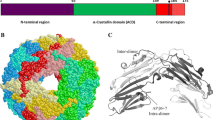
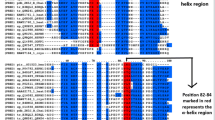
Abstract
Small heat shock proteins (sHSPs) are present in all kingdoms of life and play fundamental roles in cell biology. sHSPs are key components of the cellular protein quality control system, acting as the first line of defense against conditions that affect protein homeostasis and proteome stability, from bacteria to plants to humans. sHSPs have the ability to bind to a large subset of substrates and to maintain them in a state competent for refolding or clearance with the assistance of the HSP70 machinery. sHSPs participate in a number of biological processes, from the cell cycle, to cell differentiation, from adaptation to stressful conditions, to apoptosis, and, even, to the transformation of a cell into a malignant state. As a consequence, sHSP malfunction has been implicated in abnormal placental development and preterm deliveries, in the prognosis of several types of cancer, and in the development of neurological diseases. Moreover, mutations in the genes encoding several mammalian sHSPs result in neurological, muscular, or cardiac age-related diseases in humans. Loss of protein homeostasis due to protein aggregation is typical of many age-related neurodegenerative and neuromuscular diseases. In light of the role of sHSPs in the clearance of un/misfolded aggregation-prone substrates, pharmacological modulation of sHSP expression or function and rescue of defective sHSPs represent possible routes to alleviate or cure protein conformation diseases. Here, we report the latest news and views on sHSPs discussed by many of the world’s experts in the sHSP field during a dedicated workshop organized in Italy (Bertinoro, CEUB, October 12–15, 2016).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrman E, Gustavsson N, Hultschig C, Boelens WC, Emanuelsson CS (2007a) Small heat shock proteins prevent aggregation of citrate synthase and bind to the N-terminal region which is absent in thermostable forms of citrate synthase. Extremophiles 11:659–666
Ahrman E, Lambert W, Aquilina JA, Robinson CV, Emanuelsson CS (2007b) Chemical cross-linking of the chloroplast localized small heat-shock protein, Hsp21, and the model substrate citrate synthase. Protein Sci 16:1464–1478
Aquilina JA, Benesch JL, Ding LL, Yaron O, Horwitz J, Robinson CV (2004) Phosphorylation of alphaB-crystallin alters chaperone function through loss of dimeric substructure. J Biol Chem 279:28675–28680
Arrigo AP (2000) sHsp as novel regulators of programmed cell death and tumorigenicity. Pathologie-biologie 48:280–288
Arrigo AP (2007) The cellular “networking” of mammalian Hsp27 and its functions in the control of protein folding, redox state and apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 594:14–26
Arrigo AP (2013) Human small heat shock proteins: protein interactomes of homo- and hetero-oligomeric complexes: an update. FEBS Lett 587:1959–1969
Arrigo AP, Ducasse C (2002) Expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Hsp27 during both the keratinocyte differentiation and dedifferentiation of HaCat cells: expression linked to changes in intracellular protein organization? Exp Gerontol 37:1247–1255
Arrigo AP, Gibert B (2012) HspB1 dynamic phospho-oligomeric structure dependent interactome as cancer therapeutic target. Curr Mol Med 12:1151–1163
Arrigo AP, Gibert B (2014) HspB1, HspB5 and HspB4 in human cancers: potent oncogenic role of some of their client proteins. Cancers 6:333–365
Baldwin AJ, Walsh P, Hansen DF, Hilton GR, Benesch JL, Sharpe S, Kay LE (2012) Probing dynamic conformations of the high-molecular-weight alphaB-crystallin heat shock protein ensemble by NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 134:15343–15350
Balogi Z et al (2008) A mutant small heat shock protein with increased thylakoid association provides an elevated resistance against UV-B damage in synechocystis 6803. J Biol Chem 283:22983–22991
Bartelt-Kirbach B, Moron M, Glomb M, Beck CM, Weller MP, Golenhofen N (2016) HspB5/alphaB-crystallin increases dendritic complexity and protects the dendritic arbor during heat shock in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:3761–3775
Benesch JL et al (2012) The quaternary organization and dynamics of the molecular chaperone HSP26 are thermally regulated. Chem Biol 17:1008–1017
