Abstract
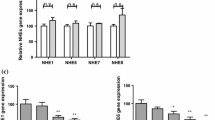
Rotavirus diarrhea is a major worldwide cause of infantile gastroenteritis; however, the mechanism responsible for intestinal fluid loss remains unclear. Water transfer across the intestinal epithelial membrane seems to occur because of aquaporins (AQPs). Accumulating evidence indicates that alterations in AQPs may play an important role in pathogenesis. Here, we focus on changes in AQPs in a mouse model of rotavirus diarrhea. In the present study, 32 of 35 mice developed diarrhea and mild dehydration within 24 hours after infection with rotavirus strain SA11. Intestinal epithelial cells demonstrated cytoplasmic vacuolation, malaligned villi, and atrophy. AQP1 expression was significantly attenuated in the ileum and colon in comparison with controls; likewise, AQP4 and -8 protein expression were significantly decreased in the colon of rotavirus diarrhea-infected mice. In contrast, AQP3 protein expression was significantly increased in the colon of rotavirus-infected mice in comparison with controls. These results indicate that rotavirus diarrhea is associated with the downregulation of AQP1, -4, and -8 expression. Therefore, AQPs play an important role in rotavirus diarrhea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2008. Rotavirus surveillance—worldwide, 2001–2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 57: 1255–1257.
Chen H, Gong S T, Ou W J. 2009. Expression of Aquaporins in Rotavirus Enteritis Treatment by Drug. Progr Modern Biomed. 17: 3258–3261. (In Chinese)
Guttman J A, Samji F N, Li Y, Deng W, Lin A, Finlay B B. 2007. Aquaporins contribute to diarrhoea caused by attaching and effacing bacterial pathogens. Cell Microbiol, 9: 131–141.
Hardin J A, Wallace L E, Wong J F, O’Loughlin E V, Urbanski S J, Gall D G. 2004. Aquaporin expression is downregulated in a murine model of colitis and in patients with ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and infectious colitis. Cell Tissue Res, 318: 313–323.
Hodges K, Gill R. 2010. Infectious diarrhea: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Gut Microbes, 1: 4–21.
Ikarashi N, Baba K, Ushiki T, Kon R, Mimura A, Toda T. 2011. The laxative effect of bisacodyl is attributable to decreased aquaporin-3 expression in the colon induced by increased PGE2 secretion from macrophages. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 301: G887–G895.
Ikarashi N, Ushiki T, Mochizuki T, Toda T, Kudo T, Baba K. 2011. Effects of magnesium sulphate administration on aquaporin 3 in rat gastrointestinal tract. Biol Pharm Bull, 34: 238–242.
Ishihara E, Nagahama M, Naruse S, Semba R, Miura T, Usami M. 2008. Neuropathological alteration of aquaporin 1 immunoreactive enteric neurons in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Auton Neurosci, 138: 31–40.
King L S, Kozono D, Agre P. 2004. From structure to disease: the evolving tale of aquaporin biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 5: 687–698.
Knipping K, McNeal M M, Crienen A, van Amerongen G, Garssen J, Van’t Land B. 2011. A gastrointestinal rotavirus infection mouse model for immune modulation studies. Virol J, 8: 109.
Krah D L. 1991. A simplified multiwell plate assay for the measurement of hepatitis A virus infectivity. Biologicals, 19: 223–227.
Laforenza U, Cova E, Gastaldi G, Tritto S, Grazioli M, LaRusso N F. 2005. Aquaporin-8 is involved in water transport in isolated superficial colonocytes from rat proximal colon. J Nutr, 135: 2329–2336.
Ma T, Jayaraman S, Wang K S, Song Y, Yang B, Li J. 2001. Defective dietary fat processing in transgenic mice lacking aquaporin-1 water channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 280: C126–C134.
Sheridan J F, Eydelloth R S, Vonderfecht S L, Aurelian L. 1983. Virus-specific immunity in neonatal and adult mouse rotavirus infection. Infect Immun, 39:917–927.
Tsujikawa T, Itoh A, Fukunaga T, Satoh J, Yasuoka T, Fujiyama Y. 2003. Alteration of aquaporin mRNA expression after small bowel resection in the rat residual ileum and colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 18: 803–808.
Wang K S, Ma T, Filiz F, Verkman A S, Bastidas J A. 2000. Colon water transport in transgenic mice lacking aquaporin-4 water channels. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 279: G463–G470.
Yamamoto T, Kuramoto H, Kadowaki M. 2007. Downregulation in aquaporin 4 and aquaporin 8 expression of the colon associated with the induction of allergic diarrhea in a mouse model of food allergy. Life Sci, 81: 115–120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, M., Yang, M., Ou, Z. et al. Involvement of aquaporins in a mouse model of rotavirus diarrhea. Virol. Sin. 29, 211–217 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-014-3469-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-014-3469-z