Abstract
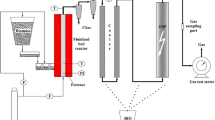
In this study, co-pyrolysis of rice husk with underutilized biomass, Napier grass and sago waste was carried out in a fixed bed reactor at 600 °C, 30 °C/min and 5 L/min nitrogen flowrate. Two-phase bio-oil (organic and aqueous) was collected and characterized using standard analytical techniques. 34.13–45.55 wt% total boil-oil yield was recorded using assorted biomass compared to pure risk husk biomass with 31.51 wt% yield. The organic phase consist mainly benzene derivatives with higher proportion in the oil from the co-pyrolysis process relative to the organic phase from the pyrolysis of the individual biomass while the aqueous phase in all cases was predominantly water, acids, ketones, aldehydes, sugars and traces of phenolics. This study has demonstrated a good approach towards increasing valorization of rice husk in a single reaction step for the production of high grade bio-oil, which can be transformed into fuel and valuable chemicals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yakub, M.I., Mohamed, S., Danladi, S.U.: Technical and economic considerations of post-combustion carbon capture in a coal fired power plant. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 7(5), 1549–1581 (2014)
Mohammed, I.Y.: Optimization and sensitivity analysis of post-combustion carbon capture using DEA solvent in a coal fired power plant. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 7(6), 1681–1690 (2015)
Mohammed, I.Y., Samah, M., Mohamed, A., Sabina, G.: Comparison of Selexol™ and Rectisol® Technologies in an Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) Plant for Clean Energy Production. Int. J. Eng. Res. 3(12), 742–744 (2014)
Report of the Paris Conference on Climate Change (COP21). http://ec.europa.eu/clima/policies/international/negotiations/paris/index_en.htm (2015). Accessed 15 May 2016
Aditiya, H.B., Chong, W.T., Mahlia, T.M.I., Sebayang, A.H., Berawi, M.A., Nur, H.: Second generation bioethanol potential from selected Malaysia’s biodiversity biomasses: a review. Waste Manag 47(Part A), 46–61 (2016)
Rachman, A., Rianse, U., Musaruddin, M., Pasolon, Y.: The potential of delivering clean locally available limitless rice husk energy in the Celebes Island Indonesia. Energy Procedia 79, 55–60 (2015)
Pode, R., Diouf, B., Pode, G.: Sustainable rural electrification using rice husk biomass energy: a case study of Cambodia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 44, 530–542 (2015)
Alias, A.B., Shallcross, D.C., Sharifah, A.S.A.K.: Rice husk combustion evolved gas analysis experiments and modelling. Biomass Bioenergy 78, 36–47 (2015)
Naghizadeh, F., Kadir, M.R.A., Doostmohammadi, A., Roozbahani, F., Iqbal, N., Taheri, M.M., Naveen, S.V., Kamarul, T.: Rice husk derived bioactive glass-ceramic as a functional bioceramic: synthesis, characterization and biological testing. J. Non Cryst. Solids 427, 54–61 (2015)
Mohammed, I.Y., Abakr, Y.A., Kazi, F.K., Yusup, S., Alshareef, I., Chin, S.A.: Pyrolysis of napier grass in a fixed bed reactor: effect of operating conditions on product yields and characteristics. BioResources 10(4), 6457–6478 (2015)
Bridgwater, A.V.: Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading. Biomass Bioenergy 38, 68–94 (2012)
Eom, I.Y., Kim, J.Y., Lee, S.M., Cho, T.S., Yeo, H., Choi, J.W.: Comparison of pyrolytic products produced from inorganic-rich and demineralized rice straw (Oryza sativa L.) by fluidized bed pyrolyzer for future biorefinery approach. Bioresour. Technol. 128, 664–672 (2012)
Sharma, A., Rao, R.: Kinetics of pyrolysis of rice husk. Bioresour. Technol. 67(1), 53–59 (1999)
