Abstract
Background
Little is known on the level of physical inactivity and its behavioral and cultural correlates among East Asian college students.
Purpose
The aim of this study is to examine and compare the level and behavioral and cultural correlates of physical inactivity among college students in Taiwan, Hong Kong, South Korea, Singapore, and Malaysia.
Method
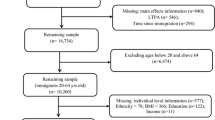
Data were collected from a representative sample of college students (N = 12,137) in five East Asian economies during the 2008–2009 academic year. The stratified random sampling (stratum: geographic region) was used to select participating institutions. The overall response rate was 77%.
Results
The percentage of physically inactive students was 7.2% for Singapore, 8.0% for Malaysia, 13.5% for Taiwan, 16.8% for Hong Kong, and 28.5% for South Korea. When gender, age, and body mass index were controlled, fruit and vegetable consumptions were significant correlates for physical inactivity across all the five economies. In Hong Kong, Korea, and Taiwan, those who engaged in binge drinking at least once during the past 2 weeks were less likely to be physically inactive than those who did not. Religion and military experience did not independently predict physical inactivity in any of the five economies.
Conclusion
Physical inactivity varies greatly across different economies in East Asia that are usually grouped together and considered a single homogeneous entity by some researchers. However, in terms of correlates of physical inactivity, findings of the current study indicate that the transversal value of physical activity might be transformed into a universal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waxman A. WHO’s global strategy on diet, physical activity and health. Scand J Nutr. 2004;48(2):58–60.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Healthy people 2010. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2000.
Ismail MN, Chee SS, Nawaswi H, Yusoff K, Lim TO, James WPT. Obesity in Malaysia. Obes Rev. 2002;3(3):203–8.
Lindner KJ. Sport participation and perceived academic performance of school children and youth. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 1999;11(2):129–43.
Wang LH, Yang HL, Chen YC, Davis R, Schwartz ME, Tam CF. A health probe in college students living in Los Angeles and in Taiwan: dietary pattern, physical activity and energy balance. Coll Student J. 2008;42(3):756–70.
Buckworth J, Nigg C. Physical activity, exercise, and sedentary behavior in college students. J Am Coll Health. 2004;53(1):28–34.
Miller K, Staten RR, Rayens MK, Noland M. Levels and characteristics of physical activity among a college student cohort. Am J Health Educ. 2005;36(4):215–20.
Nguyen-Michel ST, Unger JB, Hamilton J, Spruijt-Metz D. Associations between physical activity and perceived stress/hassles in college students. Stress Health. 2006;22(3):179–88.
Eisenmann JC, Bartee RT, Wang MQ. Physical activity, TV viewing, and weight in U.S. youth: 1999 youth risk behavior survey. Obes Res. 2002;10(5):379–85.
Gordon-Larsen P, Adair LS, Popkin BM. Ethnic differences in physical activity and inactivity patterns and overweight status. Obes Res. 2002;10(3):141–9.
Harring HA, Montgomery K, Hardin J. Perceptions of body weight, weight management strategies, and depressive symptoms among us college students. J Am Coll Health. 2010;59(1):43–50.
Seo D-C, Nehl E, Agley J, Ma S-M. Relations between physical activity and behavioral and perceptual correlates among midwestern college students. J Am Coll Health. 2007;56(2):187–97.
Olchowski AE, Graham JW, Beverly EA, Dupkanick CW. Cigarette smoking, physical activity, and the health status of college students. J Appl Soc Psychol. 2009;39(3):683–706.
Nelson M, Lust K, Story M, Ehlinger E. Alcohol use, eating patterns, and weight behaviors in a university population. Am J Health Behav. 2009;33(3):227–37.
Abdullah A, Wong C, Yam H, Fielding R. Factors related to non-participation in physical activity among the students in Hong Kong. Int J Sports Med. 2005;26(7):611–5.
Seo D-C, Torabi MR, Jiang N, Fernandez-Rojas X, Park B-H. Cross-cultural comparison of lack of regular physical activity among college students: universal versus transversal. Int J Behav Med. 2009;16(4):355–9.