Benesch JL, Aquilina JA, Ruotolo BT, Sobott F, Robinson CV (2006) Tandem mass spectrometry reveals the quaternary organization of macromolecular assemblies. Chem Biol 13:597–605
Benjamin IJ, Shelton J, Garry DJ, Richardson JA (1997) Temporospatial expression of the small HSP/alpha B-crystallin in cardiac and skeletal muscle during mouse development. Dev Dyn 208:75–84
Boncoraglio A, Minoia M, Carra S (2012) The family of mammalian small heat shock proteins (HSPBs): implications in protein deposit diseases and motor neuropathies. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:1657–1669
Bourrelle-Langlois M, Morrow G, Finet S, Tanguay RM (2016) In vitro structural and functional characterization of the small heat shock proteins (sHSP) of the cyanophage S-ShM2 and its host, Synechococcus sp. WH7803. PLoS One 11:e0162233
Bova MP, Yaron O, Huang Q, Ding L, Haley DA, Stewart PL, Horwitz J (1999) Mutation R120G in alphaB-crystallin, which is linked to a desmin-related myopathy, results in an irregular structure and defective chaperone-like function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:6137–6142
Bruey JM, Paul C, Fromentin A, Hilpert S, Arrigo AP, Solary E, Garrido C (2000) Differential regulation of HSP27 oligomerization in tumor cells grown in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 19:4855–4863
Bruinsma IB et al (2011) Inhibition of alpha-synuclein aggregation by small heat shock proteins. Proteins 79:2956–2967
Bryantsev AL, Loktionova SA, Ilyinskaya OP, Tararak EM, Kampinga HH, Kabakov AE (2002) Distribution, phosphorylation, and activities of Hsp25 in heat-stressed H9c2 myoblasts: a functional link to cytoprotection. Cell Stress Chaperones 7:146–155
Bult CJ et al. (1996) Complete genome sequence of the methanogenic archaeon, Methanococcus jannaschii Science (New York, NY 273:1058–1073
Candido EP (2002) The small heat shock proteins of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: structure, regulation and biology. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 28:61–78
Caspers GJ, Leunissen JA, de Jong WW (1995) The expanding small heat-shock protein family, and structure predictions of the conserved “alpha-crystallin domain”. J Mol Evol 40:238–248
Cox D, Carver JA, Ecroyd H (2014) Preventing alpha-synuclein aggregation: the role of the small heat-shock molecular chaperone proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:1830–1843
Cox D, Selig E, Griffin MD, Carver JA, Ecroyd H (2016) Small heat-shock proteins prevent alpha-synuclein aggregation via transient interactions and their efficacy is affected by the rate of aggregation. J Biol Chem 291:22618–22629
Crippa V et al (2010) The small heat shock protein B8 (HspB8) promotes autophagic removal of misfolded proteins involved in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Hum Mol Genet 19:3440–3456
De Los RP, Goloubinoff P (2016) Hsp70 chaperones use ATP to remodel native protein oligomers and stable aggregates by entropic pulling. Nat Struct Mol Biol 23:766–769
de Marco A, Vigh L, Diamant S, Goloubinoff P (2005) Native folding of aggregation-prone recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by osmolytes, plasmid- or benzyl alcohol-overexpressed molecular chaperones. Cell Stress Chaperones 10:329–339
Delbecq SP, Klevit RE (2013) One size does not fit all: the oligomeric states of alphaB crystallin. FEBS Lett 587:1073–1080
Delbecq SP, Rosenbaum JC, Klevit RE (2015) A mechanism of subunit recruitment in human small heat shock protein oligomers. Biochemistry 54:4276–4284
den Engelsman J, Gerrits D, de Jong WW, Robbins J, Kato K, Boelens WC (2005) Nuclear import of {alpha}B-crystallin is phosphorylation-dependent and hampered by hyperphosphorylation of the myopathy-related mutant R120G. J Biol Chem 280:37139–37148
den Hoed M et al (2013) Identification of heart rate-associated loci and their effects on cardiac conduction and rhythm disorders. Nat Genet 45:621–631
Doshi BM, Hightower LE, Lee J (2009) The role of Hsp27 and actin in the regulation of movement in human cancer cells responding to heat shock. Cell Stress Chaperones 14:445–457
Ecroyd H, Carver JA (2009) Crystallin proteins and amyloid fibrils. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:62–81
Ecroyd H et al (2007) Mimicking phosphorylation of alphaB-crystallin affects its chaperone activity. The Biochemical journal 401:129–141
