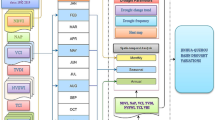
Abstract
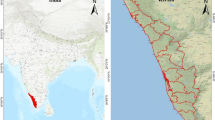
Located on the southeast edge of the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau, Aba County is the core area of the Returning Grazing Land to Grassland Project (RGLGP) on the plateau. For the purpose of monitoring the grassland change before and after the grassland protection project in Aba County, Landsat images acquired in 1996, 2003 and 2009 were analyzed. Using Spectral Mixture Analysis (SMA) model, sub-pixel fractions of land cover components were obtained: bright vegetation (BV), dark vegetation (DV), bright soil (BS), dark soil (DS) and water. Fraction images present the distribution and proportions of typical land cover components in this study. Fractions BV and BS were chosen as two indicators for grassland degradation. Thereafter, Change Vector Analysis (CVA) model was applied on the two indicators. After the performance of the CVA model, change results which consisted of both grassland degradation and vegetation re-growth were obtained, showing the change patterns of grassland degradation and vegetation re-growing in Aba County between two gaps: from 1996 to 2003 (before the RGLGP) and from 2003 to 2009 (after the RGLGP). The change patterns of grassland degradation and vegetation re-growing can effectively assist in the development of environmental restoration measures and in the RGLGP plans for the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aba County People’s Government, P.R.China. (2012). The basic situation of Aba. http://www.abaxian.gov.cn/xqgk/jbxq/201506/t20150612_1073279.html. Accessed on December 16, 2015.
Akiyama, T., & Kawamura, K. (2007). Grassland degradation in China: Methods of monitoring, management and restoration. Grassland Science, 53(1), 1–17. doi:10.1111/j.1744-697X.2007.00073.x.
Asner, G. P., Borghi, C. E., & Ojeda, R. A. (2003). Desertification in central Argentina: Changes in ecosystem carbon and nitrogen from imaging spectroscopy. Ecological Applications, 13(3), 629–648. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(2003)013[0629:DICACI]2.0.CO;2.
Beyene, S. (2013). Rangeland degradation in a semi-arid communal savannah of Swaziland: Long-term dip-tank use effects on woody plant structure, cover and their indigenous use in three soil types. Land Degradation and Development, 26(4), 311–323. doi:10.1002/ldr.2203.
Brandt, J. S., & Townsend, P. A. (2006). Land use–land cover conversion, regeneration and degradation in the high elevation Bolivian Andes. Landscape Ecology, 21(4), 607–623. doi:10.1007/s10980-005-4120-z.
Cai, D., Guan, Y., Guo, S., Zhang, C., & Fraedrich, K. (2014). Mapping plant functional types over broad mountainous regions: A hierarchical soft time-space classification applied to the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 6(4), 3511–3532. doi:10.3390/rs6043511.
Cai, H., Yang, X., & Xu, X. (2015). Human-induced grassland degradation/restoration in the central Tibetan Plateau: The effects of ecological protection and restoration projects. Ecological Engineering, 83(83), 112–119. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.06.031.
Chaudhry, F., Wu, C. C., & Liu, W. (2006). Pixel purity index-based algorithms for endmember extraction from hyperspectral imagery. Recent Advances in Hyperspectral Signal and Image Processing, 661(2), 29–62.
Chen, B. X., Tao, J., Wu, J. S., Wang, J. S., Zhang, J. L., Shi, P. L., et al. (2013). Causes and restoration of degraded alpine grassland in northern Tiber. Journal of Resources and Ecology, 4(1), 43–49. doi:10.5814/j.issn.1674-764x.2013.01.006.
Chien, W. H., Wang, T. S., Yeh, H. C., & Hsieh, T. K. (2016). Study of NDVI application on turbidity in reservoirs. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 44(5), 1–8. doi:10.1007/s12524-015-0533-6.
Collado, A. D., Chuvieco, E., & Camarasa, A. (2002). Satellite remote sensing analysis to monitor desertification processes in the crop-rangeland boundary of Argentina. Journal of Arid Environments, 52(1), 121–133. doi:10.1006/jare.2001.0980.
Dawelbait, M., & Morari, F. (2012). Monitoring desertification in a savannah region in Sudan using landsat images and spectral mixture analysis. Journal of Arid Environments, 80(80), 45–55. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2011.12.011.
Dennison, P. E., & Roberts, D. A. (2003). Endmember selection for multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis using endmember average RMSE. Remote Sensing of Environment, 87(2–3), 123–135. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00135-4.
Dong, Q. M., Zhao, X. Q., Wu, G. L., & Chang, X. F. (2015). Optimization yak grazing stocking rate in an alpine grassland of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(5), 2497–2503. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3597-7.
Elmore, A. J., Mustard, J. F., Manning, S. J., & Lobell, D. B. (2000). Quantifying vegetation change in semiarid environments: Precision and accuracy of spectral mixture analysis and the normalized difference vegetation index. Remote Sensing of Environment, 73(1), 87–102. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(00)00100-0.
