Abstract
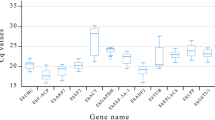
The qRT-PCR method has been widely used to detect gene expression level in plants, helping to understand the molecular mechanisms. However, there are few researches which focus on the selection of the internal reference genes in Forsythia. To select the appropriate reference genes of Forsythia aimed at qRT-PCR normalization, twelve candidate reference genes were selected from our transcriptome data. Their expression was assessed by RT-PCR analysis in 47 Forsythia samples, including 12 species cultivars, different organs and tissues. GeNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper software were used to select the appropriate reference genes, AG and PSY were used to verify the accuracy of the outcome. The results showed that UKN1 was a stable reference gene in leaves of twelve Forsythia germplasms and in different developmental stages of fruits. MTP, ABCT + MTP, and ABCT + MTP + TIP were stable reference genes in different organs. ACT and SDH were stable reference genes in different flower tissues and different developmental stages of the flower buds. When Forsythia plants were stressed with PEG or ABA, SDH + UKN1 + G6PD was the stable reference gene group for qRT-PCR. The results provided the basis for investigating the physiological and biochemical processes of Forsythia related to medicinal and ornamental properties, and drought-resistance in the level of gene expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves MS, Al-Sadi AM, Carvalho CM (2018) Selection of reference genes for quantitative PCR analysis in Citrus aurantifolia during phytoplasma infection. Trop Plant Pathol 43:402–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-018-0224-2
Andersen CK, Jensen JL, Qrntoft FT (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Chi X, Hu R, Yang Q, Zhang X, Pan L, Chen N et al (2012) Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in peanut by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Mol Genet Genom 287(2):167–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-011-0665-5
Domonkos I, Kis M, Gombos Z, Ughy B (2013) Carotenoids, versatile components of oxygenic photosynthesis. Prog Lipid Res 52:539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2013.07.001
Flinn CL, Ashworth EN (1999) Supercooling in dormant flower buds of Forsythia, and the correlation between pistil size and bud hardiness. J Environ Hortic 17:57–62
Fu J, WangY Huang H, Zhang C, Dai S (2013) Reference gene selection for RT-qPCR analysis of Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium during its flowering stages. Mol Breed 31:205–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9784-x
Gachon C, Mingam A, Charrier B (2004) Real-time PCR: What relevance to plant studies? J Exp Bot 55:1445–1454. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh181
Galpaz N, Wang Q, Menda N, Dani Z, Joseph H (2008) Abscisic acid deficiency in the tomato mutant high-pigment 3 leading to increased plastid number and higher fruit lycopene content. Plant J 53:717–730. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03362.x
Ge Y, Wang Y, Chen P, Wang Y, Hou C, Wu Y, Zhang M, Li L, Huo C, Shi Q, Gao H (2016) Polyhydroxy triterpenoids and phenolic constituents from Forsythia suspensa (thunb.) vahl leaves. J Agric Food Chem 64:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04509
Gong L, Song JL, Gan XY, Liu X, Chen YC, Guo ZQ, Song YX (2018) Correlation analysis of StNCED1 expression level and ABA content of Potato under simulated drought stress. J Plant Gene Resour 19:561–567. https://doi.org/10.13430/j.cnki.jpgr.2018.03.023
Guo H, Liu AH, Ye M, Yang M, Guo DA (2007) Characterization of phenolic compounds in the fruits of Forsythia suspensa by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 21:715–729. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.2875
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Guénin S, Pelloux J, Lefebvre JF, Louvet R, Rusterucci C, Moritz T, Guerineau F, Bellini C, Van Wuytswinkel O (2010) The lack of a systematic validation of reference genes: a serious pitfall undervalued in reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6:609–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00346.x
Hong Y (2016) Molecular mechanism of light-dependent anthocyanin biosynthesis in Chrysanthemum × morifolium [D]. Beijing Forestry University
Hou JH, Gao ZH, Zhang Z, Chen SM, Ando T, Zhang JY, Wang XW (2010) Isolation and characterization of an agamous, homologue pmag, from the japanese apricot (Prunus mume, sieb. et zucc.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0248-3
Hu R, Fan C, Li H, Zhang Q, Fu YF (2009) Evaluation of putative reference genes for gene expression normalization in soybean by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-93
Kou XY, Zhang L, Yang SZ, Li GH, Ye JL (2017) Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR analysis in peach fruit under different experimental conditions. Sci Hortic 225:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.07.004
Li W, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Wang G, Song D, Zhang Y (2017) Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in staminate and perfect flowers of andromonoecious Taihangia rupestris. Front Plant Sci 8:729. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00729
