Abstract
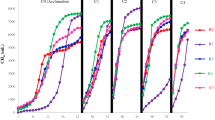
The adaptability of a thermophilic anaerobic digester stabilized long-term with poultry litter as sole feedstock was measured with regard to co-digestion with dairy cattle manure. Both feedstocks have low C/N ratios but differ in carbohydrates, protein, and fiber content. The digester was a pilot-scale (40 m3) sCSTR (semi-continuously stirred tank reactor) with a 20-day hydraulic retention time (HRT). Dairy manure was added as three step-wise increases in concentration: 20, 40, and 80%. At 20% dairy manure, methane production was unchanged (17–19 m3 day−1). But as the fraction of dairy manure increased, methane, ammonia, sCOD, acetate, and propionate decreased. At 80% dairy manure, methane volume dropped by 60%. Acetate concentration decreased from an initial 878 ± 209 mg L−1 during poultry litter mono-digestion to 285 ± 169 mg L−1 with 80% dairy manure. Upon returning to mono-digestion, methane production was on a trajectory of recovery although acetate remained low. Bacterial community structure shifted during co-digestion, but community resilience was also underway following return to the original feedstock for one HRT. The dominant bacterial phylotypes belonged to the groups Thermotogales, Synergistales, Clostridiales, and Halanaerobiales, and three uncharacterized orders (MBA08, SHA-98, OPB54) in class Clostridia. Co-digestion led to a shift in dominance with reductions in Thermotogales and OPB54, and an increase in MBA08. This experiment provides guidance for digester operators who wish to mix livestock and poultry manures for thermophilic co-digestion.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
DNA sequences have been submitted to GenBank.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
anaerobic digestion
- CAFO:
-
concentrated animal feeding operations
- CCA:
-
canonical correspondence analysis
- C/N:
-
carbon to nitrogen ratio
- HRT:
-
hydraulic retention time
- PCA:
-
Principal Component Analysis
- RDP:
-
Ribosomal Database Project
- SAOB:
-
syntrophic acetate oxidizing bacteria
- sCOD:
-
soluble chemical oxygen demand
- sCSTR:
-
semi-continuous stirred tank reactor
- T:
-
treatment period
- USDA:
-
United States Department of Agriculture
- WVSU:
-
West Virginia State University
References
Sommer SG, Christensen ML, Schmidt T, Jensen LS (2013) Animal manure recycling: treatment and management. Wiley
AgSTAR, Environmental Protection Agency (2020) Biogas Recovery in the Agriculture Sector. www.epa.gov/agstar
Mata-Alvarez J, Dosta J, Romero-Guiza MS, Fonoll X, Peces M, Astals S (2014) A critical review on anaerobic co-digestion achievements between 2010-2013. Renew Sust Energ Rev 36:412–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.04.039
Esposito G, Frunzo L, Giordano A, Liotta F, Panico A, Pirozzi F (2012) Anaerobic co-digestion of organic wastes. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 11:325–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-012-9277-8
Usack JG, Angenent LT (2015) Comparing the inhibitory thresholds of dairy manure co-digesters after prolonged acclimation periods: part 1 – performance and operating limits. Water Res 87:446–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.055
Yue Z, Chen R, Yang F, MacLellan J, Marsh T, Liu Y, Liao W (2013) Effects of dairy manure and corn stover co-digestion on anaerobic microbes and corresponding digestion performance. Bioresour Technol 128:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.115
Callaghan FJ, Wase DAJ, Thayanithy K, Forster CF (1999) Co-digestion of waste organic solids: batch studies. Bioresour Technol 67:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(98)00108-4
Sakar S, Yetilmezsoy K, Kocak E (2009) Anaerobic digestion technology in poultry and livestock waste treatment – a literature review. Waste Manag Res 27:3–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X07079060
Güngör-Demirci G, Demirer GN (2004) Effect of initial COD concentration, nutrient addition, temperature and microbial acclimation on anaerobic treatability of broiler and cattle manure. Bioresour Technol 93:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2003.10.019
Zhang Y, Zamudio Cañas EM, Zhu S, Linville JL, Chen S, He Q (2011) Robustness of archaeal populations in anaerobic co-digestion of dairy and poultry wastes. Bioresour Technol 102:779–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.08.104
Regueiro L, Veiga P, Figueroa M, Lema J, Carballa M (2014) Influence of transitional states on the microbial ecology of anaerobic digesters treating solid wastes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(5):2015–2027. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5378-8
USEPA (2000) Guide to field storage of biosolids and other organic by-products used in agriculture and for soil resource management. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, p 134
Labatut RA, Angenent LT, Scott NR (2014) Conventional mesophilic vs. thermophilic anaerobic digestion: a trade-off between performance and stability? Water Res 53:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.01.035
Müller B, Sun L, Westerholm M, Schnürer A (2016) Bacterial community composition and fhs profiles of low- and high-ammonia biogas digesters reveal novel syntrophic acetate-oxidising bacteria. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0454-9
Smith AM, Sharma D, Lappin-Scott H, Burton S, Huber DH (2014) Microbial community structure of a pilot-scale thermophilic anaerobic digester treating poultry litter. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(5):2321–2334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5144-y
USDA (2017) Census of agriculture
