Abstract
Background
To review the available evidence from prospective studies on the safety and tolerability of the ketogenic diet (KD) for the treatment of refractory childhood epilepsy.
Methods
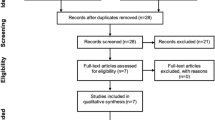
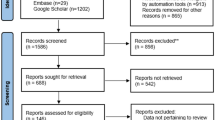
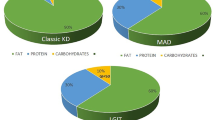
A comprehensive bibliographic search was performed with the aim of retrieving prospective studies that monitored adverse effects (AEs) in children after receiving the classic or medium-chain triglyceride KD therapy for refractory epilepsy.
Results
A total of 45 studies were retrieved, including 7 randomized controlled trials. More than 40 categories of AEs were reported. The most common AEs included gastrointestinal disturbances (40.6%), hyperlipidemia (12.8%), hyperuricemia (4.4%), lethargy (4.1%), infectious diseases (3.8%) and hypoproteinemia (3.8%). Severe AEs, such as respiratory failure and pancreatitis, occurred in no more than 0.5% of children. Specifically, patients receiving KD therapy should be monitored for osteopenia, urological stones, right ventricular diastolic dysfunction, and growth disturbance. The total retention rates of the diet for 1 year and 2 years were 45.7% and 29.2%, respectively. Nearly half of the patients discontinued the diet because of lack of efficacy. AEs were not the main reason for the KD discontinuation. None of the 24 deaths reported after initiation of the diet was attributed to the KD.
Conclusions
KD is a relatively safe dietary therapy. However, because the KD can cause various AEs, it should be implemented under careful medical supervision. Continuous follow-up is needed to address the long-term impact of the diet on the overall health of children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sillanpää M, Schmidt D. Natural history of treated childhoodonset epilepsy: prospective, long-term population-based study. Brain 2006;129:617–624.
Winesett SP, Bessone SK, Kossoff EH. The ketogenic diet in pharmacoresistant childhood epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother 2015;15:621–628.
Keene DL. A systematic review of the use of the ketogenic diet in childhood epilepsy. Pediatr Neurol 2006;35:1–5.
Lefevre F, Aronson N. Ketogenic diet for the treatment of refractory epilepsy in children: a systematic review of efficacy. Pediatrics 2000;105:e46.
Ketogenic Diet Study Group of the Subspecialty Group of Neurology, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association. Prospective multicenter study on long-term ketogenic diet therapy for intractable childhood epilepsy. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2013;51:276–282. [In Chinese]
Rho JM. How does the ketogenic diet induce anti-seizure effects? Neurosci Lett 2017;637:4–10.
Kwiterovich PO Jr, Vining EP, Pyzik P, Skolasky R Jr, Freeman JM. Effect of a high-fat ketogenic diet on plasma levels of lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins in children. JAMA 2003;290:912–920.
Williams S, Basualdo-Hammond C, Curtis R, Schuller R. Growth retardation in children with epilepsy on the ketogenic diet: a retrospective chart review. J Am Diet Assoc 2002;102:405–407.
Peterson SJ, Tangney CC, Pimentel-Zablah EM, Hjelmgren B, Booth G, Berry-Kravis E. Changes in growth and seizure reduction in children on the ketogenic diet as a treatment for intractable epilepsy. J Am Diet Assoc 2005;105:718–725.
Kielb S, Koo HP, Bloom DA, Faerber GJ. Nephrolithiasis associated with the ketogenic diet. J Urol 2000;164:464–466.
Bergqvist AG, Schall JI, Gallagher PR, Cnaan A, Stallings VA. Fasting versus gradual initiation of the ketogenic diet: a prospective, randomized clinical trial of efficacy. Epilepsia 2005;46:1810–1819.
Seo JH, Lee YM, Lee JS, Kang HC, Kim HD. Efficacy and tolerability of the ketogenic diet according to lipid:nonlipid ratios-comparison of 3:1 with 4:1 diet. Epilepsia 2007;48:801–805.
Neal EG, Chaffe HM, Edwards N, Lawson MS, Schwartz RH, Cross JH. Growth of children on classical and medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diets. Pediatrics 2008;122:e334–e340.
Neal EG, Chaffe H, Schwartz RH, Lawson MS, Edwards N, Fitzsimmons G, et al. A randomized trial of classical and medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diets in the treatment of childhood epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009;50:1109–1117.
Kang HC, Lee YJ, Lee JS, Lee EJ, Eom S, You SJ, et al. Comparison of short-versus long-term ketogenic diet for intractable infantile spasms. Epilepsia 2011;52:781–787.
