Abstract
Piezo1 is a mechanically gated ion channel responsible for converting mechanical stimuli into electrical signals in mammals, playing critical roles in vascular development and blood pressure regulation. Dysfunction of Piezo1 has been linked to several disorders, including hereditary xerocytosis (gain-of-function) and generalised lymphatic dysplasia (loss-of-function), as well as a common polymorphism associated with protection against severe malaria. Despite the important physiological roles played by Piezo1, its recent discovery means that many aspects underlying its function are areas of active research. The recently elucidated cryo-EM structures of Piezo1 have paved the way for computational studies, specifically molecular dynamic simulations, to examine the protein’s behaviour at an atomistic level. These studies provide valuable insights to Piezo1’s interactions with surrounding membrane lipids, a small-molecule agonist named Yoda1, and Piezo1’s activation mechanisms. In this review, we summarise and discuss recent papers which use computational techniques in combination with experimental approaches such as electrophysiology/mutagenesis studies to investigate Piezo1. We also discuss how to mitigate some shortcomings associated with using computational techniques to study Piezo1 and outline potential avenues of future research.


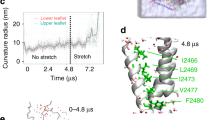
adapted from Botello-Smith et al. (2019) under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andolfo I, Alper SL, De Franceschi L, Auriemma C, Russo R, De Falco L, Vallefuoco F, Esposito MR, Vandorpe DH, Shmukler BE, Narayan R, Montanaro D, D’Armiento M, Vetro A, Limongelli I, Zuffardi O, Glader BE, Schrier SL, Brugnara C, Stewart GW, Delaunay J, Iolascon A (2013) Multiple clinical forms of dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis arise from mutations in PIEZO1. Blood 121(19):3925–3935. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-02-482489
Bae C, Gnanasambandam R, Nicolai C, Sachs F, Gottlieb PA (2013) Xerocytosis is caused by mutations that alter the kinetics of the mechanosensitive channel PIEZO1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(12):E1162. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219777110
Bavi N, Richardson J, Heu C, Martinac B, Poole K (2019) PIEZO1-mediated currents are modulated by substrate mechanics. ACS Nano 13(11):13545–13559. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b07499
Borbiro I, Doreen B, Tibor R (2015) Activation of TRPV1 channels inhibits mechanosensitive Piezo channel activity by depleting membrane phosphoinositides. Sci Sig 8(363):ra15. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2005667
Botello-Smith WM, Jiang W, Zhang H, Ozkan AD, Lin Y-C, Pham CN, Lacroix JJ, Luo Y (2019) A mechanism for the activation of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel by the small molecule Yoda1. Nat Commun 10(1):4503. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12501-1
Buyan A, Cox CD, Barnoud J, Li J, Chan HSM, Martinac B, Marrink SJ, Corry B (2020) Piezo1 forms specific, functionally important interactions with phosphoinositides and cholesterol. Biophys J 119(8):1683–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2020.07.043
Cansell M, Gouygou J-P, Jozefonvicz J, Letourneur D (1997) Lipid composition of cultured endothelial cells in relation to their growth. Lipids 32(1):39–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-997-0006-3
Chidlow JH Jr, Sessa WC (2010) Caveolae, caveolins, and cavins: complex control of cellular signalling and inflammation. Cardiovasc Res 86(2):219–225. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq075
Chong J, De Vecchis D, Hyman AJ, Povstyan OV, Ludlow MJ, Shi J, Beech DJ, Kalli AC (2021) Modelling of full-length Piezo1 suggests importance of the proximal N-terminus for dome structure. Biophys J . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2021.02.003