Perera R, Perera P, Vlosky RP, Darby P (2010) Potential of using poultry litter as a feedstock for energy production. Louisiana State University Forest Products Development Center
Bombardiere J, Espinosa-Solares T, Domaschko M, Chatfield M (2007) Thermophilic anaerobic digester performance under different feed-loading frequency. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 137–140:765–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-181-3_63
Espinosa-Solares T, Bombardiere J, Chatfield M, Domaschko M, Easter M, Stafford DA, Castillo-Angeles S, Castellanos-Hernandez N (2006) Macroscopic mass and energy balance of a pilot plant anaerobic bioreactor operated under thermophilic conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 129-132:959–968
Huber DH, Ramirez-Garcia A, Chavarria-Palma JE, Espinosa-Solares T, Lhilhi Noundou V, Montenegro-Garcia NA, Adeleye A, Martin CS (2020) Stress induced by crude glycerol in a thermophilic digester: microbial community divergence and resilience, but slow process recovery. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:10769–10781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10965-6
Bombardiere J, Espinosa-Solares T, Chatfield M, Domaschko M, Easter M, Stafford DA, Castillo-Angeles S, Castellanos-Hernandez N (2005) Influence of hydraulic retention time on the performance of a pilot plant thermophilic anaerobic bioreactor. ADSW Conference Proceedings, Vol 2, Process Engineering 283-289
Espinosa-Solares T, Valle-Guadarrama S, Bombardiere J, Domaschko M, Easter M (2009) Effect of heating strategy on power consumption and performance of a pilot plant anaerobic digester. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 156:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8487-6
Sharma D, Espinosa-Solares T, Huber DH (2013) Thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of poultry litter and thin stillage. Bioresour Technol 136:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.03.005
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Gonzalez Pena A, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. AEM 72:5069–5072. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03006-05
Lozupone C, Lladser ME, Knights D, Stombaugh J, Knight R (2011) UniFrac: an effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. ISME J 5:169–172. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.133
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26:266–267. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp636
Raivo K (2019) Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap
de Leeuw J, Mair P (2009) Simple and Canonical Correspondence Analysis Using the R Package anacor. J Stat Softw 31. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v031.i05
Huber DH, Chavarria-Palma JE, Malkaram SA, Montenegro-Garcia N, Lhilhi Noundou V, Ugwuanyi IR, Espinosa-Solares T (2018) Metagenome sequences of a thermophilic anaerobic digester adapted to a low C/N ratio, high-ammonia feedstock (poultry litter). Genome Announcements 6(25):e00598–e00518. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00598-18
Speece RE (1996) Anaerobic biotechnology for industrial wastewaters. Archaea Press, Nashville
Boe K, Angelidaki I (2009) Serial CSTR digester configuration for improving biogas production from manure. Water Res 43:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.09.041
Hattori S (2008) Syntrophic acetate-oxidizing microbes in methanogenic environments. Microbes Environ 23:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.23.118
Batstone DJ, Keller J, Angelidaki I, Kalyuzhnyi SV, Pavlostathis SG, Rozzi A, Sanders WTM, Siegrist H, Vavilin VA (2002) Anaerobic digestion model no. 1 (ADM1), IWA Task Group for Mathematical Modeling of Anaerobic Digestion Processes. IWA Publishing, London, p 77
Rivera-Salvador V, Lopez-Cruz IL, Espinosa-Solares T, Aranda-Barradas JS, Huber DH, Sharma D, Toledo JU (2014) Application of anaerobic digestion model no. 1 to describe the syntrophic acetate oxidation of poultry litter in thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Bioresour Technol 167:495–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.06.008
Ahring BK, Sandberg M, Angelidaki (1995) Volatile fatty acids as indicators of process imbalance in anaerobic digestors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:559–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00218466
Shrestha S, Fonoll X, Khanal SK, Raskin L (2017) Biological strategies for enhanced hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass during anaerobic digestion: current status and future perspectives. Bioresour Technol 245:1245–1257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.089
Shade A, Peter H, Allison SD, Baho DL, Berga M, Burgmann H, Huber DH, Langenheder S, Lennon JT, Martiny JBH, Matulich KL, Schmidt TM, Handelsman J (2012) Fundamentals of microbial community resistance and resilience. Front Microbiol 3:417. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2012.00417
Vandermeer J, Perfecto I (2019) Hysteresis and critical transitions in a coffee agroecosystem. PNAS 116(30):15074–15079. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902773116
Angelidaki I, Ahring BK (1993) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of livestock waste: the effect of ammonia. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:560–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242955
De Vrieze J, Gildemyn S, Vilchez-Vargas JR, Jauregui R, Pieper DH, Verstraete W, Boon N (2015) Inoculum selection is crucial to ensure operational stability in anaerobic digestion. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:189–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6046-3
