Abstract
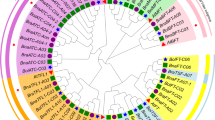
The AP2/ERF transcription factor family plays an important role in different biological processes such as growth, development and response to abiotic and biotic stresses in plants. The genome-wide analysis identified 531 AP2/ERF genes in Brassica napus (oilseed rape or canola) that ranged from 333 to 6440 bp in genomic and 273–2493 bp in coding DNA sequence length. We classified BnAP2/ERF proteins into five subfamilies including AP2 (58 genes), ERF (250 genes), DREB/CBF (194 genes), RAV (26 genes), and Soloist (3 genes). Furthermore, AP2/ERF proteins were subdivided into 15 groups according to the AP2/ERF classification in Arabidopsis. The number of exons in BnAP2/ERF genes was from one to eleven and most of these genes in the same subfamily had the same exon–intron pattern. The results also indicated that the composition of conserved motifs in most proteins in each group was similar. The intron–exon patterns and the composition of conserved motifs validated the BnAP2/ERF transcription factors phylogenetic classification. Based on the results of genome distribution, BnAP2/ERF genes were located unevenly on the 19 B. napus chromosomes. The results indicated that gene duplication may play an important role in genome expansion of B. napus. Furthermore, genome evolution of B. napus using orthologous and paralogous identification was studied. We found 278, 380 and 366 orthologous gene pairs between B. napus with A. thaliana, B. rapa and B. oleracea, respectively. The results of this study will be useful in investigation of functional role and molecular mechanisms of BnAP2/ERF transcription factors genes in response to different stresses.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni A, Dixit S, Jetter R, Thoenes E, van Arkel G, Pereira A (2004) The SHINE clade of AP2 domain transcription factors activates wax biosynthesis, alters cuticle properties, and confers drought tolerance when overexpressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2463–2480
Allen MD, Yamasaki K, Ohme-Takagi M, Tateno M, Suzuki M (1998) A novel mode of DNA recognition by a b-sheet revealed by the solution structure of the GCC-box binding domain in complex with DNA. EMBO J 17:5484–5496
Atashi Shirazi F, Razi H, Niazi A, Alemzadeh A (2019) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a stress-responsive WRKY transcription factor gene, BnWRKY57, from Brassica napus. Plant Omics J 12:37–47
Bartels D, Sunkar R (2005) Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:23–58
Berrocal-Lobo M, Molina A, Solano R (2002) Constitutive expression of ETHYLENE-RESPONSE-FACTOR1 in Arabidopsis confers resistance to several necrotrophic fungi. Plant J 29:23–32
Brenner WG, Ramireddy E, Heyl A, Schmulling T (2012) Gene regulation by cytokinin in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 3:8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00008
Broun P, Poindexter P, Osborne E, Jiang CZ, Riechmann JL (2004) WIN1, a transcriptional activator of epidermal wax accumulation in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4706–4711
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu S, Parkin IAP, Tang H, Wang X, Chiquet J, Belcram H, Tong C, Samans B, Corréa M, Silva CD, Just J, Falentin C, Koh CS, Clainche IL, Bernard M, Bento P, Noel B, Labadie K, Alberti A, Charles M, Armaud D, Guo H, Daviaud C, Alamery S, Jabbari K, Zhao M, Edger PP, Chelaifa H, Tack D, Lassalle G, Mestiri I, Schnel N, Le Paslier MC, Fan G, Renault V, Bayer PE, Golicz AA, Manoli S, Lee TH, Thi VHD, Chalabi S, Hu Q, Fan C, Tollenaere R, Lu Y, Battail C, Shen J, Sidebottom CHD, Wang X, Canaguier A, Chauveau A, Bérard A, Deniot G, Guan M, Liu Z, Sun F, Lim YP, Lyons E, Town CD, Bancroft I, Wang X, Meng J, Ma J, Pires JC, King GJ, Brunel D, Delourme R, Renard M, Aury JM, Adams KL, Batley J, Snowdon RJ, Tost J, Edwards D, Zhou Y, Hua W, Sharpe AG, Paterson AH, Guan C, Wincker P (2014) Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345:950–953
Franklin KA (2009) Light and temperature signal crosstalk in plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:63–68
Fujimoto SY, Ohta M, Usui A, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2000) Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors act as transcriptional activators or repressors of GCC box-mediated gene expression. Plant Cell 12:393–404
Ghoreishi G, Alemzadeh A, Mojarad M, Djavaheri M (2017) Bioremediation capability and characterization of bacteria isolated from petroleum contaminated soils in Iran. Sustain Environ Res 27:195–202
Gilmour SJ, Sebolt AM, Salazar MP, Everard JD, Thomashow MF (2000) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis CBF3 transcriptional activator mimics multiple biochemical changes associated with cold acclimation. Plant Physiol 124:1854–1865
Gu YQ, Yang C, Thara VK, Zhou J, Martin GB (2000) Pti4 is induced by ethylene and salicylic acid, and its product is phosphorylated by the Pto kinase. Plant Cell 12:771–786
Gu YQ, Wildermuth MC, Chakravarthy S, Loh YT, Yang C, He X, Han Y, Martin GB (2002) Tomato transcription factors pti4, pti5, and pti6 activate defense responses when expressed in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:817–831
Haake V, Cook D, Riechmann JL, Pineda O, Thomashow MF, Zhang JZ (2002) Transcription factor CBF4 is a regulator of drought adaptation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 130:639–648
Haghir S, Alemzadeh A (2018) Cloning and molecular characterization of TaERF6, a gene encoding a bread wheat ethylene response factor. Mol Biol Res Commun 7:153–163
Kizis D, Pages M (2002) Maize DRE-binding proteins DBF1 and DBF2 are involved in rab17 regulation through the drought-responsive element in an ABA-dependent pathway. Plant J 30:679–689