Cordero-Morales JF, Vásquez V (2018) How lipids contribute to ion channel function, a fat perspective on direct and indirect interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol 51:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2018.03.015
Corradi V, Mendez-Villuendas E, Ingólfsson HI, Ruo-Xu Gu, Siuda I, Melo MN, Moussatova A, DeGagné LJ, Sejdiu BI, Singh G, Wassenaar TA, Magnero KD, Marrink SJ, Peter Tieleman D (2018) Lipid–protein interactions are unique fingerprints for membrane proteins. ACS Cent Sci 4(6):709–717. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.8b00143
Coste B, Jayanti M, Manuela S, Taryn JE, Sanjeev R, Matt JP, Adrienne ED, Ardem P (2010) Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically-activated cation channels. Sci (New York, N.Y.) 330(6000):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1193270
Cox CD, Bae C, Ziegler L, Hartley S, Nikolova-Krstevski V, Rohde PR, Ng C-A, Sachs F, Gottlieb PA, Martinac B (2016) Removal of the mechanoprotective influence of the cytoskeleton reveals PIEZO1 is gated by bilayer tension. Nat Commun 7(1):10366. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10366
Cox CD, Bavi N, Martinac B (2019) Biophysical principles of ion-channel-mediated mechanosensory transduction. Cell Rep 29(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.08.075
De Vecchis D, Beech DJ, Kalli AC (2021) Molecular dynamics simulations of Piezo1 channel opening by increases in membrane tension. Biophys J 120(8):1510–1521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2021.02.006
Deplazes E, Louhivuori M, Jayatilaka D, Marrink SJ, Corry B (2012) Structural investigation of MscL gating using experimental data and coarse grained MD simulations. PLoS Comput Biol 8(9):e1002683–e1002683. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002683
Dror RO, Dirks RM, J. p Grossman, Huafeng Xu, and David E. Shaw. (2012) Biomolecular simulation: a computational microscope for molecular biology. Annu Rev Biophys 41(1):429–452. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155245
Evans EL, Cuthbertson K, Endesh N, Rode B, Blythe NM, Hyman AJ, Hall SJ, Gaunt HJ, Ludlow MJ, Foster R, Beech DJ (2018) Yoda1 analogue (Dooku1) which antagonizes Yoda1-evoked activation of Piezo1 and aortic relaxation. Br J Pharmacol 175(10):1744–1759. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14188
Fotiou, Elisavet, Silvia Martin-Almedina, Michael A. Simpson, Shin Lin, Kristiana Gordon, Glen Brice, Giles Atton, Iona Jeffery, David C. Rees, Cyril Mignot, Julie Vogt, Tessa Homfray, Michael P. Snyder, Stanley G. Rockson, Steve Jeffery, Peter S. Mortimer, Sahar Mansour, and Pia Ostergaard. (2015) "Novel mutations in PIEZO1 cause an autosomal recessive generalized lymphatic dysplasia with non-immune hydrops fetalis." Nature Communications 6. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9085
Ge J, Li W, Zhao Q, Li N, Chen M, Zhi P, Li R, Gao N, Xiao B, Yang M (2015) Architecture of the mammalian mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nature 527(7576):64–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15247
Geng J, Liu W, Zhou H, Zhang T, Wang Li, Zhang M, Li Y, Shen Bo, Li X, Xiao B (2020) A plug-and-latch mechanism for gating the mechanosensitive Piezo channel. Neuron 106(3):438-451.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.02.010
Gimpl G, Burger K, Fahrenholz F (1997) Cholesterol as modulator of receptor function. Biochemistry 36(36):10959–10974. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi963138w
Glogowska E, Schneider ER, Maksimova Y, Schulz VP, Lezon-Geyda K, John Wu, Radhakrishnan K, Keel SB, Mahoney D, Freidmann AM, Altura RA, Gracheva EO, Bagriantsev SN, Kalfa TA, Gallagher PG (2017) Novel mechanisms of PIEZO1 dysfunction in hereditary xerocytosis. Blood 130(16):1845–1856. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2017-05-786004
Goossens K, De Winter H (2018) Molecular dynamics simulations of membrane proteins: an overview. J Chem Inf Model 58(11):2193–2202. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00639
