Abstract
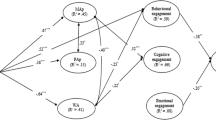
This study examined the phenomenon of academic cheating while focusing on the unique and interactive effects of sociocultural variables on academic motivation, goal orientation and self-efficacy perception of 221 Muslim and Jewish female students. A mixed quantitative and qualitative research design with Multivariate-Analysis of Covariance, Step-wise Discriminant Function Analysis, Path Analysis and semi-structured interviews have been used to clarify the data obtained in various scales. Path Analysis indicated that the main factor predicting the tendency to neutralize academic cheating was the performance goal of pleasing parents mediated by extrinsic motivation. Further analysis showed between-ethnic-groups differences with Muslim students being more extrinsically motivated by the performance goal of pleasing the parents. Content analysis of the interviews conducted with 22 students showed that, in contrast to the Jewish students’ individualistic perspective, Muslim students' collective perspective put them under tremendous pressure to succeed due to the rippling effect of success on all spheres of life e.g., family’s honor, community standing, and future marriage prospects.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Mizrahi nowadays refers to Arab and Sepharadic Jews who immigrated from Muslim countries in Asia and Africa. The Mizrahi living in the periphery of Israel are characterized by low education and low SES.
References
Abu-Baker K (2005) The impact of social values on the psychology of gender among Arab couples: a view from psychotherapy. Psychiatry Related Science 42:106–115
Abu-Rabia A (2000) Employment and unemployment among the Negev Bedouin. Nomadic Peoples 4:84–93
Abu-Zeid AH (1965) Honour and shame: The values of Mediterranean society. Weidenfeld, London
Al-Haj M (1995) Education, empowerment and control: The case of the Arabs in Israel. SUNY, New York
Al-Haj M (2003) Higher education among the Arabs in Israel: formal policy between empowerment and control. Higher Education Policy 16:351–368
Baker SR (2004) Intrinsic, extrinsic and anti-motivational orientations: their role in university adjustment, stress, well-being and subsequent academic performance. Current Psychology Developmental 23:189–202
Bandura A (1986) The explanatory and predictive scope of self-efficacy theory. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology 4:359–373
Bandura A (1997) Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. Freeman, New York
Barakat, H. (2000) Arab Society in the twentieth century: A study in the change of situation and relations. Beirut Center of Arab Unity Research. (Arabic)
Bennett R (2005) Factors associated with student plagiarism in post-1992 University. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education 30:137–162
Bentler PM (1995) EQS structural equations program manual. Multivariate Software, Inc., Encino
Blumer H (1969) Symbolic interactionism. Prentice Hall, Englewoods Cliffs
Brewer EW, Burgess DN (2005) Professor’s role in motivating students to attend class. Journal of Industrial Teacher Education 42:937–942
Bronfenbrenner U (1979) The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Council for Higher Education. (2009). Planning and Budgeting Committee 34/35 report. Retrieved July 20, 2010 from http://www.che.org.il/download/files /contents_1.pdf (Hebrew)
Creswell JW (2003) Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches, 2nd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Denzin NK (2001) Interpretive interactionism, 2nd edn. Sage, Newbury Park
Diamantopoulos A, Siguaw JA (2000) Introducing Lisrel: A guide for the uninitiated. Sage, Los Angeles
Diekhoff GM, LaBeff EE, Clark RE, Williams LE, Francis B, Haines VJ (1996) College cheating: ten years later. Research in Higher Education 37:487–502
Dwairy M (1997) Addressing the repressed needs of the Arabic client. Cultural Diversity and Mental Health 3:1–12
Eccles JS (1983) Expectancies, values, and academic behaviors. In: Spence JT (ed) Achievement and achievement motives: Psychological and sociological approaches. Freeman, San Francisco, pp 75–146
Edelman M (2000) The new Israeli constitution. Middle Eastern Studies 36:1–27
Elliot A, Harackiewicz J (1996) Approach and avoidance achievement goals and intrinsic motivation: a mediational analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 70:461–475