Ji-Lu, Z.: Bio-oil from fast pyrolysis of rice husk: yields and related properties and improvement of the pyrolysis system. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 80(1), 30–35 (2007)
Naqvi, S.R., Uemura, Y., Osman, N.B., Yusup, S., Nuruddin, M.F.: Physiochemical properties of pyrolysis oil derived from fast pyrolysis of wet and dried rice husk in a free fall reactor. Appl. Mech. Mater. 625, 604–607 (2014)
Zhai, M., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Dong, P., Qi, G.: Characteristics of rice husk tar pyrolysis by external flue gas. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 40(34), 10780–10787 (2015)
Zhai, M., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Dong, P., Qi, G., Huang, Y.: Characteristics of rice husk tar secondary thermal cracking. Energy 93(Part 2), 1321–1327 (2015)
Alvarez, J., Lopez, G., Amutio, M., Bilbao, J., Olazar, M.: Bio-oil production from rice husk fast pyrolysis in a conical spouted bed reactor. Fuel 128, 162–169 (2014)
Qian, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, J.: Pressurized pyrolysis of rice husk in an inert gas sweeping fixed-bed reactor with a focus on bio-oil deoxygenation. Bioresour. Technol. 174, 95–102 (2014)
Zhang, S., Dong, Q., Zhang, L., Xiong, Y.: Effects of water washing and torrefaction on the pyrolysis behavior and kinetics of rice husk through TGA and Py-GC/MS. Bioresour. Technol. 199, 352–361 (2016)
Hsu, C.-P., Huang, A.-N., Kuo, H.-P.: Analysis of the rice husk pyrolysis products from a fluidized bed reactor. Procedia Eng. 102, 1183–1186 (2015)
Naqvi, S.R., Uemura, Y., Yusup, S.: Fast pyrolysis of rice husk in a drop type pyrolyzer for bio-oil and bio-char production. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 8(5), 294–298 (2014)
Naqvi, S.R., Uemura, Y., Yusup, S., Sugiur, Y., Nishiyama, N., Naqvi, M.: The role of zeolite structure and acidity in catalytic deoxygenation of biomass pyrolysis vapors. Energy Procedia 75, 793–800 (2015)
Naqvi, S.R., Uemura, Y., Yusup, S.: Catalytic pyrolysis of paddy husk in a drop type pyrolyzer for bio-oil production: the role of temperature and catalyst. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 106, 57–62 (2014)
Bakar, M.S.A., Titiloye, J.O.: Catalytic pyrolysis of rice husk for bio-oil production. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 103, 362–368 (2013)
Mohammed, I.Y., Kazi, F.K., Yusup, S., Alaba, P.A., Sani, Y.M., Abakr, Y.A.: Catalytic intermediate pyrolysis of napier grass in a fixed bed reactor with ZSM-5, HZSM-5 and zinc-exchanged zeolite-A as the catalyst. Energies 9, 246 (2016)
Abnisa, F., Daud, W.M.A.W.: A review on co-pyrolysis of biomass: an optional technique to obtain a high-grade pyrolysis oil. Energy Convers. Manag. 87, 71–85 (2014)
Martínez, J.D., Veses, A., Mastral, A.M., Murillo, R., Navarro, M.V., Puy, N., Artigues, A., Bartrolí, J., García, T.: Co-pyrolysis of biomass with waste tyres: upgrading of liquid bio-fuel. Fuel Process. Technol. 119, 263–271 (2014)
Alvarez, J., Amutio, M., Lopez, G., Bilbao, J., Olazar, M.: Fast co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and lignocellulosic biomass in a conical spouted bed reactor. Fuel 159, 810–818 (2015)
Wu, Z., Wang, S., Zhao, J., Chen, L., Meng, H.: Thermochemical behavior and char morphology analysis of blended bituminous coal and lignocellulosic biomass model compound co-pyrolysis: effects of cellulose and carboxymethylcellulose sodium. Fuel 171, 65–73 (2016)
Chen, W., Shi, S., Zhang, J., Chen, M., Zhou, X.: Co-pyrolysis of waste newspaper with high-density polyethylene: synergistic effect and oil characterization. Energy Convers. Manag. 112, 41–48 (2016)
