Abstract
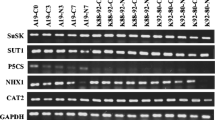
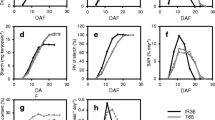
The aim of this investigation was to compare the transcriptional expression of starch metabolism, involving genes and physiological characters, in seedlings of two contrasting salt-tolerant rice genotypes, in response to salt-stress. The soluble sugar content in rice seedlings of both salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive genotypes was enriched, relating to starch degradation, in plants subjected to 200 mM NaCl. In the salt-tolerant cultivar Pokkali, a major source of carbon may be that derived from the photosynthetic system and starch degradation. In starch degradation, only Pho and PWD genes in Pokkali were upregulated in plants subjected to salt stress. In contrast, the photosynthetic abilities of IR29 salt-susceptible cultivar dropped significantly, relating to growth reduction. The major source of carbohydrate in salt-stressed seedlings of the IR29 cultivar may be gained from starch metabolism, regulated by ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (AGP), starch synthase (SS), starch branching enzyme (SBE), starch debranching enzyme (ISA), glucan-water dikinase (GWD), dispropotionating enzyme (DPE), phospho glucan-water dikinase (PWD) and starch phosphorylase (Pho). Also, the major route of soluble sugar in salt-stressed Pokkali seedlings was derived from photosynthesis and starch metabolism. This was identified as novel information in the present study.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balibrea ME, Amico JD, Balarín MC, Pérez-Afocea FP (2000) Carbon partitioning and sucrose metabolism in tomato plants growing under salinity. Physiol Plant 110:503–511
Ballicora MA, Iglesias AA, Preiss J (2004) ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase: a regulatory enzyme for plant starch synthesis. Photosyn Res 79:1–24
Brumós J, Colmenero-Flores JM, Conesa A, Izquierdo P, Sánchez G, Iglesias DJ, López-Climent MF, Gómez-Cadenas A, Talón M (2009) Membrane transporters and carbon metabolism implicated in chloride homeostasis differentiate salt stress responses in tolerant and sensitive Citrus rootstocks. Funct Integr Genom 9:293–309
Cha-um S, Supaibulwatana K, Kirdmanee C (2006) Water relation, photosynthetic ability, and growth of Thai jasmine rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cv. KDML105) to salt stress by application of exogenous glycinebetaine and choline. J Agron Crop Sci 192:25–36
Cha-um S, Supaibulwatana K, Kirdmanee C (2007) Glycinebetaine accumulation, physiological characterizations, and growth efficiency in salt tolerant and salt sensitive lines of indica rice (Oryza sativa L. spp. indica) response to salt stress. J Agron Crop Sci 193:157–166
Cha-um S, Charoenpanich A, Roytrakul S, Kirdmanee C (2009) Sugar accumulation, photosynthesis and growth of two indica rice varieties in response to salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 31:477–486
Cha-um S, Ashraf M, Kirdmanee C (2010) Screening upland rice (Oryza sativa L. spp. indica) genotypes for salt-tolerance using multivariate cluster analysis. Afri J Biotechnol 9:4731–4740
Chen HJ, Chen JY, Wang SJ (2008) Molecular regulation of starch accumulation in rice seedling leaves in response to salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 30:135–142
Chinnusamy V, Jagendorf A, Zhu JK (2005) Understanding and improving salt tolerance in plants. Crop Sci 45:437–448
Djanaguiraman M, Sheeba JA, Shanker AK, Devi DD, Bangarusamy U (2006) Rice can acclimate to lethal level of salinity by pretreatment with sublethal level of salinity through osmotic adjustment. Plant Soil 284:363–373
Ferdose J, Kawasaki M, Taniguchi M, Miyake H (2009) Differential sensitivity of rice cultivars to salinity and its relation to ion accumulation and root tip structure. Plant Prod Sci 12:453–461
Ghosh N, Adak MK, Ghosh PD, Gupta S, Gupta DNS, Mandal C (2011) Differential responses of two rice varieties to salt stress. Plant Biotechnol Rep 5:89–103
Golldack D, Quigley F, Michalowski CB, Kamasani UR, Bohnert HJ (2003) Salinity stress-tolerant and –sensitive rice (Oryza sativa L.) regulate AKT1-type potassium channel transcripts differently. Plant Mol Biol 51:71–81
Gupta AK, Kaur N (2005) Sugar signalling and gene expression in relation to carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stresses in plants. J Biosci 30:761–776
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 51:463–499
James MG, Denyer K, Myers AM (2003) Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:215–222
Kader MA, Lindberg S (2005) Uptake of sodium in protoplasts of salt-sensitive and salt tolerant cultivars of rice, Oryza sativa L. determined by the fluorescent dye SBFI. J Exp Bot 56:3149–3158
Kafi M, Stewart WS, Borland AM (2003) Carbohydrate and proline contents in leaves, roots and apices of salt-tolerant and salt sensitive wheat cultivars. Russ J Plant Physiol 50:174–182
Kanai M, Higuchi K, Hagihara T, Konishi T, Ishii T, Fujita N, Nakamura Y, Maeda Y, Tadano T (2007) Common reed produces starch granules at the shoot base in response to salt stress. New Phytol 176:572–580
Karkacier M, Erbas M, Usiu MK, Aksu M (2003) Comparison of different extraction and detection methods for sugar using amino-bonded phase HPLC. J Chromatogr Sci 41:331–333