Fawkner M, Keremidchieva G (2004) Plagiarism, cheating and academic dishonesty – have you been there? Information & Security: An International Journal 14:113–137
Finn KV, Frone MR (2004) Academic performance and cheating: moderating role of school identification and self-efficacy. The Journal of Educational Research 97:115–121
Francis B (2005) British-Chinese pupils’ and parents’ constructions of the value of education. Research papers from the School of Education. Roehampton University, U.K
Franklyn-Stokes A, Newstead S (1995) Undergraduate cheating: who does what and why? Studies in Higher Education 20:159–172
Gracia L (2007) Academic dishonesty – whose fault is it anyway? Teaching Research and Development Project: Final Report. Warwick University, U.K
Haines VJ, Diekhoff GM, LaBeff EE, Clark RC (1986) College cheating: immaturity, lack of commitment, and the neutralizing attitude. Research in Higher Education 25:342–354
Haj-Yahia M (1997) Toward culturally sensitive intervention with Arab families in Israel. Contemporary Family Therapy 17:429–447
Hard SF, Conway JM, Moran AC (2006) Faculty and college student beliefs about the frequency of student academic misconduct. Journal of Higher Education 77:1058–1080
Harding T, Mayhew M, Finelli C, Carpenter D (2007) The theory of planned behavior as a model of academic dishonesty in humanities and engineering undergraduates. Ethics & Behavior 17:255–279
Hershkovitz S (2000) Expanding access to higher education. The Commission for Higher Education, Planning and Budget Committee, Jerusalem, Hebrew
Hickey DT, Granade J (2004) The influence of sociocultural theory on our theories of engagement and motivation. In: McInerney DM, Van Etten S (eds) Big theories revisited: Research on sociocultural influences on motivation and learning, vol 4. Information Age, Greenwich, pp 223–247
Hickey DT, McCaslin M (2001) Comparative and sociocultural analyses of context and motivation. In: Volet SS, Järvelä S (eds) Motivation in learning contexts: Theoretical and methodological implications. Pergamon/Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 33–56
Hirschi T (1969) Causes of delinquency. University of California Press, Berkeley and Los Angeles
Hofstede G (1991) Cultures and organizations: Software of the mind. McGraw-Hill, London
Holsti OR (1969) Content analysis for the social sciences and humanities. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Karipidis, R. (2002). Aren’t they good enough? What’s holding them back? Re-envisioning education and democracy public intellectual essay. Retrieved from http://www.macalester.edu/courses/educ59/PIE/Karipidis-%20PIE.htm
Knesset Research and Information Centre. (2010). Employment among Arab female academics. Retrieved December 21, 2010 from http://www.knesset.gov.il/mmm/data/pdf/m02443.pdf (Hebrew)
Layish A (1992) The Arabs in Israel: Continuity and change. Institution for Arab Studies, Givat Haviva, Hebrew
Levy, R., & Bocks, B. (2012). A growing dangerous to academy world. Purchasing and copying academic studies. Retrieved May 2, 2012 from Bar Ilan University Internet Magazine: http://www.barilan-magazine.co.il/ (Hebrew)
Midgley C (ed) (2002) Goals, goal structures, and patterns of adaptive learning. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Mahwah
Midgley C, Maehr ML, Hruda LZ, Anderman E, Anderman L, Freeman KE, Gheen M, Kaplan A, Kumar R, Middleton MJ, Nelson J, Rosser R, Urdan T (2000) Manual for the Patterns of Adaptive Learning Scales (PALS). University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Retrieved from http://www.umich.edu/~pals/manuals.html
Mikulincer M, Weller A, Florian V (1993) Sense of closeness to parents and family rulers: a study of Arab and Jewish youth in Israel. International Journal of Psychology 28:323–335
Miller KA (1988) Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior. Contemporary Sociology 17:253–253
Moneta GB (2004) The flow model of intrinsic motivation in Chinese: cultural and personal moderators. Journal of Happiness Studies 5:181–217
Muhand M (2005) Local elections in the Arab Palestinian minority in Israel: The strengthening of the clans and fall of the parties. In: Rekhes E, Ozacky-Lazar S (eds) Municipal elections in the Arab and Druze Sectors (2003): Clans, ethnic groups and parties. Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, pp 18–24