Singh K, Lee K, Worley J, Risse LM, Das KC (2010) Anaerobic digestion of poultry litter: a review. Appl Eng Agric 26(4):677–688. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.32061
Meneses-Reyes JC, Hernandez-Eugenio G, Huber DH, Balagurusamy N, Espinosa-Solares T (2018) Oil-extracted Chlorella vulgaris biomass and glycerol bioconversion to methane via continuous anaerobic co-digestion with chicken litter. Renew Energy 128:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.053
Wang X, Yang G, Feng Y, Ren G, Han X (2012) Optimizing feeding composition and carbon-nitrogen ratios for improved methane yield during anaerobic co-digestion of dairy, chicken manure and wheat straw. Bioresour Technol 120:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.058
Zhang W, Werner JJ, Matthew AT, Angenent LT (2014) Substrates type drives variation in reactor microbiomes of anaerobic digesters. Bioresour Technol 151:397–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.004
Regueiro L, Spirito CM, Usack JG, Hospodsky D, Werner JJ, Angenent LT (2015) Comparing the inhibitory thresholds of dairy manure co-digesters after prolonged acclimation periods: part 2 – correlations between microbiomes and environment. Water Res 87:458–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.05.046
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The Ribosomal Database Project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn879
Ben Hania W, Godbane R, Postec A, Hamdi M, Ollivier B, Fardeau ML (2011) Defluviitoga tunisiensis gen. nov, sp. nov., a novel thermophilic bacterium isolated from a mesothermic anaerobic whey digester. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1377–1382. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.033720-0
Maus I, Cibis KG, Wibberg D, Winkler A, Stolze Y, Konig H, Puhler A, Schluter A (2015) Complete genome sequence of the strain Defluviitoga tunisiensis L3, isolated from a thermophilic, production-scale biogas plant. J Biotechnol 203:17–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.03.006
Cibis KG, Gneipel A, Konig H (2016) Isolation of acetic, propionic and butyric acid-forming bacteria from biogas plants. J Biotechnol 220:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.01.008
Pervin HM, Dennis PG, Lim HJ, Tyson GW, Batstone DJ, Bond PL (2013) Drivers of microbial community composition in mesophilic and thermophilic temperature-phased anaerobic digestion pre-treatment reactors. Water Res 47:7098–7108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.07.053
Yabu H, Sakai C, Fujiwara T, Nishio N, Nakashimada Y (2011) Thermophilic two-stage dry anaerobic digestion of model garbage with ammonia stripping. J Biosci Bioeng 111:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.10.011
Nobu MK, Narihiro T, Rinke C, Kamagata Y, Tringe SG, Woyke T, Liu WT (2015) Microbial dark matter ecogenomics reveals complex synergistic networks in a methanogenic bioreactor. ISME J 9:1710–1722. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.256
Liu Y, Qiao JT, Yuan XZ, Guo RB, Qiu YL (2014) Hydrogenispora ethanolica gen. nov., sp. Nov., an anaerobic carbohydrate-fermenting bacterium from anaerobic sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1756–1762. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.060186-0
Ito T, Yoshiguchi K, Ariesyady HD, Okabe S (2011) Identification of a novel acetate-utilizing bacterium belonging to Synergistes group 4 in anaerobic digester sludge. ISME 5:1844–1856. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2011.59
Mesbah NM, Wiegel J (2012) Life under multiple extreme conditions: diversity and physiology of the halophilic alkalithermophiles. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:4074–4082. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00050-12
Guo J, Peng Y, Ni BJ, Han X, Fan L, Yuan Z (2015) Dissecting microbial community structure and methane-producing pathways of a full-scale anaerobic reactor digesting activated sludge from wastewater treatment by metagenomics sequencing. Microb Cell Factories 14:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-015-0218-4
Moset V, Poulsen M, Wahid R, Højberg O, Møller HB (2015) Mesophilic versus thermophilic anaerobic digestion of cattle manure: methane productivity and microbial ecology. Microb Biotechnol 8:787–800. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12271
Jiang Y, Dennehy C, Lawlor PG, Hu Z, McCabe M, Cormican P, Zhan X, Gardiner GE (2019) Exploring the roles of and interactions among microbes in dry co-digestion of food waste and pig manure using high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1344-0
MacDonald JM, McBride WD (2009) The transformation of U.S. livestock agriculture: scale, efficiency, and risks. Economic Information Bulletin Number No. 43. Economic Research Service, U.S. Dept. of Agriculture
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the US Department of Agriculture NIFA grant awards no. 2010-38850-20747 and no. 2009-38850-19795 to DHH.
Funding
This study was funded by USDA NIFA grant awards 2010-38850-20747 and 2009-38850-19795 to DHH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DHH and TES designed the research. DHH conducted the experiment and wrote the manuscript. DHH, JCP, and TES analyzed the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huber, D.H., Chavarria-Palma, J.E. & Espinosa-Solares, T. Co-digestion of Dairy Cattle Waste in a Pilot-Scale Thermophilic Digester Adapted to Poultry Litter Feedstock: Stress, Recovery, and Microbiome Response. Bioenerg. Res. 14, 1349–1359 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-020-10233-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-020-10233-5