Abstract
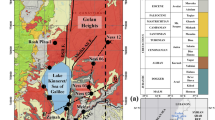
The water resources in the Guanahacabibes Peninsula are distributed in two areas. The northeastern area is characterized by swamps, wetlands and lagoons, with a low contribution of seawater, whereas the area in the southwestern plain shows a considerable development of the karst structures that limits the existence of superficial waters but permits the ingression of the surrounding seawater. In this latter area, the groundwater showed a marked increase in salinity with the depth. In particular, groundwater with a seawater fraction of 0.1 had the lowest Ca-(Mg)-carbonates saturation indexes calculated by modeling the mixing between freshwater and seawater using different software, thermodynamic databases and equations for activity coefficients. Generally, seawater and groundwaters with an added seawater fraction above 0.60–0.65 showed similar oversaturated indexes in high-Mg calcites and pure Ca-carbonates (calcite and aragonite). Differently, in the groundwater that showed carbonates undersaturation (generally with a seawater fraction between 0.02 and 0.60), the saturation indexes in high-Mg calcites were 0.2 lower than pure Ca-carbonates. Locally, the bacterial reduction of the dissolved sulfate enhanced the dissolution of the limestone, contributing to the increased development of the karst structures and the seawater intrusion. Finally, the presence near the coastline of fresh Ca- and Na-bicarbonate waters was in accordance with the upward flow of the shallow freshwater during the formation of the saline wedge. However, the oxygen and hydrogen stable isotope composition of the waters showed a probable contribution to the area from a deep aquifer that is recharged in the highest reliefs of the province (Cordillera de Guaniguanico).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agegian CR, Mackenzie FT (1989) Calcareous organisms and sediment mineralogy on a mid-depth bank in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Pac Sci 43:55–66
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (2007) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, 2nd edn. A. A. Balkema, The Netherlands
Arellano DM, Feitoó R, Seller KP, Stickler W, Rauert W (1989) Estudio isotópico de la llanura costera sur, provincia Pinar del Río, Cuba. Isotope Hydrology Investigations in Latin America, IAEA-TECDOC-502. Austria, Vienna, pp 229–243
Arellano M, Molerio León LF, Suri Hijos (1992) A Efecto de altitud del 18O en zona de articulación de llanura cripto-karsitica con carso de montaña. In: Llanos HJ, Antiguedad I, Morell I, Eraso A (eds) I Taller Internacional sobre Cuencas Experimentales en el Karst, Matanzas, Cuba. Grupo de Trabajo Internacional Cuencas Experimentales Karsticas, Universitat Jaume I de Castelló, pp 29–42
Back W (1966) Hydrochemical facies and ground-water flow patterns in northern part of the Atlantic Coastal Plain. US Geological Survey Professional Paper 498–A
Back W, Hanshaw BB, Herman JS, Van Oriel JN (1986) Differential dissolution of a Pleistocene reef in the ground-water m1 xing zone of coastal Yucatan. Mex Geol 14:137–140
Bethke CM (2008) Geochemical and biogeochemical reaction modeling. Cambridge University Press, New York
Bethke CM, Yeakel S (2008) The Geochemist’s workbench release 7.0—Essentials guide. Hydrogeology program, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois
Boschetti T, Venturelli G, Toscani L, Barbieri M, Mucchino C (2005) The Bagni di Lucca thermal waters (Tuscany, Italy): an example of Ca-SO4 waters with high Na/Cl and low Ca/SO4 ratios. J Hydrol 307:270–293
Budd DA, Vacher HL (2004) Matrix permeability of the confined Floridan aquifer Florida, USA. Hydrogeol J 12:531–549
Cabrera Bermúdez J, Guardado Lacaba R, Peláez García R, González Cabrera N (2004) Regionalizacion hidrogeologica de la Provincia de Pinar del Rio er un SIG. Minería y Geología 1–2:24–31