Murdock T, Anderman E (2006) Motivational perspectives on student cheating: toward an integrated model of academic dishonesty. Educational Psychologist 41:129–145
Murdock T, Hale N, Weber M (2001) Predictors of cheating among early adolescents: academic and social motivations. Contemporary Educational Psychology 26:96–115
Nonis S, Swift C (2001) An examination of the relationship between academic dishonesty and workplace dishonesty: a multicampus investigation. The Journal of Education for Business 77:69–77
Panelo ND (2010) The model minority student: Asian American students and the relationships between acculturation to Western values, family pressures, and mental health concerns. The Vermont Connection 31:147–155
Passow HJ, Mayhew MJ, Finelli CJ, Harding TS, Carpenter DO (2007) Factors influencing engineering students’ decisions to cheat by type of assessment. Research in Higher Education 47:643–684
Patton M (2002) Qualitative research and evaluation methods, 3rd edn. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks
Peled, Y., Barczyk, C., Eshet, Y., & Grinautski, K. (2012). Learning motivation and student academic dishonesty: A comparison between face-to-face and online courses. In Proceedings of society for information technology & teacher education international conference, 25 October 2012 (pp. 752–759). Chesapeake: AACE
Philips M, Horton V (2000) Cybercheating: has morality evaporated in business education? International Journal of Educational Management 14:150–155
Pintrich P, Schunk D (2002) Motivation in education: Theory, research, and applications. Prentice Hall Merrill, Englewood Cliffs
Pintrich P, Smith D, Garcia T, Mckeachie W (1993) Reliability and predictive validity of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ). Educational and Psychological Measurement 53:801–813
Rabideau, S. T. (2005). Effects of achievement motivation on behavior. Retrieved from http://www.personalityresearch.org/papers/rabideau.html
Rocha, M., & Teixeira, A. (2005). Crime without punishment: an update review of the determinants of cheating among University students. FEP Working Papers no. 191. Retrieved May 20, 2010, from http://www.fep.up.pt/investigacao/workingpapers/05.10.14_WP191_brand aoteixeira.pdf
Ryan R, Deci E (2000) Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations: classic definitions and new directions. Contemporary Educational Psychology 25:54–67
Scott MB, Lyman SM (1968) Accounts. American Sociological Review 31:46–62
Smith K, Davy J, Easterling D (2004) An examination of cheating and its antecedents among marketing and management majors. Journal of Business Ethics 50:63–80
Stephens J, Young M, Calbrese T (2007) Does moral judgment go offline when students are online? A comparative analysis of undergraduates’ beliefs and behaviors related to conventional and digital cheating. Ethics & Behavior 17:233–254
Strauss A (1987) Qualitative analysis for social scientists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sykes G, Matza D (1957) Techniques of neutralization: a theory of delinquency. American Sociological Review 22:664–670
Topalli V (2005) When being good is bad: an expansion of neutralization theory. Criminology 43:797–835
Vansteenkiste M, Lens W, Deci EL (2006) Intrinsic versus extrinsic goal contents in self- determination theory: another look at the quality of academic motivation. Educational Psychologist 41:19–31
Vygotsky LS (1978) Mind in society. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Walker C, Greene B, Mansell R (2006) Identification with academics, intrinsic/extrinsic motivation, and self-efficacy as predictors of cognitive engagement. Learning and Individual Differences 16:1–12
Wentzel KR, Watkins DE (2002) Peer-relationships and collaborative learningas contexts for academic enablers. School Psychology Review 31:366–377
Whitley B Jr, Keith-Spiegel P (2002) Academic dishonesty: An educator’s guide. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah
Wigfield A, Eccles J (1992) The development of achievement task values: a theoretical analysis. Developmental Review 12:265–310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dorit Alt and Brenda Geiger for joint and equal authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alt, D., Geiger, B. Goal Orientations and Tendency to Neutralize Academic Cheating: An Ecological Perspective. Psychol Stud 57, 404–416 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-012-0161-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-012-0161-y