Abstract
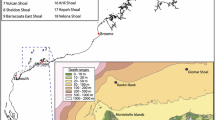
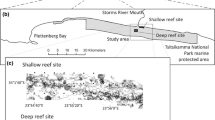
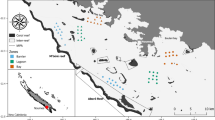
The Queensland Plateau in the Coral Sea off north-eastern Australia supports numerous submerged and emergent reefs. Osprey Reef is an emergent reef at the northern tip of the plateau ~1500 m in elevation. Over such a large depth gradient, a wide range of abiotic factors (e.g., light, temperature, substratum etc.) are likely to influence benthic zonation. Despite the importance of understanding the biodiversity of Australia’s Coral Sea, there is a lack of biological information on deep-water habitats below diving depths. Here, we used a deep-water ROV transect to capture video, still photos and live samples over a depth range spanning 92 to 787 m at North Horn on Osprey Reef. Video analysis, combined with bathymetry data, was used to identify the zones of geomorphology and the benthic assemblages along the depth gradient. There were marked changes in the geomorphology and the substrate along this depth gradient which likely influence the associated benthos. Cluster analysis indicated five benthic assemblage groups, which showed clear zonation patterns and were generally predictable based on the depth and sedimentary environment. These results are the first quantitative observations to such depths and confirm that the waters of the Coral Sea support diverse benthic assemblages, ranging from shallow-water coral reefs to mesophotic coral ecosystems, to deep-water azooxanthellate corals and sponge gardens. The knowledge provided by our study can inform management plans for the Coral Sea Commonwealth Marine Reserve that incorporate the deeper reef habitats and help to minimise future damage to these marine ecosystems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson TJ, Chochrane GR, Roberts DA, Chezar H, Hatcher G (2007) A rapid method to characterize seabed habitats and associated macro-organisms. In: Todd BJ, Greene HG (eds) Marine Geological and Benthic Habitat Mapping, Special Publication 47. Geological Association of Canada, St John’s, pp 71–80
Barnett A, Abrantes KG, Semour J, Fitzpatrick R (2012) Residency and spatial use by reef sharks of an isolated seamount and its implications for conservation. PLoS ONE 7:e36574. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036574
Beaman RJ, Webster JM (2008) Gloria Knolls: a new coldwater coral habitat on the Great Barrier Reef margin, Australia. In: Neil H, Tracey D (eds) 4th International Symposium on Deep-Sea Corals, 1–5 December 2008. Wellington, New Zealand, p 248
Bongaerts P, Bridge TCL, Kline DI, Muir PR, Wallace CC, Beaman RJ, Hoegh-Guldberg O (2011) Mesophotic coral ecosystems on the walls of Coral Sea atolls. Coral Reefs 30:335. doi:10.1007/s00338-011-0725-7
Bostock HC et al (2015) The carbonate mineralogy and distribution of habitat-forming deep-sea corals in the southwest pacific region. Deep-Sea Res I 100:88–104. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2015.02.008
Bridge TCL, Done TJ, Beaman RJ, Friedman A, Williams SB, Pizarro O, Webster JM (2011) Topography, substratum and benthic macrofaunal relationships on a tropical mesophotic shelf margin, central Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 30:143–153. doi:10.1007/s00338-010-0677-3
Bridge TCL, Fabricius KE, Bongaerts P, Wallace CC, Muir PR, Done TJ, Webster JM (2012) Diversity of Scleractinia and Octocorallia in the mesophotic zone of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 31:179–189. doi:10.1007/s00338-011-0828-1
Bridge TCL, Hughes TP, Guinotte JM, Bongaerts P (2013) Call to protect all coral reefs. Nat Clim Chang 3:528–530. doi:10.1038/nclimate1879
Bridge TCL, Grech AM, Pressey RL (2015) Factors influencing incidental representation of previously unknown features in Marine Protected Areas. Conserv Biol. doi:10.1111/cobi.12557
Carney RS (2005) Zonation of deep biota on continental margins. In: Gibson RN, Atkinson RJA, Gordon JDM (eds) Oceanography and marine biology: an annual review, vol 43, Taylor & Francis. New York, U.S.A., pp 211–278