Mcnamara S, Pellett H (1993) Flower bud hardiness of Forsythia cultivars. J Environ Hortic 11:39–40
Peng F, James S, Niclas O, Reid KE, Lund ST (2006) An optimized grapevine RNA isolation procedure and statistical determination of reference genes for real-time RT-PCR during berry development. BMC Plant Biol 6(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-6-27
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: bestkeeper-excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47
Piao XL, Jang MH, Cui J, Piao X (2008) Lignans from the fruits of Forsythia suspensa. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:1980–1984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.01.115
Rivera-Vega L, Mamidala P, Koch JL, Mason ME, Mittapalli O (2011) Evaluation of reference genes for expression studies in ash (Fraxinus spp.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:242–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-011-0340-3
Rosati C, Simoneau P, Treutter D (2003) Engineering of flower color in Forsythia by expression of two independently transformed dihydroflavonol 4-reductase and anthocyanidin synthase genes of flavonoid pathway. Mol Breed 12:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026364618719
Rosati C, Cadic A, Duron M, Simoneau P (2007) Forsythia. In: Pua EC, Davey MR (eds) Transgenic crops VI. Biotechnol agriculture and forestry, vol 61. Springer, Berlin, pp 299–318
Sampson DR (1971) Mating group ratios in distylic Forsythia (Oleaceae). Can J Genet Cytol 13:368–371. https://doi.org/10.1139/g71-057
Satake H, Ono E, Murata J (2013) Recent advances in the metabolic engineering of lignan biosynthesis pathways for the production of transgenic plant-based foods and supplements. J Agric Food Chem 61:11721–11729. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4007104
Satake H, Koyama T, Bahabadi SE, Matsumoto E, Ono E, Murata J (2015) Essences in metabolic engineering of lignan biosynthesis. Metabolites 5:270–290. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo5020270
Shiraishi A, Jun M, Erika M, Shin M, Eiichiro O, Honoo S (2016) De novo transcriptomes of Forsythia koreana using a novel assembly method: insight into tissue- and species-specific expression of lignan biosynthesis-related gene. PLOS ONE 11:e0164805. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164805
Tong ZG, Gao ZH, Wang F, Zhang Z, Zhou J (2009) Selection of reliable reference genes for gene expression studies in peach using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-71
Vandesompele J, De PK, Pattyn F, Bruce P, Nadine VR, Paepe AD, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genom Biol 3:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Wang X (2016) Selection of candidate reference genes for gene expression studies by RT-qPCR in soybean [D]. Shanxi Agricultural University
Wang JY, Shen JS, Gu MM, Wang J, Cheng TR, Pan HT, Zhang QX (2017) Leaf coloration and photosynthetic characteristics of hybrids between Forsythia ‘Courtaneur’ and Forsythia koreana ‘Suwon Gold’. HortScience 52:1661–1667. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI12177-17
Xu LF, Hua X, Yuwei C, Panpan Y, Yayan F, Yuchao T, Yuan SX, Ming J (2017) Validation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR during bicolor tepal development in asiatic hybrid lilies (Lilium spp.). Front Plant Sci 8:669. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00669
Yan J (2012) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis in citrus. Mol Biol Rep 39:1831–1838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-011-0925-9
Zhao P, Feng A, Ming T (2007) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi on drought resistance of Forsythia suspensa. Acta Bot Boreali Occident Sin 27:396–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2075(07)60055-7
Acknowledgements
The funding was supported by the World-Class Discipline Construction and Characteristic Development Guidance Funds for Beijing Forestry University (Grant No. 2019XKJS0323), Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Project (Grant No. Z181100002418006), Fundamental Research Fund for the Central University (Grant No. 2015ZCQ-YL-03), National Key Clinical Specialty Discipline Construction Program of China (CN), Hebei Provincial Department of science and Technology Project (Grant No. 18226316D), Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong (CN) (Grant No. HBCT2018060203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1
Expression stability, ranking and pairwise variation of 12 candidate reference genes in in different species, different cultivars of F. intermedia and F. koreana, and different style types by geNorm software. (A, Ranking in different Forsythia speciesl; B, Ranking in different cultivars of F. intermedia; C, Ranking in different cultivars of F.koreana; D, Ranking in species and cultivars with Style type ‘S’; E, Ranking in species and cultivars with Style type ‘L’) (TIFF 12317 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Wu, Y., Jiang, Z. et al. Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for gene expression studies in Forsythia. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 173–188 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00731-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00731-y