Abstract
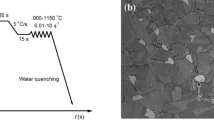
In the present investigation, hot deformation by uniaxial compression of a microalloyed steel has been carried out, using a deformation dilatometer, after homogenization at 1200 °C for 20 min up to strains of 0.4, 0.8 and 1.2 at different temperatures of 900, 1000 and 1100 °C, at a constant strain rate of 2 s−1 followed by water quenching. In all the deformation conditions, initiation of dynamic recrystallization (DRX) is observed, however, stress peaks are not observed in the specimens deformed at 900 and 1000 °C. The specimens deformed at 900 °C showed a combination of acicular ferrite (AF) and bainite (B) microstructure. There is an increase in the acicular ferrite fraction with increase in strain at all these deformation temperatures. At high deformation temperature of 1100 °C, coarsening of DRXed grains is observed. This is attributed to the common limitations involved in fast quenching of the DRXed microstructure, which leads to increase in grain size by metadynamic recrystallization (MDRX). The strain free prior austenite grains promote the formation of large fraction of both bainite and martensite in the transformed microstructures during cooling. The length and width of bainitic ferrite laths also increases with increase in deformation temperature from 900 to 1100 °C and decrease in deformation strain.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vervynckt S, Verbeken K, Lopez B and Jonas J J, Int Mater Rev 57 (2012) 187.
Nafisi S, Arafin M A, Collins L and Szpunar J, Mater Sci Eng A 531 (2012) 2.
Zhang X, Gao H, Zhang X and Yang Y, Mater Sci Eng A 531 (2012) 84.
Bott I D S, De Souza L F G, Teixeira J C G and P R Rios, Metall Mater Trans A 36 (2005) 443.
Klinkenberg C, Bilgen C, Rodriguez-Ibabe J M, Lopez B and Uranga P, Mater Sci Forum 706–709 (2012) 2752.
Reip C P, Shanmugam S and Misra R D K, Mater Sci Eng A 424 (2006) 307.
Isasti N, Jorge-Badiola D, Taheri M L and Uranga P, Metall Mater Trans A 44 (2013) 3552.
Isasti N, Jorge-Badiola D, Taheri M L, Lopez B and Uranga P, Metall Mater Trans A 42 (2011) 3729.
Khulka K and Aleksandrov S, Metallurgist 50 (2006) 137.
Kostryzhev A G, Alshahrani A, Zhu C, Ringer S P and Pereloma E V, Mater Sci Eng A 581 (2013) 16.
Siciliano F J and Jonas J J, Metall Mater Trans A 31 (2000) 511.
Samuel F H, Yue S, Jonas J J and Zbinden B A, Iron Steel Inst Jpn Int 29 (1989) 878.
Pereda B, Fernandez A I, Lopez B and Rodriguez-Ibabe J M, ISIJ Int 47 (2007) 860.
Ebrahimi G R, Momeni A and Eskandari H, Iran J Mater Form 2 (2015) 43.
Deardo A J, Int Mater Rev 48 (2003) 371.
Opiela M and Ozgowicz W, J Achiev Mater Manuf Eng 55 (2012) 759.
Ryan N D and McQueen H J, Can Metall Q 29 (1990) 147.
Stewart G R, Jonas J J and Montheillet F, ISIJ Int 44 (2004) 1581.
Poliak E I and Jonas J J, Acta Mater 44 (1996) 127.
Poliak E I and Jonas J J, ISIJ Int 43 (2003) 692.
Poliak E I and Jonas J J, ISIJ Int 43 (2003) 684.
Najafizadeh A and Jonas J J, ISIJ Int 46 (2006) 1679.
Mandal G K, Stanford N, Hodgson P and Beynon J H, Mat Sci Eng A 556 (2012) 685.
Suikkanen P P, Cayron C, DeArdo A J and Karjalainen L P, J Mater Sci Technol 27 (2011) 920.
Mourino N S, Petrov R, Bae J, Kim K and Kestens L, Mater Sci Forum 638 (2010) 3068.
Backe L, Modeling the microstructural evolution during hot deformation of microalloyed steels, Ph D Thesis, School of Industrial Engineering and Management, Material Science and Engineering, Stockholm (2009).
Qiao G, Xiao F, Zhang X, Cao Y and Liao B, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 19 (2009) 1395.
Vervynckt S, Verbekena K, Thibaux P and Houbaert Y, Mater Sci Eng A 528 (2011) 5519.
Ebrahimi G R, Arabshahi H and Javdani M, J Mech Eng Res 2 (2010) 92.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Director, CSIR-National Metallurgical Laboratory for his kind permission to publish this work. The authors also thank Prof. W. Bleck, IEHK, RWTH-Aachen, Germany for his kind permission to carry out the dilatometry at the institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, G.K., Rajinikanth, V., Kumar, S. et al. Microstructure Evolution During Hot Deformation of a Micro-Alloyed Steel. Trans Indian Inst Met 70, 1019–1033 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0895-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0895-7