Kerepesi I, Galiba G (2000) Osmotic and salt stress-induced alteration in soluble carbohydrate content in wheat seedlings. Crop Sci 40:482–487
Khelil A, Menu T, Ricard B (2007) Adaptive response to salt involving carbohydrate metabolism in leaves of a salt-sensitive tomato cultivar. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:551–559
Kötting O, Kossmann J, Zeeman SC, Lloyd JR (2010) Regulation of starch metabolism: the age of enlightenment. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:321–329
Lee KS, Choi WY, Ko JC, Kim TS, Gregorio GB (2003) Salinity tolerance of japonica and indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) at seedling stage. Planta 216:1043–1046
Lee SK, Hwang SK, Han M, Eom JS, Kang HG, Han Y, Choi SB, Cho MH, Bhoo SH, An G, Hahn TR, Okita TW, Jeon JS (2007) Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 65:531–546
Liu T, van Staden J (2001) Partitioning of carbohydrate in salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant soybean callus cultures under salinity stress and its subsequent relief. Plant Growth Regul 33:13–17
Loggini B, Scartazza A, Brugnoli E, Navari-Izzo F (1999) Antioxidant defense system, pigment composition, and photosynthetic efficiency in two wheat cultivars subjected to drought. Plant Physiol 119:1091–1099
Malagoli P, Britto DT, Schulze LM, Kronzucker HJ (2008) Futile Na+ cycling at the root plasma membrane in rice (Oryza sativa L.): kinetic, energetics, and relationship to salinity tolerance. J Exp Bot 59:4109–4117
Mansour MMF, Salama KHA (2004) Cellular basis of salinity tolerance in plants. Environ Exp Bot 52:113–122
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence – a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51:659–668
McCleary BV, Monaghan DA (2002) Measurement of resistant starch. J AOAC Inter 85:665–675
Morsy MR, Jouve L, Hausman JF, Hoffmann SJM (2007) Alteration of oxidative and carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes contrasting in chilling tolerance. J Plant Physiol 164:157–167
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Orzechowski S (2008) Starch metabolism in leaves. Acta Biochim Polonic 55:435–445
Praxedes SC, de Lacerda CF, Ferreira TM, Prisco JT, DaMatta FM, Gomes-Filho E (2011) Salt tolerance is unrelated to carbohydrate metabolism in cowpea cultivars. Acta Physiol Plant 33:887–896
Qadir M, Tubeileh A, Akhtar J, Larbi A, Minhas PS, Khan MA (2008) Productivity enhancement of salt–affected environments through crop diversification. Land Degrad Develop 19:429–453
Rosa M, Hilal M, González JA, Prado FE (2009) Low-temperature effect on enzyme activities involved in sucrose-starch partitioning in salt-stressed and salt-acclimated cotyledons of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:300–307
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Senadheera P, Singh RK, Maathuis FJM (2009) Differentially expressed membrane transporters in rice roots may contribute to cultivar dependent salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 60:2553–2563
Tanji KK (2002) Salinity in the soil environment. In: Lauchli A, Luttge U (eds) Salinity environment–plant–molecules. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 21–51
Tetlow IJ (2006) Understanding storage starch biosynthesis in plants: a means to quality improvement. Can J Bot 84:1167–1185
Tiwari BS, Bose A, Giiosii B (1997) Photosynthesis in rice under a salt stress. Photosynthetica 34:303–306
Voigt EL, Almeida TD, Chagas RM, Ponte LFA, Viégas RA, Silveira JAG (2009) Source-sink regulation of cotyledonary reserve mobilization during cashew (Anacadium occidentale) seedling establishment under NaCl salinity. J Plant Physiol 166:80–89
Walia H, Wilson C, Condamine P, Liu X, Ismail AM, Zeng L, Wanamaker SI, Mandal J, Xu J, Cui X, Close TJ (2005) Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage. Plant Physiol 139:822–835
Wang SJ, Liu LF, Chen CK, Chen LW (2006) Regulation of granule-bound starch synthase I gene expression in rice leaves by temperature and drought stress. Biol Plant 50:537–541
Wang RL, Hua C, Zhou F, Zhou QC (2009) Effects of NaCl stress on photochemical activity and thylakoid membrane polypeptide composition of a salt-tolerant and a salt-sensitive rice cultivar. Photosynthetica 47:125–127
Yin YG, Kobayashi Y, Sanuki A, Kondo S, Fukuda N, Ezura H, Sugaya S, Matsukura C (2010) Salinity induces carbohydrate accumulation and sugar-regulated starch biosynthetic genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. cv. ‘Micro-Tom’) fruits in an ABA- and osmotic stress-independent manner. J Exp Bot 61:563–574
Zeeman SC, Smith SM, Smith AM (2007) The diurnal metabolism of leaf starch. Biochem J 401:13–28
Zeeman SC, Kossmann J, Smith AM (2010) Starch its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:209–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theerawitaya, C., Boriboonkaset, T., Cha-um, S. et al. Transcriptional regulations of the genes of starch metabolism and physiological changes in response to salt stress rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 18, 197–208 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-012-0114-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-012-0114-x