Abstract
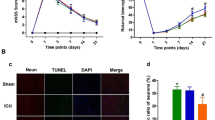
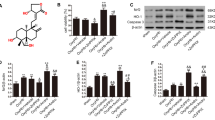
Intracerebral hemorrhage causes high mortality and morbidity, but its therapy methods are limited. In the present study, pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) was demonstrated to have beneficial effects on an intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) model. This study explored the effects and underlying mechanisms of PEMF in a mouse model of ICH and cultured BV2 cells. PEMF was applied 4 hours after collagenase-induced ICH at day 0 and 4 hours per day for seven consecutive days. The expression levels of proinflammatory factors were assessed by ELISA kits and western blotting. Hematoma volume was measured by histological analysis. The effects of PEMF on phagocytosis of the erythrocytes were observed in cultured BV2 cells and ICH mouse models. Seven days after ICH, the hematoma volume was significantly reduced in PEMF-treated animals compared to nontreated mice. We found that PEMF decreased the hematoma volume and the expression levels of proinflammatory factors after ICH. Moreover, PEMF enhanced the erythrophagocytosis of microglia via CD36. Furthermore, we found that downregulation CD36 with Genistein blocked the effects of PEMF-induced hematoma clearance and anti-inflammations effects. Thus, the PEMF-mediated promotion of neurological functions may at least partly involve anti-inflammatory processes and hematoma clearance. These results suggest that PEMF treatment promoted the hematoma clearance and alleviated the inflammation after ICH.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Q, Xue M, Yong VW (2020) Microglia and macrophage phenotypes in intracerebral haemorrhage injury: therapeutic opportunities. Brain 143:1297–1314
Chan AK, Tang X, Mummaneni NV, Coughlin D, Liebenberg E, Ouyang A, Dudli S, Lauricella M, Zhang N, Waldorff EI, Ryaby JT, Lotz JC (2019) Pulsed electromagnetic fields reduce acute inflammation in the injured rat-tail intervertebral disc. JOR Spine 2:e1069
Chang CF, Cai L, Wang J (2015) Translational intracerebral hemorrhage: a need for transparent descriptions of fresh tissue sampling and preclinical model quality. Transl Stroke Res 6:384–389
Chang CF, Massey J, Osherov A, Angenendt da Costa LH, Sansing LH (2020) Bexarotene enhances macrophage erythrophagocytosis and hematoma clearance in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 51:612–618
Chen W, Guo C, Huang S, Jia Z, Wang J, Zhong J, Ge H, Yuan J, Chen T, Liu X, Hu R, Yin Y, Feng H (2020) MitoQ attenuates brain damage by polarizing microglia towards the M2 phenotype through inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome after ICH. Pharmacol Res 161:105122
Ekker MS, Verhoeven JI, Vaartjes I, Jolink WMT, Klijn CJM, de Leeuw FE (2019) Association of stroke among adults aged 18 to 49 years with long-term mortality. JAMA 321:2113–2123
Fang H, Chen J, Lin S, Wang P, Wang Y, Xiong X, Yang Q (2014) CD36-mediated hematoma absorption following intracerebral hemorrhage: negative regulation by TLR4 signaling. J Immunol 192:5984–5992
Flores JJ, Klebe D, Rolland WB, Lekic T, Krafft PR, Zhang JH (2016) PPARgamma-induced upregulation of CD36 enhances hematoma resolution and attenuates long-term neurological deficits after germinal matrix hemorrhage in neonatal rats. Neurobiol Dis 87:124–133
Fu X, Zeng H, Zhao J, Zhou G, Zhou H, Zhuang J, Xu C, Li J, Peng Y, Cao Y, Li Y, Chen H, Wang L, Yan F, Chen G (2021) Inhibition of dectin-1 ameliorates neuroinflammation by regulating microglia/macrophage phenotype after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Transl Stroke Res