Zaafouri, K., Trabelsi, A.B.H., Krichah, S., Ouerghi, A., Aydi, A., Claumann, C.A., Wüst, Z.A., Naoui, S., Bergaoui, L., Hamdi, M.: Enhancement of biofuels production by means of co-pyrolysis of Posidonia oceanica (L.) and frying oil wastes: experimental study and process modeling. Bioresour. Technol. 207, 387–398 (2016)
Mohammed, I.Y., Abakr, Y.A., Kazi, F.K., Yusup, S., Alshareef, I., Chin, S.A.: Comprehensive characterization of napier grass as a feedstock for thermochemical conversion. Energies 8(5), 3403–3417 (2015)
Mohammed, I.Y., Abakr, Y.A., Kabir, F., Yusup, S.: Effects of pretreatments of Napier grass with deionized water, sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide on pyrolysis oil characteristics. Waste Biomass Valoriz. (2016). doi:10.1007/s12649-016-9594-1
Standard test method for water using volumetric Karl Fischer titration, ASTM E203, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA (2001)
Mohammed, I.Y., Kazi, F.K., Abakr, Y.A., Yusuf, S., Razzaque, M.A.: Novel method for the determination of water content and higher heating value of pyrolysis oil. BioResources 10(2), 2681–2690 (2015)
Lim, C.H., Mohammed, I.Y., Abakr, Y.A., Kazi, F.K., Yusup, S., Lam, H.L.: Element characteristic tolerance for semi-batch fixed bed biomass pyrolysis. Chem. Eng. Trans. 45, 1285–1290 (2015)
Mohammed, I.Y., Abakr, Y.A., Kabir, F., Yusup, S.: Effect of aqueous pretreatment on pyrolysis characteristics of napier grass. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 10(11), 1487–1496 (2015)
Yakub, M.I., Abdalla, A.Y., Feroz, K.K., Suzana, Y., Ibraheem, A., Chin, S.A.: Pyrolysis of oil palm residues in a fixed bed tubular reactor. J. Power Energy Eng. 3(04), 185 (2015)
Bordoloi, N., Narzari, R., Chutia, R.S., Bhaskar, T., Kataki, R.: Pyrolysis of Mesua ferrea and Pongamia glabra seed cover: characterization of bio-oil and its sub-fractions. Bioresour. Technol. 178, 83–89 (2015)
Deshmukh, Y., Yadav, V., Nigam, N., Yadav, A., Khare, P.: Quality of bio-oil by pyrolysis of distilled spent of Cymbopogon flexuosus. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 115, 43–50 (2015)
Wang, Z., Wang, F., Cao, J., Wang, J.: Pyrolysis of pine wood in a slowly heating fixed-bed reactor: potassium carbonate versus calcium hydroxide as a catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 91(8), 942–950 (2010)
Lin, Y.Y., Zhang, C., Zhang, M.C., Zhang, J.A.: Deoxygenation of bio-oil during pyrolysis of biomass in the presence of CaO in a fluidized-bed reactor. Energy Fuels 24, 5686–5695 (2010)
Couher, C., Commandre, J.M., Salvador, S.: Failure of the component additivity rule to predict gas yields of biomass in flash pyrolysis at 950 C. Biomass Bioenergy 33, 316–326 (2009)
Couher, C., Commandre, J.M., Salvador, S.: Is it possible to predict gas yields of any biomass after rapid pyrolysis at high temperature from its composition in cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin? Fuel 88, 408–417 (2009)
Mohammad, I.J., Mohammad, G.R., Ashfaque, A.C., Nanjappa, A.: Biofuels production through biomass pyrolysis—a technological review. Energies 5, 4952–5001 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the Crops for the Future (CFF) and University of Nottingham under the Grant BioP1-005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, I.Y., Lim, C.H., Kazi, F.K. et al. Co-pyrolysis of Rice Husk with Underutilized Biomass Species: A Sustainable Route for Production of Precursors for Fuels and Valuable Chemicals. Waste Biomass Valor 8, 911–921 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9599-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9599-9