Evgrafov OV et al (2004) Mutant small heat-shock protein 27 causes axonal Charcot-Marie-tooth disease and distal hereditary motor neuropathy. Nat Genet 36:602–606
Eyles SJ, Gierasch LM (2010) Nature’s molecular sponges: small heat shock proteins grow into their chaperone roles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:2727–2728
Fontaine JM, Rest JS, Welsh MJ, Benndorf R (2003) The sperm outer dense fiber protein is the 10th member of the superfamily of mammalian small stress proteins. Cell Stress Chaperones 8:62–69
Gaestel M (2002) sHsp-phosphorylation: enzymes, signaling pathways and functional implications. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 28:151–169
Ghaoui R et al (2016) Mutations in HSPB8 causing a new phenotype of distal myopathy and motor neuropathy. Neurology 86:391–398
Giese KC, Basha E, Catague BY, Vierling E (2005) Evidence for an essential function of the N terminus of a small heat shock protein in vivo, independent of in vitro chaperone activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:18896–18901
Giese KC, Vierling E (2002) Changes in oligomerization are essential for the chaperone activity of a small heat shock protein in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem 277:46310–46318
Golenhofen N, Bartelt-Kirbach B (2016) The impact of small heat shock proteins (HspBs) in Alzheimer’s and other neurological diseases. Curr Pharm Des 22:4050–4062
Haslbeck M, Peschek J, Buchner J, Weinkauf S (2016) Structure and function of alpha-crystallins: traversing from in vitro to in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta 1860:149–166
Haslbeck M, Vierling E (2015) A first line of stress defense: small heat shock proteins and their function in protein homeostasis. J Mol Biol 427:1537–1548
Heirbaut M, Beelen S, Strelkov SV, Weeks SD (2014) Dissecting the functional role of the N-terminal domain of the human small heat shock protein HSPB6. PLoS One 9:e105892
Heirbaut M et al (2016) The preferential heterodimerization of human small heat shock proteins HSPB1 and HSPB6 is dictated by the N-terminal domain. Arch Biochem Biophys 610:41–50
Hishiya A, Salman MN, Carra S, Kampinga HH, Takayama S (2010) BAG3 directly interacts with mutated alphaB-crystallin to suppress its aggregation and toxicity. PLoS One 6:e16828
Hochberg GK et al (2014) The structured core domain of alphaB-crystallin can prevent amyloid fibrillation and associated toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E1562–E1570
Hong SW, Vierling E (2000) Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana defective in the acquisition of tolerance to high temperature stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4392–4397
Hoogstra-Berends F et al (2012) Heat shock protein-inducing compounds as therapeutics to restore proteostasis in atrial fibrillation. Trends in cardiovascular medicine 22:62–68
Irobi J et al (2004) Hot-spot residue in small heat-shock protein 22 causes distal motor neuropathy. Nat Genet 36:597–601
Jaspard E, Hunault G (2016) sHSPdb: a database for the analysis of small heat shock proteins. BMC Plant Biol 16:135
Kamradt MC, Chen F, Sam S, Cryns VL (2002) The small heat shock protein alpha B-crystallin negatively regulates apoptosis during myogenic differentiation by inhibiting caspase-3 activation. J Biol Chem 277:38731–38736
Kamradt MC et al (2005) The small heat shock protein alpha B-crystallin is a novel inhibitor of TRAIL-induced apoptosis that suppresses the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem 280:11059–11066
Kappe G, Franck E, Verschuure P, Boelens WC, Leunissen JA, de Jong WW (2003) The human genome encodes 10 alpha-crystallin-related small heat shock proteins: HspB1-10. Cell Stress Chaperones 8:53–61
Ke L et al (2011) HSPB1, HSPB6, HSPB7 and HSPB8 protect against RhoA GTPase-induced remodeling in tachypaced atrial myocytes. PLoS One 6:e20395
Kim KK, Kim R, Kim SH (1998) Crystal structure of a small heat-shock protein. Nature 394:595–599
Klosowska A, Chamera T, Liberek K (2016) Adenosine diphosphate restricts the protein remodeling activity of the Hsp104 chaperone to Hsp70 assisted disaggregation eLife 5
Kolb SJ et al (2010) Mutant small heat shock protein B3 causes motor neuropathy: utility of a candidate gene approach. Neurology 74:502–506
Kondrat FD, Struwe WB, Benesch JL (2015) Native mass spectrometry: towards high-throughput structural proteomics. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 1261:349–371
