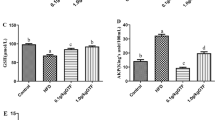
Abstract
Total flavones of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch (GTF) are main components of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch, which have anti-oxidation and lipid-lowering effects. However, its protective effects on the intestinal tissue of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) are unknown. The aims of the study were to evaluate the protective effects of GTF on the intestinal tissue of tilapia after high-fat diet (HFD) feeding. Tilapia (initial weight 30 ± 1 g) received diets containing four doses of GTF (0.05, 0.1, 0.5, and 1.0 g/kg diet) for 90 days. The intestinal tissues were collected to determine biochemical parameter, gene expression and protein level. The results showed that the HFD reduced antioxidant indexes and increased the fat level, lipid oxidation products in the intestinal tissue relative to the control. Adding GTF to the HFD resulted in an increase of antioxidant indexes, fat level and lipid oxidation products decreased after 60, 90 days. In the HFD group, mRNA level of fatty acid transport protein 1 (FATP1) was increased at 60 day and then decreased at 90 day. The mRNA levels of fatty acid binding protein 1 (FABP1) and sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c (SREBP 1c) were significantly increased at 60 or 90 day after HFD feeding. The mRNA levels of acetate coenzyme A carboxylase (ACCA) peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ) and PPAR-α were decreased significantly at 30, 60 and/or 90 days after HFD feeding. Western blotting results also showed that nuclear factor (NF)-κβ C-Rel (NF-κβ C-Rel) and mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 (MAPK8) protein expression in intestinal tissue increased after consumption of the HFD. However, adding GTF to the HFD reversed the changes of genes related to fatty acid synthesis and metabolism, and the level of NF-κβ c-Rel and MAPK8 at different degrees. Overall, these results indicated that GTF promoted decomposition and metabolism of fatty acids in intestinal tissue, alleviated oxidative stress damage caused by the HFD, and had certain protective effects on the intestinal tissue of tilapia.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, El-Araby DA (2021) Immune and antioxidative effects of dietary licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) on performance of nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) and its susceptibility to aeromonas hydrophila infection. Aquaculture 530:735828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735828
Adineh H, Naderi M, Yousefi M, Khademi Hamidi M, Ahmadifar E, Hoseini SM (2021) Dietary licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) improves growth, lipid metabolism, antioxidant and immune responses, and resistance to crowding stress in common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquac Nutr 27:417–426. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13194
Albillos A, de Gottardi A, Rescigno M (2020) The gut-liver axis in liver disease: pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol 72:558–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.003
Aoki N, Yoshida D, Ishikawa R, Ando M, Nakamura K, Tahara Y, Shibata S (2014) A single daily meal at the beginning of the active or inactive period inhibits food deprivation-induced fatty liver in mice. Nutr Res (new York, NY) 34:613–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2014.06.004
Brun P, Castagliuolo I, Di Leo V, Buda A, Pinzani M, Palù G, Martines D (2007) Increased intestinal permeability in obese mice: new evidence in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292:G518-525. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00024.2006
Cai GS, Su H, Zhang J (2020) Protective effect of probiotics in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicine 99:e21464. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000021464
Cao LP, Jia R, Du JL, Ding WD, Yin GJ (2012) Protective effect of Glycyrrhiza glabra extract against tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP)-induced Hepatotoxicity in primary cultured hepatocytes of jian carp(Cyprinus carpio var. jian). J Agric Biotechnol 20:1192–1200. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2012.10.012
Chang SS, Zhou D, Meng GL, Wu F, Wang S, Chen X, Xu JL (2012) Effect of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on oxidative stress of hyperlipidemic fatty liver in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J Chin Materia Medica 37:3102–3106
Cui YM, Yu LJ, Ao MZ, Hu J, Cao J (2007) Study on antioxidantive effects of total flavonoids of Glycyrrhiza on edible oils. Food Sci 28:119–121. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.11.023
Dai YY, Yuan YM, Yuan Y, Zhou Z (2020) Analysis on the safety of tilapia industry in China Jiangsu. Agric Sci 48:327–332. https://doi.org/10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2020.13.065
Dai YY, Yuan YM, Yuan Y, Zhang HY (2021) Supply and demand analysis of tilapia industry in China. Chin Agric Sci Bull 37:144–149
Dias J, Rueda-Jasso R, Panserat S, Conceio LECD, Dinis MT (2015) Effect of dietary carbohydrate-to-lipid ratios on growth, lipid deposition and metabolic hepatic enzymes in juvenile Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup). Aquac Res 35:1122–1130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2004.01135.x