Gomez-Ochoa I, Gomez-Ochoa P, Gomez-Casal F, Cativiela E, Larrad-Mur L (2011) Pulsed electromagnetic fields decrease proinflammatory cytokine secretion (IL-1beta and TNF-alpha) on human fibroblast-like cell culture. Rheumatol Int 31:1283–1289
Grant G, Cadossi R, Steinberg G (1994) Protection against focal cerebral ischemia following exposure to a pulsed electromagnetic field. Bioelectromagnetics 15:205–216
Kenny EM, Fidan E, Yang Q, Anthonymuthu TS, New LA, Meyer EA, Wang H, Kochanek PM, Dixon CE, Kagan VE, Bayir H (2019) Ferroptosis contributes to neuronal death and functional outcome after traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med 47:410–418
Krishnamurthi RV, Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson LM, Truelsen T, O’Donnell M, Venketasubramanian N, Barker-Collo S, Lawes CM, Wang W, Shinohara Y, Witt E, Ezzati M, Naghavi M, Murray C, Global Burden of Diseases IRFS, Group GBDSE (2013) Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob Health 1:e259-281
Lan X, Han X, Li Q, Yang QW, Wang J (2017) Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol 13:420–433
Li Q, Lan X, Han X, Durham F, Wan J, Weiland A, Koehler RC, Wang J (2021) Microglia-derived interleukin-10 accelerates post-intracerebral hemorrhage hematoma clearance by regulating CD36. Brain Behav Immun 94:437–457
Liu J, Liu L, Wang X, Jiang R, Bai Q, Wang G (2021) Microglia: a double-edged sword in intracerebral hemorrhage from basic mechanisms to clinical research. Front Immunol 12:675660
Matsumoto Y, Larose J, Kent OA, Lim M, Changoor A, Zhang L, Storozhuk Y, Mao X, Grynpas MD, Cong F, Rottapel R (2017) RANKL coordinates multiple osteoclastogenic pathways by regulating expression of ubiquitin ligase RNF146. J Clin Invest 127:1303–1315
Ouyang J, Zhang B, Kuang L, Yang P, Du X, Qi H, Su N, Jin M, Yang J, Xie Y, Tan Q, Chen H, Chen S, Jiang W, Liu M, Luo X, He M, Ni Z, Chen L (2020) Pulsed electromagnetic field inhibits synovitis via enhancing the efferocytosis of macrophages. Biomed Res Int 2020:4307385
Rasouli J, Lekhraj R, White NM, Flamm ES, Pilla AA, Strauch B, Casper D (2012) Attenuation of interleukin-1beta by pulsed electromagnetic fields after traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Lett 519:4–8
Sherrard RM, Morellini N, Jourdan N, El-Esawi M, Arthaut LD, Niessner C, Rouyer F, Klarsfeld A, Doulazmi M, Witczak J, d’Harlingue A, Mariani J, McLure I, Martino CF, Ahmad M (2018) Low-intensity electromagnetic fields induce human cryptochrome to modulate intracellular reactive oxygen species. PLoS Biol 16:e2006229
Varani K, Vincenzi F, Ravani A, Pasquini S, Merighi S, Gessi S, Setti S, Cadossi M, Borea PA, Cadossi R (2017) Adenosine receptors as a biological pathway for the anti-inflammatory and beneficial effects of low frequency low energy pulsed electromagnetic fields. Mediators Inflamm 2017:2740963
Vincenzi F, Ravani A, Pasquini S, Merighi S, Gessi S, Setti S, Cadossi R, Borea PA, Varani K (2017) Pulsed electromagnetic field exposure reduces hypoxia and inflammation damage in neuron-like and microglial cells. J Cell Physiol 232:1200–1208
Vinhas A, Almeida AF, Goncalves AI, Rodrigues MT, Gomes ME (2020) Magnetic stimulation drives macrophage polarization in cell to-cell communication with IL-1beta primed tendon cells. Int J Mol Sci 21
Wang J (2010) Preclinical and clinical research on inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol 92:463–477
Wang T, Nowrangi D, Yu L, Lu T, Tang J, Han B, Ding Y, Fu F, Zhang JH (2018) Activation of dopamine D1 receptor decreased NLRP3-mediated inflammation in intracerebral hemorrhage mice. J Neuroinflammation 15:2
Wang P, Tang C, Wu J, Yang Y, Yan Z, Liu X, Shao X, Zhai M, Gao J, Liang S, Luo E, Jing D (2019) Pulsed electromagnetic fields regulate osteocyte apoptosis, RANKL/OPG expression, and its control of osteoclastogenesis depending on the presence of primary cilia. J Cell Physiol 234:10588–10601