Lambert H, Charette SJ, Bernier AF, Guimond A, Landry J (1999) HSP27 multimerization mediated by phosphorylation-sensitive intermolecular interactions at the amino terminus. J Biol Chem 274:9378–9385
Lambert W et al (2011) Subunit arrangement in the dodecameric chloroplast small heat shock protein Hsp21. Protein Sci 20:291–301
Lavoie JN, Gingras-Breton G, Tanguay RM, Landry J (1993) Induction of Chinese hamster HSP27 gene expression in mouse cells confers resistance to heat shock. HSP27 stabilization of the microfilament organization. J Biol Chem 268:3420–3429
Lavoie JN, Lambert H, Hickey E, Weber LA, Landry J (1995) Modulation of cellular thermoresistance and actin filament stability accompanies phosphorylation-induced changes in the oligomeric structure of heat shock protein 27. Mol Cell Biol 15:505–516
Litt M, Kramer P, LaMorticella DM, Murphey W, Lovrien EW, Weleber RG (1998) Autosomal dominant congenital cataract associated with a missense mutation in the human alpha crystallin gene CRYAA. Hum Mol Genet 7:471–474
Maaroufi H, Tanguay RM (2013) Analysis and phylogeny of small heat shock proteins from marine viruses and their cyanobacteria host. PLoS One 8:e81207
Mainz A et al (2015) The chaperone alphaB-crystallin uses different interfaces to capture an amorphous and an amyloid client. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22:898–905
McDonald ET, Bortolus M, Koteiche HA, McHaourab HS (2012) Sequence, structure, and dynamic determinants of Hsp27 (HspB1) equilibrium dissociation are encoded by the N-terminal domain. Biochemistry 51:1257–1268
McHaourab HS, Dodson EK, Koteiche HA (2002) Mechanism of chaperone function in small heat shock proteins. Two-mode binding of the excited states of T4 lysozyme mutants by alphaA-crystallin. J Biol Chem 277:40557–40566
McLoughlin F, Basha E, Fowler ME, Kim M, Bordowitz J, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Vierling E (2016) Class I and II small heat shock proteins together with HSP101 protect protein translation factors during heat stress. Plant Physiol 172:1221–1236
Mehlen P, Hickey E, Weber LA, Arrigo AP (1997) Large unphosphorylated aggregates as the active form of hsp27 which controls intracellular reactive oxygen species and glutathione levels and generates a protection against TNFalpha in NIH-3T3-ras cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 241:187–192
Michaud S, Lavoie S, Guimond MO, Tanguay RM (2008) The nuclear localization of Drosophila Hsp27 is dependent on a monopartite arginine-rich NLS and is uncoupled from its association to nuclear speckles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:1200–1210
Mitzelfelt KA et al (2016) The human 343delT HSPB5 chaperone associated with early-onset skeletal myopathy causes defects in protein solubility. J Biol Chem 291:14939–14953
Morrison LE, Hoover HE, Thuerauf DJ, Glembotski CC (2003) Mimicking phosphorylation of alphaB-crystallin on serine-59 is necessary and sufficient to provide maximal protection of cardiac myocytes from apoptosis. Circ Res 92:203–211
Morrow G, Hightower LE, Tanguay RM (2015) Small heat shock proteins: big folding machines. Cell Stress Chaperones 20:207–212
Moutaoufik MT, Morrow G, Maaroufi H, Ferard C, Finet S, Tanguay RM (2016) Oligomerization and chaperone-like activity of Drosophila melanogaster small heat shock protein DmHsp27 and three arginine mutants in the alpha-crystallin domain. Cell Stress Chaperones. doi:10.1007/s12192-016-0748-7
Mymrikov EV, Daake M, Richter B, Haslbeck M, Buchner J (2016) The chaperone activity and substrate spectrum of human small heat shock proteins The Journal of biological chemistry
Nefedova VV, Sudnitsyna MV, Gusev NB (2016) Interaction of small heat shock proteins with light component of neurofilaments (NFL). Cell Stress Chaperones. doi:10.1007/s12192-016-0757-6
Nicholl ID, Quinlan RA (1994) Chaperone activity of alpha-crystallins modulates intermediate filament assembly. EMBO J 13:945–953
Painter AJ, Jaya N, Basha E, Vierling E, Robinson CV, Benesch JL (2008) Real-time monitoring of protein complexes reveals their quaternary organization and dynamics. Chem Biol 15:246–253
Parcellier A et al (2006) HSP27 favors ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of p27Kip1 and helps S-phase re-entry in stressed cells. FASEB J 20:1179–1181