Cabrera M, Peñalver LL (2001) Contribución a la estratigrafía de los depósitos cuaternarios de Cuba. Cuaternario y geomorfología, 15: 37–49
CASS (2003) Phase I Report—Technical appendix A: salinity and total dissolved solids. United States Department of Interior—Bureau of Reclamation, Central Arizona Salinity Study, Lower Colorado Region, Phoenix Area Office. http://www.usbr.gov/lc/phoenix/programs/cass/pdf/Phase1/ATechapdxTDS.pdf
Cerón RM, Cerón JV, Córdova AV, Zavala J, Muriel M (2005) Chemical composition of precipitation at coastal and marine sampling sites in Mexico. Global NEST J 7:212–221
Choquette PW, Pray LC (1970) Geologic nomenclature and classification of porosity in sedimentary carbonates. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 54:207–250
Cooke RC, Kepkay PE (1984) Apparent calcite supersaturation at the ocean surface: why the present solubility product of pure calcite in seawater does not predict the correct solubility of the salt in nature. Mar Chem 15:59–69
Corbella M, Ayora C (2003) Role of fluid mixing in deep dissolution of carbonates. Geologica Acta 4:305–313
Custodio E (1987) Hydrogeochemistry and tracers. In: Custodio E (ed) Ground-water problems in coastal areas. Studies and reports in hydrology no. 45. UNESCO, Belgium, pp 213–269
Denis R, Díaz Guanche C (1993) Características geologicas y geomorfologicas de la Península Guanahacabibes. Dirección Provincial de Planificación Física, Pinar del Río, Cuba
Díaz Guanche C, Aldana Vilas C, Farfán González H (2013) Mapping Groundwater Vulnerability in Guanahacabibes National Park, Western of Cuba. In: Farfán González H, Corvea Porras JL, de Bustamante Gutiérrez I, LaMoreaux JW (eds) Management of water resources in protected areas. Springer, Berlin, pp 87–94
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater—19th edition. American Public Health Association-American Water Works Association-Water Environment Federation (APHA-AWWA-WEF), Washington, (USA)
Emerson S, Hedges J (2003) Sediment diagenesis and benthic flux. In: Elderfield H, Holland HD, Turekian KK (eds) The oceans and marine geochemistry—treatise on geochemistry. Elsevier, New York
Epstein S, Mayeda T (1953) Variations of 18O/16O ratio in natural waters. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 4:213–224
Fagundo Castillo JR, González Hernandez P (1999) Agricultural use and water quality at karstic Cuban western plain. Int J Speleol 28:175-185
Fagundo JR, Valdés JJ, Pajon JM, de la Cruz A (1986) Caracterizacion geoquimica y geomatematica de formaciones geologicas y sedimentos de la cuenca del rio cuyaguateje. Relacion las caracteristicas hidroquimicas de los acuiferos. Voluntad hidráulica 23:43–48
Florea LJ, McGee DK (2010) Stable isotopic and geochemical variability within shallow groundwater beneath a hardwood hammock and surface water in an adjoining slough (Everglades National Park, Florida, USA). Isot Environ Health Stud 46:190–209
Florea LJ, Vacher HL (2006) Morphologic features of conduits and aquifer response in the unconfined floridian aquifer system, west central Florida. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 12th Symposium on the Geology of the Bahamas and Other Carbonate Regions, Gerace Research Center, San Salvador, Bahamas
Garrels R, Wollast R (1978) Equilibrium criteria for two-component solids reacting with fixed composition in an aqueous phase—example: the magnesian calcite, discussion. Am J Sci 278:1469–1474
Gat JR (2010) Isotope hydrology: a study of the water cycle vol 6. series on environmental science and management. Imperial College Press, London
Glynn PD, Reardon EJ (1990) Solid-solution aqueous-solution equilibria: thermodynamic theory and representation. Am J Sci 290:164–201
Gonfiantini R (1986) Environmental isotopes in lake studies. In: Fritz P, Fontes J-C (eds) Handbook of environmental isotopes geochemistry, vol 2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 113–168