Xu C, Zhang C, Ji J, Wang C, Yang J, Geng B, Zhao T, Zhou H, Mu X, Pan J, Hu S, Lv Y, Chen X, Wen H, You Q (2018) CD36 deficiency attenuates immune-mediated hepatitis in mice by modulating the proapoptotic effects of CXC chemokine ligand 10. Hepatology 67:1943–1955
Xu Y, Nowrangi D, Liang H, Wang T, Yu L, Lu T, Lu Z, Zhang JH, Luo B, Tang J (2020) DKK3 attenuates JNK and AP-1 induced inflammation via Kremen-1 and DVL-1 in mice following intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neuroinflammation 17:130
Xue M, Yong VW (2020) Neuroinflammation in intracerebral haemorrhage: immunotherapies with potential for translation. Lancet Neurol 19:1023–1032
Yang S, Nakamura T, Hua Y, Keep RF, Younger JG, He Y, Hoff JT, Xi G (2006) The role of complement C3 in intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1490–1495
Yang Y, Luo P, Xu H, Dai S, Rao W, Peng C, Ma W, Wang J, Xu H, Zhang L, Zhang S, Fei Z (2017) RNF146 inhibits excessive autophagy by modulating the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway in glutamate excitotoxicity injury. Front Cell Neurosci 11:59
Zhang H, Yang Y, Yang E, Tian Z, Huang Y, Zhang Z, Bao M, Liao D, Ge J, Wang C, Li X, Luo P (2022) Pulsed electromagnetic fields protect against brain ischemia by modulating the astrocytic cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol
Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Lu H, Yang Q, Wu H, Wang J (2017) Microglial polarization and inflammatory mediators after intracerebral hemorrhage. Mol Neurobiol 54:1874–1886
Zhao X, Sun G, Zhang J, Strong R, Song W, Gonzales N, Grotta JC, Aronowski J (2007) Hematoma resolution as a target for intracerebral hemorrhage treatment: role for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in microglia/macrophages. Ann Neurol 61:352–362
Zhao X, Grotta J, Gonzales N, Aronowski J (2009) Hematoma resolution as a therapeutic target: the role of microglia/macrophages. Stroke 40:S92-94
Zhao X, Sun G, Ting SM, Song S, Zhang J, Edwards NJ, Aronowski J (2015) Cleaning up after ICH: the role of Nrf2 in modulating microglia function and hematoma clearance. J Neurochem 133:144–152
Zong X, Dong Y, Li Y, Yang L, Li Y, Yang B, Tucker L, Zhao N, Brann DW, Yan X, Hu S, Zhang Q (2020) Beneficial effects of theta-burst transcranial magnetic stimulation on stroke injury via improving neuronal microenvironment and mitochondrial integrity. Transl Stroke Res 11:450–467
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province, China (no. 2021JQ-344, no. 2020JQ-231); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 82171363, no. 82171321, no. 81901186); and Youth Nova Program of Shaanxi Province, China (no. 2021KJXX-19).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuefan Yang designed, performed, and analyzed most figures. Pan Wang and Anlai Liu performed the behavior test. Shuhui Dai, Jialiang Wei, and Zhuoyuan Zhang provided studying materials and technical support. Zedong Yan and Xiuquan Wu performed the statistics work. Xin Li, Peng Luo, and Erping Luo conceived and coordinated the study and wrote the paper. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Air Force Medical University.
Consent for Publication
All authors listed agree to publish this article.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Wang, P., Liu, A. et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Protects Against Brain Injury After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Involvement of Anti-Inflammatory Processes and Hematoma Clearance via CD36. J Mol Neurosci 72, 2150–2161 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02063-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-022-02063-1