Abstract
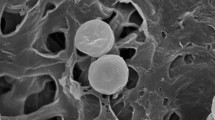
A mesophilic, facultative, anaerobic, xylanolytic-cellulolytic bacterium, TW1T, was isolated from sludge in an anaerobic digester fed with pineapple waste. Cells stained Gram-positive, were spore-forming, and had the morphology of straight to slightly curved rods. Growth was observed in the temperature range of 30 to 50°C (optimum 37°C) and the pH range of 6.0 to 7.5 (optimum pH 7.0) under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The strain contained meso-diaminopimelic acid in the cell-wall peptidoglycan. The predominant isoprenoid quinone was menaquinone with seven isoprene units (MK-7). Anteiso-C15:0, iso-C16:0, anteiso-C17:0, and C16:0 were the predominant cellular fatty acids. The G+C content of the DNA was 49.5 mol%. A phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA showed that strain TW1T belonged within the genus Paenibacillus and was closely related to Paenibacillus cellulosilyticus LMG 22232T, P. curdlanolyticus KCTC 3759T, and P. kobensis KCTC 3761T with 97.7, 97.5, and 97.3% sequence similarity, respectively. The DNA-DNA hybridization values between the isolate and type strains of P. cellulosilyticus LMG 22232T, P. curdlanolyticus KCTC 3759T, and P. kobensis KCTC 3761T were found to be 18.6, 18.3, and 18.0%, respectively. The protein and xylanase patterns of strain TW1T were quite different from those of the type strains of closely related Paenibacillus species. On the basis of DNA-DNA relatedness and phenotypic analyses, phylogenetic data and the enzymatic pattern presented in this study, strain TW1T should be classified as a novel species of the genus Paenibacillus, for which the name Paenibacillus xylaniclasticus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is TW1T (=NBRC 106381T =KCTC 13719T =TISTR 1914T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baik, K.S., Choe, H.N., Park, S.C., Kim, E.M., and Seong, C.N. 2011. Paenibacillus wooponensis sp. nov., isolated from wetland freshwater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.61, 2763–2768.
Barrow, G.L. and Feltham, R.K.A. 1993. Cowan and Steel’s Manual for the Identification of Medical Bacteria, 3rd ed. pp. 331. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Berg, B., von Hofstan, B., and Pettersson, G. 1972. Growth and cellulase formation by Celluvibrio fulvus. J. Appl. Bacteriol.35, 201–214.
Bhat, M.K. 2000. Cellulases and related enzymes in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv.18, 355–383.
Bozzola, J.J. and Russell, L.D. 1999. Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists, 2nd ed. pp. 670. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Boston, M.A., USA.
Chun, J., Lee, J.H., Jung, Y., Kim, M., Kim, S., Kim, B.K., and Lim, Y.W. 2007. EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.57, 2259–2261.
Ezaki, T., Hashimoto, Y., and Yabuuchi, E. 1989. Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternation to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.39, 224–229.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution39, 783–791.
Kanzawa, Y., Harada, A., Takeuchi, M., Yokota, A., and Harada, T. 1995. Bacillus curdlanolyticus sp. nov. and Bacillus kobensis sp. nov., which hydrolyze resistant curdlan. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.45, 515–521.
Khianngam, S., Akaracharanya, A., Tanasupawat, S., Lee, K.C., and Lee, J.S. 2009. Paenibacillus thailandensis sp. nov. and Paenibacillus nanensis sp. nov., xylanase-producing bacteria isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.59, 564–568.
Khianngam, S., Tanasupawat, S., Akaracharanya, A., Kim, K.K., Lee, K.C., and Lee, J.S. 2011. Paenibacillus xylanisolvens sp. nov., a xylan-degrading bacterium from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.61, 160–164.
Kim, B.C., Lee, K.H., Kim, M.N., Kim, E.M., Rhee, M.S., Kwon, O.Y., and Shin, K.S. 2009. Paenibacillus pinihumi sp. nov., a cellulolytic bacterium isolated from the rhizosphere of Pinus densiflora. J. Microbiol.47, 530–535.
Kimura, M. 1980. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol.16, 111–120.
Kohring, S., Wiegel, J., and Mayer, F. 1990. Subunit composition and glycosidic activities of the cellulase complex from Clostridium thermocellum JW20. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.56, 3798–3804.
Komagata, K. and Suzuki, K. 1987. Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol.19, 161–207.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature227, 680–685.
Lee, J.C. and Yoon, K.H. 2008. Paenibacillus woosongensis sp. nov., a xylanolytic bacterium isolated from forest soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.58, 612–616.