Park AM et al (2016) Heat shock protein 27 plays a pivotal role in myofibroblast differentiation and in the development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One 11:e0148998. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0148998
Perng MD, Cairns L, van den IP, Prescott A, Hutcheson AM, Quinlan RA (1999a) Intermediate filament interactions can be altered by HSP27 and alphaB-crystallin. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 13):2099–2112
Perng MD, Huang YS, Quinlan RA (2016) Purification of protein chaperones and their functional assays with intermediate filaments. Methods Enzymol 569:155–175
Perng MD, Muchowski PJ, van Den IP, Wu GJ, Hutcheson AM, Clark JI, Quinlan RA (1999b) The cardiomyopathy and lens cataract mutation in alphaB-crystallin alters its protein structure, chaperone activity, and interaction with intermediate filaments in vitro. J Biol Chem 274:33235–33243
Perng MD, Wen SF, van den IP, Prescott AR, Quinlan RA (2004) Desmin aggregate formation by R120G alphaB-crystallin is caused by altered filament interactions and is dependent upon network status in cells. Mol Biol Cell 15:2335–2346
Peschek J, Braun N, Franzmann TM, Georgalis Y, Haslbeck M, Weinkauf S, Buchner J (2009) The eye lens chaperone alpha-crystallin forms defined globular assemblies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13272–13277
Qian J et al (2009) Blockade of Hsp20 phosphorylation exacerbates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressed autophagy and increased cell death. Circ Res 105:1223–1231
Quinlan R, Van Den Ijssel P (1999) Fatal attraction: when chaperone turns harlot. Nat Med 5:25–26
Rajagopal P, Tse E, Borst AJ, Delbecq SP, Shi L, Southworth DR, Klevit RE (2015) A conserved histidine modulates HSPB5 structure to trigger chaperone activity in response to stress-related acidosis eLife 4
Rajasekaran NS et al (2007) Human alpha B-crystallin mutation causes oxido-reductive stress and protein aggregation cardiomyopathy in mice. Cell 130:427–439
Richter K, Haslbeck M, Buchner J (2010) The heat shock response: life on the verge of death. Mol Cell 40:253–266
Rogalla T et al (1999) Regulation of Hsp27 oligomerization, chaperone function, and protective activity against oxidative stress/tumor necrosis factor alpha by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 274:18947–18956
Rouse J et al (1994) A novel kinase cascade triggered by stress and heat shock that stimulates MAPKAP kinase-2 and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins. Cell 78:1027–1037
Rusmini P, Crippa V, Giorgetti E, Boncoraglio A, Cristofani R, Carra S, Poletti A (2013) Clearance of the mutant androgen receptor in motoneuronal models of spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Neurobiol Aging 34:2585–2603
Schmidt T, Fischer D, Andreadaki A, Bartelt-Kirbach B, Golenhofen N (2016) Induction and phosphorylation of the small heat shock proteins HspB1/Hsp25 and HspB5/alphaB-crystallin in the rat retina upon optic nerve injury. Cell Stress Chaperones 21:167–178
Shi J, Koteiche HA, McDonald ET, Fox TL, Stewart PL, McHaourab HS (2012) Cryoelectron microscopy analysis of small heat shock protein 16.5 (Hsp16.5) complexes with T4 lysozyme reveals the structural basis of multimode binding. J Biol Chem 288:4819–4830
Simon S et al (2007) Myopathy-associated alphaB-crystallin mutants: abnormal phosphorylation, intracellular location, and interactions with other small heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem 282:34276–34287
Sluchanko NN, Artemova NV, Sudnitsyna MV, Safenkova IV, Antson AA, Levitsky DI, Gusev NB (2012) Monomeric 14-3-3zeta has a chaperone-like activity and is stabilized by phosphorylated HspB6. Biochemistry 51:6127–6138
Sluchanko NN, Roman SG, Chebotareva NA, Gusev NB (2014) Chaperone-like activity of monomeric human 14-3-3zeta on different protein substrates. Arch Biochem Biophys 549:32–39
Sluchanko NN, Sudnitsyna MV, Seit-Nebi AS, Antson AA, Gusev NB (2011) Properties of the monomeric form of human 14-3-3zeta protein and its interaction with tau and HspB6. Biochemistry 50:9797–9808
Stengel F et al (2012) Dissecting heterogeneous molecular chaperone complexes using a mass spectrum deconvolution approach. Chem Biol 19:599–607
Stengel F et al (2010) Quaternary dynamics and plasticity underlie small heat shock protein chaperone function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:2007–2012