Raju KN, Gulati S, Kabra M, Agarwala A, Sharma S, Pandey RM, et al. Efficacy of 4:1 (classic) versus 2.5:1 ketogenic ratio diets in refractory epilepsy in young children: a randomized open labeled study. Epilepsy Res 2011;96:96–100.
Christodoulides SS, Neal EG, Fitzsimmons G, Chaffe HM, Jeanes YM, Aitkenhead H, et al. The effect of the classical and medium chain triglyceride ketogenic diet on vitamin and mineral levels. J Hum Nutr Diet 2012;25:16–26.
Hu Y, Lu XG, Wen JL, Wang C, Chen L, Chen Y, et al. Randomized control study on two different protocols of ketogenic diet for refractory epilepsy in children. Chin Pediatr Emerg Med 2012;19:473–476. [In Chinese]
El-Rashidy OF, Nassar MF, Abdel-Hamid IA, Shatla RH, Abdel-Hamid MH, Gabr SS, et al. Modified Atkins diet vs classic ketogenic formula in intractable epilepsy. Acta Neurol Scand 2013;128:402–408.
Ballaban-Gil K, Callahan C, O’Dell C, Pappo M, Moshé S, Shinnar S. Complications of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 1998;39:744–748.
Vining EP, Freeman JM, Ballaban-Gil K, Camfield CS, Camfield PR, Holmes GL, et al. A multicenter study of the efficacy of the ketogenic diet. Arch Neurol 1998;55:1433–1437.
Furth SL, Casey JC, Pyzik PL, Neu AM, Docimo SG, Vining EP, et al. Risk factors for urolithiasis in children on the ketogenic diet. Pediatr Nephrol 2000;15:125–128.
Lightstone L, Shinnar S, Callahan CM, O’Dell C, Moshe SL, Ballaban-Gil KR. Reasons for failure of the ketogenic diet. J Neurosci Nurs 2001;6:292–295.
Freeman JM, Vining EP, Pillas DJ, Pyzik PL, Casey JC, Kelly LM. The efficacy of the ketogenic diet-1998: a prospective evaluation of intervention in 150 children. Pediatrics 1998;102:1358–1363.
Hemingway C, Freeman JM, Pillas DJ, Pyzik PL. The ketogenic diet: a 3- to 6-year follow-up of 150 children enrolled prospectively. Pediatrics 2001;108:898–905.
Vining EP, Pyzik P, McGrogan J, Hladky H, Anand A, Kriegler S, et al. Growth of children on the ketogenic diet. Dev Med Child Neurol 2002;44:796–802.
Liu YM, Williams S, Basualdo-Hammond C, Stephens D, Curtis R. A prospective study: growth and nutritional status of children treated with the ketogenic diet. J Am Diet Assoc 2003;103:707–712.
Hosain SA, La Vega-Talbott M, Solomon GE. Ketogenic diet in pediatric epilepsy patients with gastrostomy feeding. Pediatr Neurol 2005;32:81–83.
Klepper J, Scheffer H, Leiendecker B, Gertsen E, Binder S, Leferink M, et al. Seizure control and acceptance of the ketogenic diet in GLUT1 deficiency syndrome: a 2- to 5-year follow-up of 15 children enrolled prospectively. Neuropediatrics 2005;36:302–308.
Caraballo RH, Cersósimo RO, Sakr D, Cresta A, Escobal N, Fejerman N. Ketogenic diet in patients with myoclonic-astatic epilepsy. Epileptic Disord 2006;8:151–155.
Rizzutti S, Ramos AM, Muszkat M, Gabbai AA. Is hospitalization really necessary during the introduction of the ketogenic diet? J Child Neurol 2007;22:33–37.
Nizamuddin J, Turner Z, Rubenstein JE, Pyzik PL, Kossoff EH. Management and risk factors for dyslipidemia with the ketogenic diet. J Child Neurol 2008;23:758–761.
Bergqvist AG, Schall JI, Stallings VA, Zemel BS. Progressive bone mineral content loss in children with intractable epilepsy treated with the ketogenic diet. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;88:1678–1684.
Nathan JK, Purandare AS, Parekh ZB, Manohar HV. Ketogenic diet in Indian children with uncontrolled epilepsy. Indian Pediatr 2009;46:669–673.
Sharma S, Gulati S, Kalra V, Agarwala A, Kabra M. Seizure control and biochemical profile on the ketogenic diet in young children with refractory epilepsy-Indian experience. Seizure 2009;18:446–449.
Spulber G, Spulber S, Hagenäs L, Amark P, Dahlin M. Growth dependence on insulin-like growth factor-1 during the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 2009;50:297–303.
Coppola G, Verrotti A, Ammendola E, Operto FF, Corte RD, Signoriello G, et al. Ketogenic diet for the treatment of catastrophic epileptic encephalopathies in childhood. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2010;14:229–234.