Cartes JE, Carrasson M (2004) Influence of trophic variables on the depth-range distributions and zonation rates of deep-sea megafauna: the case of the Western Mediterranean assemblages. Deep-Sea Res I 51:263–279. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2003.10.001
Ceccarelli DM et al (2013) The Coral Sea: Physical Environment, Ecosystem Status and Biodiversity Assets. In: Lesser M (ed) Advances in marine biology, vol 66. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 213–290. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-408096-6.00004-3
Church JA (1987) East Australian Current adjacent to the Great Barrier Reef. Aust J Mar Freshwat Res 38:671–683
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2006) PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Colin PL (2009) Marine environments of Palau. Coral Reef Research Foundation, Koror
Davies AJ, Guinotte JM (2011) Global habitat suitability for framework-forming cold-water corals. PLoS ONE 6:e18483. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018483
Davies PJ, Symonds PA, Feary DA, Pigram CJ (1988) Facies models in exploration - the carbonate platforms of north-east Australia. APEA J 28:123–143
Davies PJ, Symonds PA, Feary DA, Pigram CJ (1989) The evolution of the carbonate platforms of northeast Australia. In: Crevello PD, Wilson JL, Sarg JF, Read JF (eds) Controls on carbonate platform and basin development, vol Special, Publication 44. SEPM Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Tulsa, pp 233–258. doi:10.2110/pec.89.44.0233
Dohrmann M, Göcke C, Janussen D, Reitner J, Lüter C, Wörheide G (2011) Systematics and spicule evolution in dictyonal sponges (Hexactinellida: Sceptrulophora) with description of two new species. Zool J Linnean Soc 163:1003–1025. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2011.00753.x
Dunn JR, Ridgeway KR (2002) Mapping ocean properties in regions of complex topography. Deep-Sea Res I 49:591–604. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(01)00069-3
Englebert N, Bongaerts P, Muir P, Hay KB, Hoegh-Guldberg O (2014) Deepest zooxanthellate corals of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. Mar Biodivers 45:1–2. doi:10.1007/s12526-014-0221-8
Grassle JF, Sanders HL, Smith WK (1979) Faunal changes with depth in the deep-sea benthos. Ambio Spec Rep 6:47–50
Hartin CA, Fine RA, Sloyan BM, Talley LD, Chereskin TK, Happell J (2011) Formation rates of Subantarctic mode water and Antarctic intermediate water within the South Pacific. Deep-Sea Res I 58:524–534. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2011.02.010
Kahng SE, Kelley CD (2007) Vertical zonation of habitat forming benthic species on a deep photosynthetic reef (50–140 m) in the Au’au Channel, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 26:679–687. doi:10.1007/s00338-007-0253-7
Kahng SE, Maragos JE (2006) The deepest zooxanthellate, scleractinian corals in the world? Coral Reefs 25:254. doi:10.1007/s00338-006-0098-5
Kahng SE, Wagner D, Lantz C, Vetter O, Gove J, Merrifield M (2012) Temperature related depth limits of warm-water corals. In: 12th Int. Coral Reef Symposium, 9C Ecology of mesophotic coral reefs, Cairns, Australia. pp 1–5
Karlińska-Batres K, Wörheide G (2013) Microbial diversity in the coralline sponge Vaceletia crypta. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:1041–1056. doi:10.1007/s10482-013-9884-6
Lambeck K, Chappell J (2001) Sea level change through the last glacial cycle. Science 292:679–685
Lüter C, Wörheide G, Reitner J (2003) A new thecideid genus and species (Brachiopoda, Recent) from submarine caves of Osprey Reef (Queensland Plateau, Coral Sea, Australia). J Nat Hist 37:1423–1432. doi:10.1080/00222930110120971
Mutter JC, Karner GD (1980) The continental margin off northeast Australia. In: Henderson RA, Stephenson PJ (eds) The geology and geophysics of Northesatern Australia. Queensland Division of the Geological Society of Australia, Brisbane, pp 47–69
Nishikawa J, Fitzpatrick R, Reimer JD, Beaman RJ, Yamamoto H, Lindsay DJ (2011) In situ observation of Denise’s pygmy seahorse Hippocampus denise associated with a gorgonian coral Annella reticulata at Osprey Reef, Australia. Galaxea J Coral Reef Stud 13:25–26. doi:10.3755/galaxea.13.25