Ljungdahl, L.G. and Eriksson, K. 1985. Ecology of microbial cellulose degradation. pp. 237–299. In Marshall, K.C. (ed.), VIII. Advances in Microbial Ecology-1985. Plenum Press, New York, N.Y., USA.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275.
Minnikin, D.E., Patel, P.V., Alshamaony, L., and Goodfellow, M. 1977. Polar lipid composition in the classification of Nocardia and related bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.27, 104–117.
Nelson, N. 1944. A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem.153, 375–380.
Oh, H.W., Kim, B.C., Lee, K.H., Kim, D.Y., Park, D.S., Park, H.M., and Bae, K.S. 2008. Paenibacillus camelliae sp. nov., isolated from fermented leaves of Camellia sinensis. J. Microbiol.46, 530–534.
Park, M.J., Kim, H.B., An, D.S., Yang, H.C., Oh, S.T., Chung, H.J., and Yang, D.C. 2007. Paenibacillus soli sp. nov., a xylanolytic bacterium isolated from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.57, 146–150.
Pason, P., Kyu, K.L., and Ratanakhanokchai, K. 2006. Paenibacillus curdlanolyticus strain B-6 xylanolytic-cellulolytic enzyme system that degrades insoluble polysaccharides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.72, 2483–2490.
Patrick, M.F., Champagen, P., Cunningham, M.F., and Whitney, R.A. 2010. A biorefinery processing perspective: treatment of lignocellulosic materials for the production of value-added products. Bioresour. Technol.101, 8915–8922.
Phitsuwan, P., Tachaapaikoon, C., Kosugi, A., Mori, Y., Kyu, K.L., and Ratanakhanokchai, K. 2010. A cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzyme complex from an alkalothermoanaerobacterium, Tepidimicrobium xylanilyticum BT14. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.20, 893–903.
Rivas, R., García-Fraile, P., Mateos, P.F., Martínez-Molina, E., and Velázquez, E. 2006. Paenibacillus cellulosilyticus sp. nov., a cellulolytic and xylanolytic bacterium isolated from the bract phyllosphere of Phoenix dactylifera. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.56, 2777–2781.
Saito, H. and Miura, K.I. 1963. Preparation of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid by phenol treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta72, 619–629.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol.4, 406–425.
Sánchez, M.M., Fritze, D., Blanco, A., Spröer, C., Tindall, B.J., Schumann, P., Kroppenstedt, R.M., Diaz, P., and Pastor, F.I.J. 2005. Paenibacillus barcinonensis sp. nov., a xylanase-producing bacterium isolated from a rice field in the Ebro River delta. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.55, 935–939.
Sasser, M. 1990. Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc., Newark, DE, USA.
Schaeffer, A.B. and Fulton, M. 1933. A simplified method of staining endospores. Science77, 194.
Shida, O., Takagi, H., Kadowaki, K., Nakamura, L.K., and Komagata, K. 1997. Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticus to the genus Paenibacillus and emended description of the genus Paenibacillus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47, 289–298.
Singleton, P. 2004. Bacteria in Biology, Biotechnology and Medicine, 6th ed. pp. 570. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., West Sussex, England.
Subaramaniyan, S. and Prema, P. 2002. Biotechnology of microbial xylanases: enzymology, molecular biology, and application. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol.22, 33–64.
Tamaoka, J. and Komagata, K. 1984. Determination of DNA base composition by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. FEMS Microbiol. Lett.25, 125–128.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2007. MEGA 4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol.24, 1596–1599.
Thompson, J.D., Gibson, T.J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D.G. 1997. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res.25, 4876–4882.
Tittsler, R.P. and Sandholzer, L.A. 1936. The use of semi-solid agar for the detection of bacterial motility. J. Bacteriol.31, 575–580.
Wayne, L.G., Brenner, D.J., Colwell, R.R., Grimont, P.A.D., Kandler, O., Krichevsky, M.I., Moore, L.H., Moore, W.E.C., Murray, R.G.E., Stackebrandt, E., andet al. 1987. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematic. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.37, 463–464.
Weisburg, W.G., Barns, S.M., Pelletier, D.A., and Lane, D.J. 1991. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol.173, 697–703.
Zhang, Y.H.P., Himmel, M.E., and Mielenz, J.R. 2006. Outlook for cellulase improvement: screening and selection strategies. Biotechnol. Adv.24, 452–481.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tachaapaikoon, C., Tanasupawat, S., Pason, P. et al. Paenibacillus xylaniclasticus sp. nov., a xylanolytic-cellulolytic bacterium isolated from sludge in an anaerobic digester. J Microbiol. 50, 394–400 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1480-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1480-3