Abstract
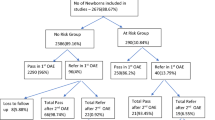
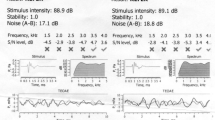
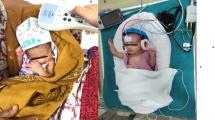
The present study was carried out with the aim of assessing the outcomes of otoacoustic hearing screening in newborns coupled with the three stage protocol. It was a hospital based observational study which was conducted over a time period of twelve months at a tertiary care institute to screen 2000 live neonates for congenital hearing impairment using OAE, followed up by tympanometry and BERA, if required. 2000 neonates were screened for hearing impairment. 406 were in high risk group and the rest in non-high risk group. Seven neonates had absent V wave on BERA. Five of them were high risk babies and the rest two were non-high risk ones. In order to ensure that early detection and effective intervention are possible for all neonates with hearing impairment, UNHS should be performed. Three stage UNHS protocol using OAE and BERA showed that the implementation of UNHS for congenital childhood hearing loss for all neonates would be beneficial.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fortnum H, Davis A (1997) Epidemiology of permanent hearing impairment in Trent region, 1985–1993. Bri J Audio 31:409–446
Ewing IR, Ewing AWG (1944) The ascertainment of deafness in infancy and early childhood. J Laryngol Otol 1:309–333
American academy of audiology childhood hearing screening guidelines (2011) http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/hearingloss/documents/AAA_Childhood%20Hearing%20Guidelines_2011.pdf. Accessed 20 Feb 2017
Samaddar S et al (2015) Universal neonatal hearing screening—a necessity and not a choice. Bengal J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg [Sl] 23(1):1–6 (ISSN 2395-2407)
Weichbold V, Nekahm-Heis D, Welzl-Mueller K (2006) Universal newborn hearing screening and postnatal hearing loss. Pediatrics 117:e631–e636
Jewel J, Varghese PV, Singh T, Varghese A (2013) Newborn hearing screening—experience at a tertiary hospital in Northwest India. Int J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2:211–214
Paul AK (2011) Early identification of hearing loss and centralized newborn hearing screening facility—the Cochin experience. Indian Pediatr 48:355–359
Kurt AS, Brian DS, Jeanie ML, Leroy AC, Mary Beth McLellan RN (2000) Universal newborn hearing screening. J Fam Pract 49(11):1012–1016
De Capua B, De Felice C (2003) Newborn hearing screening by transient evoked otoacoustic emissions: analysis of response as a function of risk factors. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 23:16–20
Kathleen RB, Margaret AK (1999) Causes of pediatric sensorineural hearing loss. Yesterday and today. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:517–521
Kanan S, Pensi CA (2013) Study of incidence of congenital anomalies in new borns. Gujarat Med J 68(2):97–99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bishnoi, R., Baghel, S., Agarwal, S. et al. Newborn Hearing Screening: Time to Act!. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 2), 1296–1299 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1352-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1352-1