Post AL, Beaman RJ, O’Brien PE, Eleaume M, Riddle MJ (2011) Community structure and benthic habitats across the George V Shelf, East Antarctica: trends through space and time. Deep-Sea Res II 58:105–118. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2010.05.020
Przeslawski R, Dundas K, Radke L, Anderson TJ (2012) Deep-sea lebensspuren of the Australian continental margins. Deep-Sea Res I 65:26–35. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2012.03.00
Sarano F, Pichon M (1988) Morphology and ecology of the deep fore reef slope at osprey reef, (coral sea). In: Choat H, Bellwood O (eds) 6th international coral reef symposium. Townsville, Australia, pp 607–611
Solokov S, Rintoul SR (2000) Circulation and water masses of the Southwest Pacific: WOCE Section P11, Papua New Guinea to Tasmania. J Mar Res 58:223–268. doi:10.1357/002224000321511151
Symonds PA, Davies PJ, Parisi A (1983) Structure and stratigraphy of the central Great Barrier Reef. BMR J Aust Geol Geophys 8:277–291
Thresher R et al (2014) Strong depth-related zonation of megabenthos on a rocky continental margin (~700–4000 m) off southern Tasmania, Australia. PLoS ONE 9:1–17. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085872
van Oppen MJH, Peplow LM, Kininmonth S, Berkelmans R (2011) Historical and contemporary factors shape the population genetic structure of the broadcast spawning coral, Acropora millepora, on the Great Barrier Reef. Mol Ecol 20:4899–4914. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05328.x
Webster JM, Davies PJ (2003) Coral variation in two deep drill cores: significance for the Pleistocene development of the Great Barrier Reef. Sediment Geol 159:61–80
Wolanski E, Norro A, King B (1995) Water circulation in the Gulf of Papua. Cont Shelf Res 15:185–212
Wörheide G (2008) A hypercalcified sponge with soft relatives: Vaceletia is a keratose demosponge. Mol Phylogenet Evol 47:433–438. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2008.01.021
Wörheide G, Hooper JNA, Degnan BM (2002) Phylogeography of western Pacific Leucetta ‘chagosensis’ (Porifera: Calcarea) from ribosomal DNA sequences: implications for population history and conservation of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area (Australia). Mol Ecol 11:1753–1768. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01570.x
Wörheide G, Vargas S, Lüter C, Reitner J (2011) Precious coral and rock sponge gardens on the deep aphotic fore-reef of Osprey Reef (Coral Sea, Australia). Coral Reefs 30:901. doi:10.1007/s00338-011-0802-y
Wörheide G, Vargas S, Lüter C, Reitner J (2012) Erratum to: Precious coral and rock sponge gardens on the deep aphotic fore-reef of Osprey Reef (Coral Sea, Australia). Coral Reefs 31:299. doi:10.1007/s00338-011-0830-7
Acknowledgments
We thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for the funding (projects Wo896/7 and Lu839/3 to GW and CL, respectively) and Marum (www.marum.de) for the ROV equipment supplied for the Deep Down Under expedition (www.deepdownunder.de). We also thank the captain, crew and scientific party aboard the MV PMG Pride who undertook the sampling during the 2009 voyage. We thank Nicolas Nowald for assistance with the ROV raw data and Andrew Gray-Spence for the Python program coding used for the video data. Taxonomic help is gratefully acknowledged from Marc Eleaume, Richard Fitzpatrick, Merrick Ekins, Phil Alderslade, Stephen Cairns, Justin Marshall, Vanessa Messmer and Rudi Kuiter. We thank the two anonymous reviewers for helping to greatly improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by P. Martinez Arbizu
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1
(XLS 278 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beaman, R.J., Bridge, T.C.L., Lüter, C. et al. Spatial patterns in the distribution of benthic assemblages across a large depth gradient in the Coral Sea, Australia. Mar Biodiv 46, 795–808 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-015-0434-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-015-0434-5