Fan, J. W., Zhong, H. P., Chen, H., Li, B., & Zhang, W. Y. (2007). Some scientific problems of grassland degradation in arid and semi-arid regions in northern China. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 29(5), 95–101. (in Chinese).
Gao, Q. Z., Wan, Y. F., Xu, H. M., Li, Y., Wangzha, J. C., & Borjigidai, A. (2010). Alpine grassland degradation index and its response to recent climate variability in northern Tibet, China. Quaternary International, 226(1), 143–150. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2009.10.035.
Geerken, R., & Ilaiwi, M. (2004). Assessment of rangeland degradation and development of a strategy for rehabilitation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 90(4), 490–504. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2004.01.015.
Ghatol, S. G., & Karale, R. L. (2000). Assessment of degraded lands of Vidarbha region using remotely sensed data. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 28(2–3), 213–219. doi:10.1007/BF02989905.
Green, A. A., Berman, M., Switzer, P., & Craig, M. D. (1988). A transformation for ordering multispectral data in terms of image quality with implications for noise removal. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 26(1), 65–74. doi:10.1109/36.3001.
Harris, R. B. (2009). Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. Journal of Arid Environments, 74(1), 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2009.06.014.
Huang, S., & Siegert, F. (2006). Land cover classification optimized to detect areas at risk of desertification in North China based on spot vegetation imagery. Journal of Arid Environments, 67(2), 308–327. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2006.02.016.
Jenks, G. F. (1967). The data model concept in statistical mapping. International Yearbook of Cartography, 7, 186–190.
Krishan, G., Kushwaha, S. P. S., & Velmurugan, A. (2009). Land degradation mapping in the upper catchment of river tons. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37(1), 119–128. doi:10.1007/s12524-009-0003-0.
Kuzera, K., Rogan, J., & Eastman, R. (2005). Monitoring vegetation re-growing and deforestation using change vector analysis: Mt. St. Helens study area. In ASPRS 2005 Annual Conference Baltimore, MD.
Li, Q-F, & Du, W-H. (2013) Effect of the different width of ridge-furrow planting on corn growth in semi-arid areas of Longdong. Grassland and Turf.
Li, H., Cai, Y. L., Chen, R. S., Chen, Q., & Yan, X. (2011). Effect assessment of the project of grain for green in the karst region in southwestern china: A case study of Bijie Prefecture. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(12), 3255–3264. (in Chinese).
Li, X. L., Gao, J., Brierley, G., Qiao, Y. M., Zhang, J., & Yang, Y. W. (2013a). Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Implications for rehabilitation. Land Degradation and Development, 24(1), 72–80. doi:10.1002/ldr.1108.
Li, X. L., Perry, L. W. G., Brierley, G., Gao, J., Zhang, J., & Yang, Y. W. (2013b). Restoration prospects for Heitutan degraded grassland in the Sanjiangyuan. Journal of Mountain Science, 10(4), 687–698. doi:10.1007/s11629-013-2557-0.
Li, Z. G., Han, G. D., Zhao, M. L., Wang, J., Wang, Z. W., & Kemp, D. R. (2015). Identifying management strategies to improve sustainability and household income for herders on the desert steppe in inner Mongolia, China. Agricultural Systems, 132, 62–72. doi:10.1016/j.agsy.2014.08.011.
Liu, M., Dries, L., Heijman, W., Huang, J., Zhu, X., Hu, Y. N., et al. (2017). The impact of ecological construction programs on grassland conservation in inner Mongolia. China: Land Degradation & Development. doi:10.1002/ldr.2692.
Lorena, R. B., Santos, J. R., Shimabukuro, Y. E., Brown, I. F., & Kux, H. J. H. (2002). A change vector analysis technique to monitor land use/land cover in sw Brazilian Amazon: Acre state. ECORA 15-Integrating Remote Sensing at the Global, Regional and Local Scale, 8-15.
Lu, D., Batistella, M., Moran, E., & Mausel, P. (2004). Application of spectral mixture analysis to Amazonian land-use and land-cover classification. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 25(23), 5345–5358. doi:10.1080/01431160412331269733.
McMaster, R., & McMaster, S. (2002). A history of twentieth-century American academic cartography. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 29(3), 312–315. doi:10.1559/152304002782008486.
Mukherjee, S., Shashtri, S., Singh, C. K., Srivastava, P. K., & Gupta, M. (2009). Effect of canal on land use/land cover using remote sensing and GIS. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 37(3), 527–537. doi:10.1007/s12524-009-0042-6.
Myint, S. W., & Okin, G. S. (2009). Modelling land-cover types using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis in a desert city. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 30(9), 2237–2257. doi:10.1080/01431160802549328.
Nackaerts, K., Vaesen, K., Muys, B., & Coppin, P. (2005). Comparative performance of a modified change vector analysis in forest change detection. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26(5), 839–852. doi:10.1080/0143116032000160462.