Gottlieb PA, Sachs F (2012) Piezo1: properties of a cation selective mechanical channel. Channels (Austin, Tex.) 6(4):214–219. https://doi.org/10.4161/chan.21050
Grouleff J, Sheeba JI, Skeby KK, Schiøtt B (2015) The influence of cholesterol on membrane protein structure, function, and dynamics studied by molecular dynamics simulations. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1848(9):1783–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.03.029
Gudipaty SA, Lindblom J, Loftus PD, Redd MJ, Edes K, Davey CF, Krishnegowda V, Rosenblatt J (2017) Mechanical stretch triggers rapid epithelial cell division through Piezo1. Nature 543(7643):118–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21407
Guo YR, MacKinnon R (2017) Structure-based membrane dome mechanism for Piezo mechanosensitivity. eLife 6:e33660. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33660
Haselwandter CA, MacKinnon R (2018) Piezo’s membrane footprint and its contribution to mechanosensitivity. eLife 7:e41968. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41968
Hulce JJ, Cognetta AB, Niphakis MJ, Tully SE, Cravatt BF (2013) Proteome-wide mapping of cholesterol-interacting proteins in mammalian cells. Nat Methods 10(3):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2368
Jeon J, Voth GA (2008) Gating of the mechanosensitive channel protein MscL: the interplay of membrane and protein. Biophys J 94(9):3497–3511. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.109850
Jiang W, Rosario JSD, Botello-Smith W, Zhao S, Lin Y-C, Zhang H, Lacroix J, Rohacs T, Luo YL (2021) Crowding-induced opening of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel in silico. Communications Biology 4(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01600-1
Jo S, Kim T, Iyer VG, Im W (2008) CHARMM-GUI: a web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J Comput Chem 29(11):1859–1865. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20945
Kefauver JM, Ward AB, Patapoutian A (2020) Discoveries in structure and physiology of mechanically activated ion channels. Nature 587(7835):567–576. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2933-1
Lacroix JJ, Botello-Smith WM, Luo Y (2018) Probing the gating mechanism of the mechanosensitive channel Piezo1 with the small molecule Yoda1. Nat Commun 9(1):2029. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04405-3
Li J, Hou B, Tumova S, Muraki K, Bruns A, Ludlow MJ, Sedo A, Hyman AJ, McKeown L, Young RS, Yuldasheva NY, Majeed Y, Wilson LA, Rode B, Bailey MA, Kim HR, Zhaojun Fu, Carter DAL, Bilton J, Imrie H, Paul Ajuh T, Dear N, Cubbon RM, Kearney MT, Raj Prasad K, Evans PC, Ainscough JFX, Beech DJ (2014) Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature 515(7526):279–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13701
Li J, Cox C, Martinac B (2021) The anchor domain is critical for Piezo1 channel mechanosensitivity. Channels 15:438–446. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336950.2021.1923199
Lin Y-C, Guo YR, Miyagi A, Levring J, MacKinnon R, Scheuring S (2019) Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature 573(7773):230–234. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2
Ma S, Cahalan S, LaMonte G, Grubaugh ND, Zeng W, Murthy SE, Paytas E, Gamini R, Lukacs V, Whitwam T, Loud M, Lohia R, Berry L, Khan SM, Janse CJ, Bandell M, Schmedt C, Wengelnik K, Su AI, Honore E, Winzeler EA, Andersen KG, Patapoutian A (2018) Common <em>PIEZO1</em> allele in African populations causes RBC dehydration and attenuates <em>Plasmodium</em> infection. Cell 173(2):443-455.e12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.047
Manna M, Miia N, Joona T, Matti J, Kulig W, Müller DJ, Rog T, Vattulainen I (2016) Mechanism of allosteric regulation of β2-adrenergic receptor by cholesterol. eLife 5:e18432. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18432
