Abstract
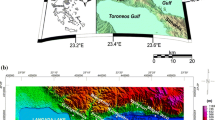
The Hammam Faroun has a particular importance due to its geothermal activity which constitutes the main geothermal resource of Egypt. The area is located on the Sinai Peninsula, a subplate bounded by two seismically active structural zones along the Gulf of Suez and Gulf of Aqaba. High-resolution ground-based gravity and magnetic data are available for the entire Hammam Faroun area, acquired as part of a national project to explore for mineral, geothermal, and hydrocarbon resources. Gravity and magnetic data were analyzed using Source Edge Detection and Source Parameter Imaging (SPI) techniques to image subsurface structures. These analyses show that the area is characterized by a set of northwest-striking faults lying parallel to the Gulf of Suez. Orthogonal patterns are also present, possibly related to rifting of the Gulf of Suez. Depth analysis using the SPI method indicates that surface faults extend to 5-km depth. Analysis of potential-field data elucidates the structurally complex subsurface structure of the Hammam Faroun area.
الملخص
منطقة حمام فرعون تعتبر من اهم المناطق ذات النشاط الحرارى فى مصر و التى تقع على الجانب الشرقى من خليج السويس بشبه جزيرة سيناء. تعتبر شبه جزيرة سيناء الواقعة بين خليج السويس غربا و خليج العقبة شرقا و البحر الاحمر جنوبا و البحر المتوسط شمالا من اهم المناطق فى العالم ذات النشاط الزلزالى. فى إطار التنمية لشبه جزيرة سيناء, تم اجراء مسوحات مغناطيسة و جاذبية بغرض استخدامها فى البحث عن المعادن و البترول و الحرارة الارضية للجزيرة.تم تحليل البيانات المغناطيسية و الجاذبية باستخدام طريقتين حديثتين: الأولى هى " كشف حواف المصدر" و الثانية " كشف خصائص المصدر" لعمل تصور عن التركيب التحت سطحى لمنطقة الدراسة. اظهرت التحليلات ان منطقة حمام فرعون تتميز بوجود صدوع و فوالق فى اتجاه الشمال الغربى موازية لخليج السويس و بعض الاتجاهات الاخرى التى تتوافق مع انفتاح خليج السويس. تحليل بيانات الاعماق تدل على ان هذه الفوالق تمتد تحت السطح لتصل لاعماق حتى 5 كم. من خلال الدراسة تبين ان بيانات المغناطيسية و الجاذبية ساهمت بشكل كبير فى عمل تصور لمنطقة حمام فرعون.الكلمة الرئيسية : حمام فرعون- خليج السويس- شبه جزيرة سيناء.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blakely RJ, Simpson RW (1986) Approximating edges of source bodies from magnetic or gravity anomalies. Geophysics 51:1494–1498
Garfunkel Z, Bartov Y (1977) Tectonics of the Suez Rift. Geol Survey Israel, Bull 71:1–41
Gawthorpe RL, Jackson CAL, Young MJ, Sharp IR, Moustafa AR, Leppard CW (2003) Fault growth, interaction, linkage and death: evolution of the Hammam Faroun fault block, Suez Rift, Egypt. J Struct Geol 25:883–895
Grauch VJS, Cordell L (1987) Limitations of determining density or magnetic boundaries from the horizontal gradient of gravity or pseudogravity data. Geophysics 52:118–121
Cordell L, Grauch VJS (1982) Reconciliation of the discrete and integral Fourier transforms. Geophysics 47(2):237–243
Hall SA (1979) A total intensity aeromagnetic map of the Red Sea and its interpretation. US Geol. Surv. Saudi Arabian Project Report, pp 275–260
Moustafa AR, Abdeen AR (1992) Structural setting of the Hammam Faraun fault block, eastern side of the Suez Rift. J Univ Kuwait Sci 19:291–310
Moustafa AR, El Shaarawy OA (1987) Tectonic setting of the northern Gulf of Suez. Bull Egyptian Geophysical Soci 5:339–368
Patton TL, Moustafa AR, Nelson Ra, Abdine SA (1994) Tectonic evolution and structural setting of the Suez Rift. AAPG Memoir 59:9–51
Roest WR, Verhoef J, Pilkington M (1992) Magnetic interpretation using 3-D analytic signal. Geophysics 57:116–125
Salem A, Williams S, Fairhead D, Smith R, Ravat D (2008) Interpretation of magnetic data using tilt-angle derivatives. Geophysics 73(1):1–10
Sharp IR, Gawthorpe RL, Armstrong B, Underhill JR (2000) Propagation history and passive rotation of mesoscale normal faults: implications for synrift stratigraphic development. Basin Res V12:285–305
Thurston JB, Smith RS (1997) Automatic conversion of magnetic data to depth, dip, and susceptibility contrast using the SPI (TM) method. Geophysics 62:807–813
Acknowledgment
I do thank Richard J. Blakley from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for his comments on the manuscript. I also thank my colleagues from the National Research Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics for their help and support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aboud, E., Selim, E.S. & El Bishlawy, A. Contribution of gravity and magnetic data in delineating the subsurface structure of Hammam Faroun area, Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 4, 249–257 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0134-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0134-1