Gonfiantini R, Araguas LA (1988) Los Isotopes Ambientales En El Estudio De La Intrusion Marina. Paper presented at the Tecnología de la Intrusión en Acuíferos Costeros. Almuñécar, Granada
Hernández R, Ramírez R, López-Portilla M, González P, Antigüedad I, Díaz S (2013) Seawater Intrusion in the Coastal Aquifer of Guanahacabibes, Pinar del Río, Cuba. In: Farfán González H, Corvea Porras JL, de Bustamante Gutiérrez I, LaMoreaux JW (eds) Management of water resources in protected areas. Springer, Berlin, pp 301–308
IAEA/WMO (2013) Global network of isotopes in precipitation. The GNIP Database. Accessible at http://www.iaea.org/water
Iturralde-Vinent MA, Gutiérrez Domech MR (1999) Some examples of karst development in Cuba. Boletín Informativo de la Comisión de Geoespeleología, 14:1–4
Jones BF, Vengosh A, Rosenthal E, Yechieli Y (1999) Geochemical Investigations. In: Bear J, Cheng AHD, Sorek S, Ouazar D, Herrera I (eds) Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers—concepts, methods and practices. Theory and applications of transport in porous media, vol 14. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 51–71
Langmuir D (1997) Aqueous environmental geochemistry. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Lin CY, Musta B, Abdullah MH (2013) Geochemical processes, evidence and thermodynamic behavior of dissolved and precipitated carbonate minerals in a modern seawater/freshwatermixing zone of a small tropical island. Appl Geochem 29:13–31
Liu CW, Chen JF (1996) The simulation of geochemical reactions in the Heng-Chun limestone formation, Taiwan. Appl Math Model 20:549–558
Mackenzie FT, Ver LM (2010) Land-sea global transfers. In: Steele JH, Thorpe SA, Turekian KK (eds) Marine chemistry & geochemistry: a derivative of encyclopedia of ocean sciences, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London, pp 485–494
Matisoff G, Bricker III OP, Holdren Jr. GR, Kaerk P (1975) Spatial and temporal variations in the interstitial water chemistry of chesapeake bay sediments. In: Church TM (ed) Marine chemistry in the coastal environment. ACS Symposium Series, vol 18. American Chemical Society, Washington, pp 343–363
Molerio León LF (1992) Composición Química e Isotópica de las Aguas de LLuvia de Cuba. Paper presented at the II Congreso Espeleológico de Latinoamérica y el Caribe, Viñales, Pinar del Río, Cuba
Molerio León LF (2012) Hidrología de trazadores en la gestión ambiental de yacimentos de petróleo onshore. Mapping 154:46–76
Molerio León L, Parise M (2009) Managing environmental problems in Cuban karstic aquifers. Environ geol 58: 275–283
Morse JW, Mackenzie FT (1990) Geochemistry of sedimentary carbonates. Developments in sedimentalogy, vol 48. Elsevier, The Netherlands
Pardo (2009) Overview. In : the geology of Cuba. AAPG Studies in Geology Series 58, pp 1–47
Parkhurst DL, Appelo CAJ (2013) Description of input and examples for PHREEQC Version 3—a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. US Geological Survey Techniques and Methods, book 6, chap A43. http://pubs.usgs.gov/tm/06/a43/. p 497
Peláez García R, González Cabrera NA (2013) Underground water of deep circulation in the national park guanahacabibes, pinar del rio province, cuba: another alternative with water supply aims. In: LaMoreaux JW, Farfán González H, Corvea Porras JL, de Bustamante Gutiérrez I (eds) Management of water resources in protected areas. Springer, Berlin, pp 179–186
Peralta Vital JL, Gil Castillo R, Leyva Bombuse D, Moleiro León L, Pin M (2005) Uso de técnicas nucleares en la evaluación de la cuenca Almendares-Vento para la gestión sostenible de sus recursos hídricos. Forum de Ciencia y Técnica. www.forumcyt.cu
Pérez M, Pubillones León María A (1988) Características microbiológicas de una laguna que ocupa una dolina cársica, Laguna del Valle de San Juan, provincia de Pinar del Río. Paper presented at the Taller Internacional sobre Hidrología del Carso en la Región del Caribe, La Habana, pp 4–12