Marrink SJ, Jelger Risselada H, Serge Yefimov D, Tieleman P, de Vries AH (2007) The MARTINI force field: coarse grained model for biomolecular simulations. J Phys Chem B 111(27):7812–7824. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp071097f
Martins JR, Penton D, Peyronnet R, Arhatte M, Moro C, Picard N, Kurt B, Patel A, Honoré E, Demolombe S (2016) Piezo1-dependent regulation of urinary osmolarity. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol 468(7):1197–1206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1811-z
Mitchell DC, Straume M, Miller JL, Litman BJ (1990) Modulation of metarhodopsin formation by cholesterol-induced ordering of bilayer lipids. Biochemistry 29(39):9143–9149. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00491a007
Nossal R (2001) Energetics of clathrin basket assembly. Traffic 2(2):138–147. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0854.2001.020208.x
Peter BJ, Kent HM, Mills IG, Yvonne Vallis P, Butler JG, Evans PR, McMahon HT (2004) BAR domains as sensors of membrane curvature: the amphiphysin BAR structure. Science 303(5657):495–499
Picard V, Guitton C, Thuret I, Rose C, Bendelac L, Ghazal K, Aguilar-Martinez P, Badens C, Barro C, Bénéteau C, Berger C, Cathébras P, Deconinck E, Delaunay J, Durand J-M, Firah N, Galactéros F, Godeau B, Jaïs X, de Jaureguiberry J-P, Le Stradic C, Lifermann F, Maffre R, Morin G, Perrin J, Proulle V, Ruivard M, Toutain F, Lahary A, Garçon L (2019) Clinical and biological features in PIEZO1-hereditary xerocytosis and Gardos channelopathy: a retrospective series of 126 patients. Haematologica 104(8):1554–1564. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.205328
Poma AB, Cieplak M, Theodorakis PE (2017) Combining the MARTINI and structure-based coarse-grained approaches for the molecular dynamics studies of conformational transitions in proteins. J Chem Theory Comput 13(3):1366–1374. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.6b00986
Poveda JA, Giudici AM, Renart ML, Morales A, González-Ros JM (2017) Towards understanding the molecular basis of ion channel modulation by lipids: mechanistic models and current paradigms. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1859(9, Part B):1507–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.04.003
Qi Y, Andolfi L, Frattini F, Mayer F, Lazzarino M, Jing Hu (2015) Membrane stiffening by STOML3 facilitates mechanosensation in sensory neurons. Nat Commun 6:8512–8512. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9512
Ranade SS, Qiu Z, Woo S-H, Hur SS, Murthy SE, Cahalan SM, Jie Xu, Mathur J, Bandell M, Coste B, Li Y-S, Chien S, Patapoutian A (2014) Piezo1, a mechanically activated ion channel, is required for vascular development in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(28):10347–10352. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1409233111
Ridone P, Pandzic E, Vassalli M, Cox CD, Macmillan A, Gottlieb PA, Martinac B (2020) Disruption of membrane cholesterol organization impairs the activity of PIEZO1 channel clusters. J Gen Physiol 152(8):e201912515. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.201912515
Romero LO, Caires R, Nickolls AR, Chesler AT, Cordero-Morales JF, Vásquez V (2020) A dietary fatty acid counteracts neuronal mechanical sensitization. Nat Commun 11(1):2997–2997. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16816-2
Romero LO, Massey AE, Mata-Daboin AD, Sierra-Valdez FJ, Chauhan SC, Cordero-Morales JF, Vásquez V (2019) Dietary fatty acids fine-tune Piezo1 mechanical response. Nat Commun 10:1200. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09055-7
Saotome K, Murthy SE, Kefauver JM, Whitwam T, Patapoutian A, Ward AB (2018) Structure of the mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1. Nature 554(7693):481–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25453
Shi J, Hyman AJ, De Vecchis D, Chong J, Laeticia Lichtenstein T, Futers S, Rouahi M, Salvayre AN, Auge N, Kalli AC, Beech DJ (2020) Sphingomyelinase disables inactivation in endogenous PIEZO1 channels. Cell Rep 33(1):108225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108225