Stromer T, Fischer E, Richter K, Haslbeck M, Buchner J (2004) Analysis of the regulation of the molecular chaperone Hsp26 by temperature-induced dissociation: the N-terminal domain is important for oligomer assembly and the binding of unfolding proteins. J Biol Chem 279:11222–11228
Strozecka J, Chrusciel E, Gorna E, Szymanska A, Zietkiewicz S, Liberek K (2012) Importance of N- and C-terminal regions of IbpA, Escherichia coli small heat shock protein, for chaperone function and oligomerization. J Biol Chem 287:2843–2853
Sudnitsyna MV, Mymrikov EV, Seit-Nebi AS, Gusev NB (2011) The role of intrinsically disordered regions in the structure and functioning of small heat shock proteins. Curr Protein Pept Sci 13:76–85
Sugiyama Y et al (2000) Muscle develops a specific form of small heat shock protein complex composed of MKBP/HSPB2 and HSPB3 during myogenic differentiation. J Biol Chem 275:1095–1104
Suzuki A et al (1998) MKBP, a novel member of the small heat shock protein family, binds and activates the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase. J Cell Biol 140:1113–1124
Takayama S, Reed JC, Homma S (2003) Heat-shock proteins as regulators of apoptosis. Oncogene 22:9041–9047
Tanguay RM, Hightower LE (2015) The big book on small heat shock proteins vol 8. Heat shock proteins 8, Series Editors: Alexzander A.A. Asea, Stuart K. Calderwood edn. Springer
Theriault JR, Lambert H, Chavez-Zobel AT, Charest G, Lavigne P, Landry J (2004) Essential role of the NH2-terminal WD/EPF motif in the phosphorylation-activated protective function of mammalian Hsp27. J Biol Chem 279:23463–23471
Toivola DM, Strnad P, Habtezion A, Omary MB (2010) Intermediate filaments take the heat as stress proteins. Trends Cell Biol 20:79–91
Toth ME, Gonda S, Vigh L, Santha M (2010) Neuroprotective effect of small heat shock protein, Hsp27, after acute and chronic alcohol administration. Cell Stress Chaperones 15:807–817
Toth ME, Vigh L, Santha M (2014) Alcohol stress, membranes, and chaperones. Cell Stress Chaperones 19:299–309
Treweek TM, Meehan S, Ecroyd H, Carver JA (2015) Small heat-shock proteins: important players in regulating cellular proteostasis. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:429–451
Treweek TM et al (2005) R120G alphaB-crystallin promotes the unfolding of reduced alpha-lactalbumin and is inherently unstable. FEBS J 272:711–724
Ungelenk S et al (2016) Small heat shock proteins sequester misfolding proteins in near-native conformation for cellular protection and efficient refolding. Nat Commun 7:13673
van Montfort RL, Basha E, Friedrich KL, Slingsby C, Vierling E (2001) Crystal structure and assembly of a eukaryotic small heat shock protein. Nat Struct Biol 8:1025–1030
Verschuure P, Tatard C, Boelens WC, Grongnet JF, David JC (2003) Expression of small heat shock proteins HspB2, HspB8, Hsp20 and cvHsp in different tissues of the perinatal developing pig. Eur J Cell Biol 82:523–530
Vicart P et al (1998) A missense mutation in the alphaB-crystallin chaperone gene causes a desmin-related myopathy. Nat Genet 20:92–95
Vos MJ, Hageman J, Carra S, Kampinga HH (2008) Structural and functional diversities between members of the human HSPB. HSPH, HSPA, and DNAJ chaperone families Biochemistry 47:7001–7011
Webster KA (2003) Serine phosphorylation and suppression of apoptosis by the small heat shock protein alphaB-crystallin. Circ Res 92:130–132
Weeks SD, Baranova EV, Heirbaut M, Beelen S, Shkumatov AV, Gusev NB, Strelkov SV (2014) Molecular structure and dynamics of the dimeric human small heat shock protein HSPB6. J Struct Biol 185:342–354
Wu SY, Zou P, Fuller AW, Mishra S, Wang Z, Schey KL, McHaourab HS (2016) Expression of cataract-linked gamma-crystallin variants in zebrafish reveals a proteostasis network that senses protein stability. J Biol Chem 291:25387–25397
Zhu Y, Bogomolovas J, Labeit S, Granzier H (2009) Single molecule force spectroscopy of the cardiac titin N2B element: effects of the molecular chaperone alphaB-crystallin with disease-causing mutations. J Biol Chem 284:13914–13923
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carra, S., Alberti, S., Arrigo, P.A. et al. The growing world of small heat shock proteins: from structure to functions. Cell Stress and Chaperones 22, 601–611 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0787-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0787-8