Methamphetamine disrupts blood-brain barrier function by induction of oxidative stress in brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:1933–1945
Rivera S, Tremblay E, Timsit S, Canals O, Ben-Ari Y, Khrestchatisky M (1997) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) is differentially induced in neurons and astrocytes after seizures: evidence for developmental, immediate early gene, and lesion response. J Neurosci 17:4223–4235
Robson MJ, Turner RC, Naser ZJ, McCurdy CR, Huber JD, Matsumoto RR (2013) SN79, a sigma receptor ligand, blocks methamphetamine-induced microglial activation and cytokine upregulation. Exp Neurol 247:134–142
Rothaug M, Becker-Pauly C, Rose-John S (2016) The role of interleukin-6 signaling in nervous tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:1218–1227
Sajja RK, Rahman S, Cucullo L (2016) Drugs of abuse and blood-brain barrier endothelial dysfunction: A focus on the role of oxidative stress. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:539–554
Seiden LS, Commins DL, Vosmer G, Axt K, Marek G (1988) Neurotoxicity in dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine terminal fields: a regional analysis in nigrostriatal and mesolimbic projections. Ann N Y Acad Sci 537:161–172
Shimamura M, Garcia JM, Prough DS, Dewitt DS, Uchida T, Shah SA, Avila MA, Hellmich HL (2005) Analysis of long-term gene expression in neurons of the hippocampal subfields following traumatic brain injury in rats. Neuroscience 131:87–97
Siman R, Noszek JC, Kegerise C (1989) Calpain I activation is specifically related to excitatory amino acid induction of hippocampal damage. J Neurosci 9:1579–1590
Smith DH, Uryu K, Saatman KE, Trojanowski JQ, McIntosh TK (2003) Protein accumulation in traumatic brain injury. Neuromolecular Med 4:59–72
Sofroniew MV, Howe CL, Mobley WC (2001) Nerve growth factor signaling, neuroprotection, and neural repair. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1217–1281
Sokolov BP, Cadet JL (2006) Methamphetamine causes alterations in the MAP kinase-related pathways in the brains of mice that display increased aggressiveness. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:956–966
Stahel PF, Kossmann T, Joller H, Trentz O, Morganti-Kossmann MC (1998) Increased interleukin-12 levels in human cerebrospinal fluid following severe head trauma. Neurosci Lett 249:123–126
Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2001) How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:463–516
Sullivan PG, Rabchevsky AG, Waldmeier PC, Springer JE (2005) Mitochondrial permeability transition in CNS trauma: cause or effect of neuronal cell death? J Neurosci Res 79:231–239
Suwanjang W, Phansuwan-Pujito P, Govitrapong P, Chetsawang B (2012) Calpastatin reduces calpain and caspase activation in methamphetamine-induced toxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cultured cells. Neurosci Lett 526:49–53
Taylor CA, Bell JM, Breiding MJ, Xu L (2017) Traumatic brain injury–related emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths—United States, 2007 and 2013. MMWR Surveill Summ 66(9):1–16. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.ss6609a1
Theodore S, Cass WA, Maragos WF (2006) Involvement of cytokines in human immunodeficiency virus-1 protein Tat and methamphetamine interactions in the striatum. Exp Neurol 199:490–498
Tipton DA, Legan ZT, Dabbous M (2010) Methamphetamine cytotoxicity and effect on LPS-stimulated IL-1beta production by human monocytes. Toxicol in Vitro 24:921–927
UNODC (2019) World Drug Report. United Nations publication, Sales No. E.19.XI.8
Vargas AM, Rivera-Rodriguez DE, Martinez LR (2020) Methamphetamine alters the TLR4 signaling pathway, NF-κB activation, and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in LPS-challenged NR-9460 microglia-like cells. Mol Immunol 121:159–166
Wallace TL, Vorhees CV, Zemlan FP, Gudelsky GA (2003) Methamphetamine enhances the cleavage of the cytoskeletal protein tau in the rat brain. Neuroscience 116:1063–1068
Warren MW, Kobeissy FH, Liu MC, Hayes RL, Gold MS, Wang KK (2005) Concurrent calpain and caspase-3 mediated proteolysis of alpha II-spectrin and tau in rat brain after methamphetamine exposure: a similar profile to traumatic brain injury. Life Sci 78:301–309
Warren MW, Kobeissy FH, Liu MC, Hayes RL, Gold MS, Wang KK (2006a) Ecstasy toxicity: a comparison to methamphetamine and traumatic brain injury. J Addict Dis 25:115–123
Warren MW, Zheng W, Kobeissy FH, Cheng Liu M, Hayes RL, Gold MS, Larner SF, Wang KK (2006b) Calpain- and caspase-mediated alphaII-spectrin and tau proteolysis in rat cerebrocortical neuronal cultures after ecstasy or methamphetamine exposure. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 1–11
Wennersten A, Holmin S, Mathiesen T (2003) Characterization of Bax and Bcl-2 in apoptosis after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat. Acta Neuropathol (berl) 105:281–288
Yamaguchi T, Kuraishi Y, Minami M, Nakai S, Hirai Y, Satoh M (1991) Methamphetamine-induced expression of interleukin-1 beta mRNA in the rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 128:90–92
Yang T, Zang S, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Jiang L, Chen X, Zhang X, Cheng J, Gao R, Xiao H, Wang J (2020) Methamphetamine induced neuroinflammation in mouse brain and microglial cell line BV2: Roles of the TLR4/TRIF/Peli1 signaling axis. Toxicol Lett 333:150–158
Yong VW, Power C, Forsyth P, Edwards DR (2001) Metalloproteinases in biology and pathology of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:502–511
Yu Q, Zhang D, Walston M, Zhang J, Liu Y, Watson RR (2002) Chronic methamphetamine exposure alters immune function in normal and retrovirus-infected mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2:951–962
Zheng LM, Ojcius DM, Garaud F, Roth C, Maxwell E, Li Z, Rong H, Chen J, Wang XY, Catino JJ, King I (1996) Interleukin-10 inhibits tumor metastasis through an NK cell-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med 184:579–584
Zhou Z, Chen H, Zhang K, Yang H, Liu J, Huang Q (2003) Protective effect of nerve growth factor on neurons after traumatic brain injury. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 14:217–224
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Zaynab Shakkour for helping in editing and correcting the article. We declare that all authors contributed significantly to the study and accepted the manuscript for submission. There are no conflicts of interest by any of the authors. All authors have read and approved the submission of the manuscript; the manuscript has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere, in whole or in part, in any language.
Funding
This study was supported in part by the Donald and Irene Dizney Eminent Scholar Chair, held by Mark Gold, M.D. Distinguished Professor, McKnight Brain Institute and also by the Department of Defense (DOD) grant # DAMD17-03–1-0066.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FK, KW, and MSG conceived and designed the study. FK and ZS collected the data. FK, SEH, and ZS contributed to data analysis. FK performed the experiments, WM, ZS, and SEH drafted the manuscript. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Declarations and Consent to Participate
All the animal experiments in our study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at the University of Florida.
Consent for Publication
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article, published on 20 September 2021, the authors have found an error. The fourth author family name is incorrect. Wael Mohammad should be "Wael Mohamed".
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobeissy, F.H., Shakkour, Z., Hayek, S.E. et al. Elevation of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory Cytokines in Rat Serum after Acute Methamphetamine Treatment and Traumatic Brain Injury. J Mol Neurosci 72, 158–168 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01886-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01886-8