Syeda R, Florendo MN, Cox CD, Kefauver JM, Santos JS, Martinac B, Patapoutian A (2016) Piezo1 channels are inherently mechanosensitive. Cell Rep 17(7):1739–1746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.033
Syeda R, Jie X, Dubin AE, Bertrand C, Mathur J, Truc H, Matzen J, Lao J, Tully DC, Engels IH, Petrassi HM, Schumacher AM, Montal M, Bandell M, Patapoutian A (2015) Chemical activation of the mechanotransduction channel Piezo1. eLife 4:e07369. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.07369
Taberner FJ, Fernández-Ballester G, Fernández-Carvajal A, Ferrer-Montiel A (2015) TRP channels interaction with lipids and its implications in disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1848(9):1818–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.03.022
Wang Li, Zhou H, Zhang M, Liu W, Deng T, Zhao Q, Li Y, Lei J, Li X, Xiao B (2019) Structure and mechanogating of the mammalian tactile channel PIEZO2. Nature 573(7773):225–229. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1505-8
Wang L, Liu X, Zhang K, Liu Z, Yi Q, Jiang J, Xia Y (2021) A bibliometric analysis and review of recent researches on Piezo (2010–2020). Channels 15(1):310–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336950.2021.1893453
Wang Y, Chi S, Guo H, Li G, Wang Li, Qiancheng Zhao Yu, Rao LZ, He W, Xiao B (2018) A lever-like transduction pathway for long-distance chemical- and mechano-gating of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nat Commun 9(1):1300. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03570-9
Wassenaar TA, Ingólfsson HI, Böckmann RA, Peter Tieleman D, Marrink SJ (2015) Computational lipidomics with insane: a versatile tool for generating custom membranes for molecular simulations. J Chem Theory Comput 11(5):2144–2155. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00209
Yefimov S, van der Giessen E, Onck PR, Marrink SJ (2008) Mechanosensitive membrane channels in action. Biophys J 94(8):2994–3002. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.119966
Zarychanski R, Schulz VP, Houston BL, Maksimova Y, Houston DS, Smith B, Rinehart J, Gallagher PG (2012) Mutations in the mechanotransduction protein PIEZO1 are associated with hereditary xerocytosis. Blood 120(9):1908–1915. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-04-422253
Wei-Zheng Z, Marshall KL, Min S, Daou I, Chapleau MW, Abboud FM, Liberles SD, Patapoutian A (2018) PIEZOs mediate neuronal sensing of blood pressure and the baroreceptor reflex. Sci (New York, N.Y.) 362(6413):464–467. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6324
Zhao Q, Kun Wu, Geng J, Chi S, Wang Y, Zhi P, Zhang M, Xiao B (2016) Ion permeation and mechanotransduction mechanisms of mechanosensitive piezo channels. Neuron 89(6):1248–1263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.046
Zhao Q, Zhou H, Chi S, Wang Y, Wang J, Geng J, Kun Wu, Liu W, Zhang T, Dong M-Q, Wang J, Li X, Xiao B (2018) Structure and mechanogating mechanism of the Piezo1 channel. Nature 554(7693):487–492. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25743
Zocher M, Zhang C, Rasmussen SGF, Kobilka BK, Müller DJ (2012) Cholesterol increases kinetic, energetic, and mechanical stability of the human β2-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(50):E3463–E3472. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1210373109
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge funding from Australian Government through the Australian Research Council (DP200100860).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Buyan, A. & Corry, B. Computational studies of Piezo1 yield insights into key lipid–protein interactions, channel activation, and agonist binding. Biophys Rev 14, 209–219 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-021-00847-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-021-00847-0