Chen L-J, Haase AM, Fox KR. Physical activity among adolescents in Taiwan. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2007;16(2):354–61.
Chia M. Physical inactivity among children and adolescents in Singapore—a paradoxical issue. Acta Kinesiologica. 2008;2(2):7–15.
Chin MK, Yang JZ, Girandola RN, Ding K, Peek-Asa C. Prevalence of obesity and body composition in Hong Kong school children. J Exerc Sci Fit. 2006;4(2):85–95.
Lee CY, Hwang SY, Ham OK. Factors associated with physical inactivity among Korean men and women. Am J Health Behav. 2007;31(5):484–94.
U.S. National Library of Medicine. Asian American health. http://asianamericanhealth.nlm.nih.gov/intro1.html Updated December 2, 2010. Accessed August 16, 2010.
Sadler GR, Ryujin L, Nguyen T, Oh G, Paik G, Kustin B. Heterogeneity within the Asian American community. Int J Equity Health 2003; 2(12). doi:10.1186/1475-9276-2-12.
Keating XD, Jianmin G, Pinero JC, Bridges DM. A meta-analysis of college students’ physical activity behaviors. J Am Coll Health. 2005;54(2):116–25.
Palencia-Roth M. Universalism and transversalism: dialogue and dialogics in a global perspective. In: Wauchope S, editor. Cultural diversity and transversal values: East-West dialogue on spiritual and secular dynamics. Paris: UNESCO; 2006. p. 38–49.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2011 State and Local Youth Risk Behavior Survey. http://www.cdc.gov/HealthyYouth/yrbs/pdf/questionnaire/2011_hs_questionnaire.pdf. Accessed February 24, 2011.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2009 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System questionnaire. http://www.cdc.gov/brfss/questionnaires/pdf-ques/2009brfss.pdf. Accessed February 24, 2011.
Banville D, Esrosiers P, Genet-Volet Y. Translating questionnaires and inventories using a cross-cultural translation technique. J Teaching Physical Educ. 2000;19:374–87.
WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004;363(9403):157–63.
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S. Applied logistic regression. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley & Sons; 2000.
Mickey J, Greenland S. A Study of the impact of confounder—selection criteria on effect estimation. Am J Epidemiol. 1989;129:125–37.
Poh BK, Safiah MY, Tahir A, et al. Physical activity pattern and energy expenditure of Malaysian adults: findings from the Malaysian Adult Nutrition Survey (MANS). Malays J Nutr. 2010;16(1):13–37.
Wong P, Lee PC. Managing obesity in Singapore schools – holistic approaches for the future. In: Aplin N, editor. Perspectives on physical education and sports science in Singapore – an eye on the Youth Olympics 2010. Singapore: McGraw-Hill; 2009.
Edgar KA, Skinner TC. Illness representations and coping as predictors of emotional well being in adolescence with type I diabetes. J Pediatr Psychol. 2003;28:485–93.
Benyamini Y, Gozlan M, Kokia E. On self-regulation of a health threat: cognitions, coping and emotions among women undergoing treatment for fertility. Cognit Ther Res. 2004;28:577–92.
Moore MJ, Werch C. Relationship between vigorous exercise frequency and substance use among first-year drinking college students. J Am Coll Health. 2008;56(6):686–90.
Crawford LA, Novak KB. Resisting peer pressure: characteristics associated with other-self discrepancies in college students’ levels of alcohol consumption. J Alcohol Drug Educ. 2007;51(1):35–62.
McArthur LH, Raedeke TD. Race and sex differences in college student physical activity correlates. Am J Health Behav. 2009;33(1):80–90.
Ramli R, Hassan S. Trends and forms of women’s participation in politics. In: Hassan SZS, editor. Malaysian women in the wake of change. Kuala Lumpur: Gender Studies Programme, Universiti Malaysia; 1998. p. 88–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, DC., Torabi, M.R., Chin, M.K. et al. A Comparison of Factors Associated with Physical Inactivity Among East Asian College Students. Int.J. Behav. Med. 19, 316–323 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12529-011-9167-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12529-011-9167-4