Hong AM, Turner Z, Hamdy RF, Kossoff EH. Infantile spasms treated with the ketogenic diet: prospective single-center experience in 104 consecutive infants. Epilepsia 2010;51:1403–1407.
Nabbout R, Copioli C, Chipaux M, Chemaly N, Desguerre I, Dulac O, et al. Ketogenic diet also benefits Dravet syndrome patients receiving stiripentol: a prospective pilot study. Epilepsia 2011;52:e54–e57.
Tagliabue A, Bertoli S, Trentani C, Borrelli P, Veggiotti P. Effects of the ketogenic diet on nutritional status, resting energy expenditure, and substrate oxidation in patients with medically refractory epilepsy: a 6-month prospective observational study. Clin Nutr 2012;31:246–249.
Sharma S, Gulati S. The ketogenic diet and the QT interval. J Clin Neurosci 2012;19:181–182.
Deng YH, Zhou JH, Li BM, Liu XR, Liao WP. Long-term retention rate and side effects of ketogenic diet in Chinese patients with refraetory epilepsy. Parenter Enter Nutr 2012;19:355–358. [In Chinese]
Pires ME, Ilea A, Bourel E, Bellavoine V, Merdariu D, Berquin P, et al. Ketogenic diet for infantile spasms refractory to firstline treatments: an open prospective study. Epilepsy Res 2013;105:189–194.
Lu ZY, Yu LF, Gong XY, Wang XH, Hua HM, Zhang LM, et al. Compliance and safety of ketogenic diet therapy for children with intractable epilepsy. Chin J Pract Pediatr 2013;28:378–381. [In Chinese]
Li BM, Tong LL, Jia GJ, Wang JW, Lei GF, Yin P, et al. Influence of ketogenic diet on the clinical effects and electroencephalogram features in 31 children with pharmacoresistant epileptic encephalopathy. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 2013;51:362–366. [In Chinese]
Caraballo RH, Fortini S, Fresler S, Armeno M, Ariela A, Cresta A, et al. Ketogenic diet in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Seizure 2014;23:751–755.
Kayyali HR, Gustafson M, Myers T, Thompson L, Williams M, Abdelmoity A. Ketogenic diet efficacy in the treatment of intractable epileptic spasms. Pediatr Neurol 2014;50:224–227.
Groleau V, Schall JI, Stallings VA, Bergqvist CA. Long-term impact of the ketogenic diet on growth and resting energy expenditure in children with intractable epilepsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 2014;56:898–904.
Kapetanakis M, Liuba P, Odermarsky M, Lundgren J, Hallböök T. Effects of ketogenic diet on vascular function. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2014;18:489–494.
Zhu DN, Xie MM, Wang JH, Wang J, Ma DY, Sun L, et al. Therapeutic effect of ketogenic diet for refractory epilepsy in children: a prospective observational study. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2014;16:513–517. [In Chinese]
Zhu DN, Xie MM, Wang J, Wang JH, Wang MM, Zhang GY, et al. Clinical observation of ketogenic diet adding for refractory epilepsy in 36 cases of children. Chin J Appl Clin Pediatr 2014;29:1483–1487. [In Chinese]
Doksöz Ö, Çeleğen K, Güzel O, Yılmaz Ü, Uysal U, İşgüder R, et al. The short-term effects of ketogenic diet on cardiac ventricular functions in epileptic children. Pediatr Neurol 2015;53:233–237.e1.
Lambrechts DA, de Kinderen RJ, Vles HS, de Louw AJ, Aldenkamp AP, Majoie MJ. The MCT-ketogenic diet as a treatment option in refractory childhood epilepsy: a prospective study with 2-year follow-up. Epilepsy Behav 2015;51:261–266.
Doksöz Ö, Güzel O, Yılmaz Ü, İşgüder R, Çeleğen K, Meşe T, et al. The short-term effect of ketogenic diet on carotid intimamedia thickness and elastic properties of the carotid artery and the aorta in epileptic children. J Child Neurol 2015;30:1646–1650.
Martin K, Jackson CF, Levy RG, Cooper PN. Ketogenic diet and other dietary treatments for epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;2:CD001903.
Kim JT, Kang HC, Song JE, Lee MJ, Lee YJ, Lee EJ, et al. Catch-up growth after long-term implementation and weaning from ketogenic diet in pediatric epileptic patients. Clin Nutr 2013;32:98–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, QY., Zhou, ZJ., Luo, R. et al. Safety and tolerability of the ketogenic diet used for the treatment of refractory childhood epilepsy: a systematic review of published prospective studies. World J Pediatr 13, 528–536 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0053-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0053-2