Perry CT, Salter MA, Harborne AR, Crowley SF, Jelks HL, Wilson RW (2011) Fish as major carbonate mud producers and missing components of the tropical carbonate factory. PNAS 10:3865–3869
Plummer LN (1975) Mixing of sea water with calcium carbonate ground water. In: Whitten EHT (ed) Quantitative studies in geological sciences. Geological Society of America Memoir, vol 142, pp 219–236
Price RM, Herman JS (1991) Geochemical investigation of salt-water intrusion into a coastal carbonate aquifer: Mallorca, Spain. Geol Soc Am Bull 103:1270–1279
Richter BC, Kreitler CW (1993) Geochemical techniques for identifying sources of ground-water salinization. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Robinove CJ, Langford RH, Brookhart JW (1958) Saline-water resources of North Dakota. US Geological Survey, USA
Rodríguez R, Bejarano C, Riverón B, Carmenate JA (2004) Composición química de las precipitaciones, deposición de sales y evaluación de la recarga en la región oriental de Cuba. Boletín Geológico y Minero 115:341-356
Rozanski K, Araguás-Araguás L (1995) Spatial and temporal variability of stable isotope composition of precipitation over the south american continent. Bulletin de l’Institut francais d’études Andins 24:379–390
Rozanski K, Araguás-Araguás L, Gonfiantini R (1993) Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation. In: Swart PK, Lohmann KC, Mckenzie J, Savin S (eds) Climate change in continental isotopic records. Geophysical monograph, vol 78. American Geophysical Union, Washington
Runnells DD (1969) Diagenesis, chemical sediments, and the mixing of natural waters. J Sediment Petrol 39:1188–1201
Sáinz ÁM, Molinero JJ, Saaltink MW (2010) Numerical modelling of coastal aquifer karst processes by means of coupled simulations of density-driven flow and reactive solute transport phenomena. In: Andreo B, Carrasco F, Durán JJ, LaMoreaux JW (eds) Advances in research in karst media. Environmental earth sciences, pp 237–242
Sanford WE, Konikow LF (1989) Simulation of calcite dissolution and porosity changes in saltwater mixing zones in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Res 25:655–667
Seale LD, Soto LR, Florea LJ, Fratesi B (2004) Karst of western Cuba: observations, geomorphology, and diagenesis. In: Davis RL, Gamble DW (eds) Proceedings of the 12th symposium on the geology of the Bahamas and other carbonate terrains. Gerace Research Center, San Salvador, pp 1–9
Stoessel RK (1992) Effects of sulfate reduction on CaCO3 dissolution and precipitation in mixing-zone fluids. J Sediment Petrol 62:873–880
Stoessell RK, Ward WC, Ford BH, Schuffert JD (1989) Water chemistry and CaCO3 dissolution in the saline part of an open-flow mixing zone, coastal Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Geol Soc Am Bull 101:159–169
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organisation, Gutenberg
Wolery TW, Jarek RL (2003) EQ3/6, version 8.0—software user’s manual. Civilian radioactive waste management system, Management and Operating Contractor, Sandia National Laboratories, Albuquerque, New Mexico
Xinping Z, Lide T, Jingmiao L (2005) Fractionation mechanism of stable isotope in evaporating water body. J Geog Sci 15:375–384
Zeebe RE, Wolf-Gladrow D (2001) CO2 in seawater: equilibrium, kinetics, isotopes. Elsevier Oceanography Series, vol 65. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers for their suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boschetti, T., González-Hernández, P., Hernández-Díaz, R. et al. Seawater intrusion in the Guanahacabibes Peninsula (Pinar del Rio Province, western Cuba): effects on karst development and water isotope composition. Environ Earth Sci 73, 5703–5719 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3825-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3825-1