Niu, T. L., Liu, X. H., Zhou-Yuan, L. I., Gao, Y. Y., Kejia, D. E., & Wang, X. (2013). The spatio-temporal changes of the grassland in Ma county, the source region of the Yellow river during 1990–2009. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 438–442. (in Chinese).
Okin, G. S., & Roberts, D. A. (2004). Remote sensing in arid environments: Challenges and opportunities. In S. L. Ustin (Ed.), Remote sensing for natural resource management and environmental monitoring (pp. 11–146). New York: Wiley.
Peddle, D. R., Hall, F. G., & Ledrew, E. F. (1999). Spectral mixture analysis and geometric-optical reflectance modeling of boreal forest biophysical structure. Remote Sensing of Environment, 67(67), 288–297. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00090-X.
Powell, R. L., Roberts, D. A., Dennison, P. E., & Hess, L. L. (2007). Sub-pixel mapping of urban land cover using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis: Manaus, Brazil. Remote Sensing of Environment, 106(2), 253–267. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2006.09.005.
Ren, J. Z. (1998). Grassland scientific research methods. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House. (in Chinese).
Röder, A., Udelhoven, T. H., Hill, J., Barrio, G., & Tsiourlis, G. (2008). Trend analysis of Landsat-TM and -ETM + imagery to monitor grazing impact in a rangeland ecosystem in Northern Greece. Remote Sensing Environment, 112, 2863–2875. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2008.01.018.
Shao, H. Y., Liu, M., Shao, Q. F., Sun, X. F., Wu, J. H., & Xiang, Z. Y. (2014). Research on eco-environmental vulnerability evaluation of the Anning Rriver Basin in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(5), 1555–1568. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3060-9.
Shao, H. Y., Sun, X. F., Wang, H. X., Zhang, X. X., Xiang, Z. Y., & Tan, R. (2016). A method to the impact assessment of the returning grazing land to grassland project on regional eco-environmental vulnerability. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 56, 155–167. doi:10.1016/j.eiar.2015.10.006.
Small, C. (2001). Estimation of urban vegetation abundance by spectral mixture analysis. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 22(7), 299–307. doi:10.1080/01431160151144369.
The Animal Husbandry Bureau of Sichuan Province. Grassland monitoring report of Sichuan Province in 2012. http://www.grassland.gov.cn/grassland-new/Item/4928.aspx,2013. Accessed on July 1, 2015.
Wessels, K. J., Pretorius, D. J., & Prince, S. D. (2008). Reality of rangeland degradation mapping with remote sensing: The South African experience. In 14th Australasian remote sensing and photogrammetry conference, Darwin, Australia.
Wu, C. (2004). Normalized spectral mixture analysis for monitoring urban composition using ETM + imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 93(4), 480–492. doi:10.1016/j.rse.2004.08.003.
Wu, C., & Murray, A. (2003). Estimating impervious surface distribution by spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sensing of Environment, 84(4), 493–505. doi:10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00136-0.
Yang, A. X., Yang, T., Ji, Q., He, Y., & Ghebrezgabher, M. G. (2014). Regional-scale grassland classification using moderate-resolution imaging spectrometer datasets based on multistep unsupervised classification and indices suitability analysis. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 8, 1261–1264. doi:10.1117/1.JRS.8.083548.
Zhang, J. T. (2006). Grassland degradation and our strategies: A case from Shanxi province, China. Rangelands, 28(1), 37–43. https://doi.org/10.2111/1551-501X(2006)28.1[37:GDAOSA]2.0.CO;2.
Zhang, Z. B., Ke, C. Q., & Shang, Y. J. (2014). Studying changes in land use within the Poyang lake region. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 42(3), 633–643. doi:10.1007/s12524-013-0348-2.
Zhao, J., Luo, T., Li, R., Li, X., & Tian, L. (2016) Grazing effect on growing season ecosystem respiration and its temperature sensitivity in alpine grasslands along a large altitudinal gradient on the central Tibetan Plateau. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 218–219, 114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.12.005.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported and funded by the National Natural Science Fund of China (Grant No. 41401659; Grant No. 41302282), the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2017SZ0088; Grant No. 2015JY0145), the Educational Commission of Sichuan Province (Grant No.13ZA0059; Grant No. 13ZB0089), Geological Survey Projects of Ministry of Land and Resources (Grant No. 1212011120019), and the National Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation (Grant No. 201510616004). We greatly appreciate the support of the China Scholarship Council, and are thankful for the support of the Scientific Innovation Team of Remote Sensing Science and Technology of Chengdu University of Technology (Grant No. KYTD201501). The authors greatly appreciate Gabriela Shirkey for her editorial advice and comments. We are also grateful for the anonymous reviewer and his insight and critical review of the manuscript. Lastly, Huaiyong Shao, the author is grateful to the Center for Global Change and Earth Observations of Michigan State University for their workspace.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Q., Shi, Y., Xiang, Z. et al. Monitoring the Grassland Change in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A Case Study on Aba County. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 46, 569–580 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-017-0721-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-017-0721-7