Lescot V, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327
Licausi F, Ohme-Takagi M, Perata P (2013) APETALA2/ethylene responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol 199:639–649
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406
Liu L, White MJ, MacRae TH (1999) Transcription factors and their genes in higher plants functional domains, evolution and regulation. Eur J Biochem 262:247–257
Liu Y, Zhao TJ, Liu JM, Liu WQ, Yan YB, Zhou HM (2006) The conserved Ala37 in the ERF/AP2 domain is essential for binding with the DRE element and the GCC box. FEBS Lett 580:1303–1308
McGrath KC, Dombrecht B, Manners JM, Schenk PM, Edgar CI, Maclean DJ, Scheible WR, Udvardi MK, Kazan K (2005) Repressor- and activator-type ethylene response factors functioning in jasmonate signaling and disease resistance identified via a genome-wide screen of Arabidopsis transcription factor gene expression. Plant Physiol 139:949–959
Mojarad M, Alemzadeh Am Ghoreishi G, Javaheri M (2016) Kerosene biodegradation ability and characterization of bacteria isolated from oil-polluted soil and water. J Environ Chem Eng 4:4323–4329
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140:411–432
Ohta M, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinshi H (2000) Three ethylene-responsive transcription factors in tobacco with distinct transactivation functions. Plant J 22:29–38
Ohta M, Matsui K, Hiratsu K, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2001) Repression domains of class II ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression. Plant Cell 13:1959–1968
Olfatmiri H, Alemzadeh A, Zakipour Z (2014) Up-regulation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase under salt stress may enable Aeluropus littoralis to cope with stress. Mol Biol Res Commun 4:65–73
Onate-Sanchez L, Singh KB (2002) Identification of Arabidopsis ethylene responsive element binding factors with distinct induction kinetics after pathogen infection. Plant Physiol 128:1313–1322
Owji H, Hajiebrahimi A, Seradj H, Hemmati S (2017) Identification and functional prediction of stress responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors in Brassica napus by genome-wide analysis. Comput Biol Chem 71:32–56
Pandey GK, Grant JJ, Cheong YH, Kim BG, Li L, Luan S (2005) ABR1, an APETALA2-domain transcription factor that functions as a repressor of ABA response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:1185–1193
Park JM, Park CJ, Lee SB, Ham BK, Shin R, Paek KH (2001) Over-expression of the tobacco Tsi1 gene encoding an EREBP/AP2-type transcription factor enhances resistance against pathogen attack and osmotic stress in tobacco. Plant Cell 13:1035–1046
Rastgoo L, Alemzadeh A, Afsharfifar A (2011) Isolation of two novel isoforms encoding zinc- and copper-transporting P1B -ATPase from Gouan (Aeluropus littoralis). Plant Omics J 4:377–383
Reche PA (2000) Lipoylating and biotinylating enzymes contain a homologous catalytic module. Protein Sci 9:1922–1929
Riechmann JL, Meyerowitz EM (1998) The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors. Biol Chem 379:633–646
Roychoudhury A, Paul S, Basu S (2013) Cross-talk between abscisic acid-dependent and abscisic acid-independent pathways during abiotic stress. Plant Cell Rep 32:985–1006
Sakuma Y, Liu Q, Dubouzet JG, Abe H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2002) DNA-binding specificity of the AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:998–1009
Sami Z, Alemzadeh A (2016) Isolation and molecular characterization of a novel Na+/H+ antiporter gene, AlNHX2, from Aeluropus littoralis and comparison of AlNHX1 and AlNHX2. Plant Omics J 9:205–212
Shigyo M, Ito M (2004) Analysis of gymnosperm two-AP2-domain-containing genes. Dev genes Environ 214:105–114
Song CP, Agarwal M, Ohta M, Guo Y, Halfter U, Wang PC, Zhu JK (2005) Role of an Arabidopsis AP2/EREBP-type transcriptional repressor in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. Plant Cell 17:2384–2396
Song X, Li Y, Hou X (2013) Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genom 14:573–588
Song X, Wang J, Ma X, Li Y, Lei T, Wang L, Ge W, Guo D, Wang Z, Li C (2016) Origination, expansion, evolutionary trajectory, and expression bias of AP2/ERF superfamily in Brassica napus. Front Plant Sci 7:1186. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01186
Suzuki N, Rivero RM, Shulaev V, Blumwald E, Mittler R (2014) Abiotic and biotic stress combinations. New Phtol 203:32–43
Tian T, Liu Y, Yan H, You Q, Yi X, Du Z, Xu W, Su Z (2017) agriGO v2.0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W122–W129
Tuteja N (2007) Abscisic acid and abiotic stress signaling. Plant Signaling Behav 2:135–138
Wei YL, Li JN, Lu J, Tang ZL, Pu DC, Chai YR (2007) Molecular cloning of Brassica napus TRANSPARENT TESTA 2 gene family encoding potential MYB regulatory proteins of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis. Mol Biol Rep 34(2):105–120
Xiao Q, Zhang F, Nacev BA, Liu JO, Pei D (2010) Protein N-terminal processing: substrate specificity of Escherichia coli and human methionine aminopeptidases. Biochemistry 49:5588–5599
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Zhou J, Tang X, Martin GB (1997) The Pto kinase conferring resistance to tomato bacterial speck disease interacts with proteins that bind a cis-element of pathogenesis-related genes. EMBO J 16:3207–3218
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Shiraz University (Grant No. SH82194-181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorbani, R., Zakipour, Z., Alemzadeh, A. et al. Genome-wide analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors family in Brassica napus. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 1463–1476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00832-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00832-z