Du ZY (2014) Causes of fatty liver in farmed fish: a review and new perspectives. J Fish China 38:1628–1638
Du JL, Cao LP, Jia R, Liu YJ, Shen YJ, Yin GJ (2015) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra extracts against TCDD-induced hepatocyte damage in jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). J Zhejiang Univ (agric Life Sci) 41:593–601
Du YP, Ou JW, Xi WT, Tang ZY, Yang BC (2020) Effects of high-fat diet and 1,2-dimethylhydrazine on intestinal tract of rats and its antioxidant mechanism. Hainan Med J 31:273–276. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2020.03.001
Du JL, Cao LP, Jia R, Wang T, Gu ZY, Zhang CY et al (2017) Oleic acid induced hepatocyte steatosis model in jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var.Jian). Prog Fish Sci 38(2):107–113. https://doi.org/10.11758/yykxjz.20160112001
El-Senousey HK, Chen B, Wang JY, Atta AM, Mohamed FR, Nie QH (2018) Effects of dietary vitamin C, vitamin E, and alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on the antioxidant defense system and immune-related gene expression in broilers exposed to oxidative stress by dexamethasone. Poult Sci 97:30–38. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pex298
Elumalai P, Kurian A, Lakshmi S, Faggio C, Esteban MA, Ringø E (2020) Herbal immunomodulators in aquaculture. Rev Fish Sci Aquac 29(1):33–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2020.1779651
Farzanegi P, Dana A, Ebrahimpoor Z, Asadi M, Azarbayjani MA (2019) Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. Eur J Sport Sci 19:994–1003. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2019.1571114
Hnasko TS, Hnasko RM (2015) The western blot. Methods Mol Biol (clifton, NJ) 1318:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2742-5_9
Hu YY, Peng JH, Feng Q (2011) The key target of Chinese medicine treatment on alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the gut. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi = Chin J Integr Tradit West Med 31(9):1269–1272
Hua B (2015) Study the antihyperlipidemic effect of the licorice flavonids and related mechanism. Ningxia Medical University
Huang CH, Xiao DY, Hu Y, Zhao YR, Liu QL (2014) Analysis on research status of fatty liver disease in aquaculture fish. Chin J Anim Nutr 26:1715–1722. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2014.07.001
Huang J, Wang Y, Ying C, Liu L, Lou Z (2018) Effects of mulberry leaf on experimental hyperlipidemia rats induced by high-fat diet. Exp Ther Med 16:547–556. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6254
Huang W, Xie P, Cai Z (2020) Lipid metabolism disorders contribute to hepatotoxicity of triclosan in mice. J Hazard Mater 384:121310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121310
Jia R et al (2019) Anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects of radix bupleuri extract against oxidative damage in tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) via Nrf2 and TLRs signaling pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol 93:395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.07.080
Jia R et al (2020a) Effects of high-fat diet on antioxidative status, apoptosis and inflammation in liver of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) via Nrf2, TLRs and JNK pathways. Fish Shellfish Immunol 104:391–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.06.025
Jia R, Cao LP, Du JL, He Q, Yin GJ (2020b) Effects of high-fat diet on steatosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in liver of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Front Mar Sci 7:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00363
Jiang F, Qian J, Chen S, Zhang W, Liu C (2011) Ligustrazine improves atherosclerosis in rat via attenuation of oxidative stress. Pharm Biol 49:856–863. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2010.551776
Jiao Y et al (2020) Monobutyl phthalate (MBP) can dysregulate the antioxidant system and induce apoptosis of zebrafish liver. Environ Pollut (barking, Essex: 1987) 257:113517
Jin J, Liu GT (2000) Research progress of NF-kB. J Int Pharm Res 3:133–137
Jin M et al (2019) Dietary choline supplementation attenuated high-fat diet-induced inflammation through regulation of lipid metabolism and suppression of NFκB activation in juvenile black seabream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii). J Nutr Sci 8:e38. https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2019.34
Kasper CS, White MR, Brown PB (2002) Betaine can replace choline in diets for juvenile nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 205:119–126
Kirpich IA, Marsano LS, McClain CJ (2015) Gut-liver axis, nutrition, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Biochem 48:923–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.06.023
Koukias N, Buzzetti E, Tsochatzis EA (2017) Intestinal hormones, gut microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Minerva Endocrinol 42:184–194. https://doi.org/10.23736/s0391-1977.16.02567-0
Kumar D, Dwivedi DK, Lahkar M, Jangra A (2019) Hepatoprotective potential of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone against alcohol and high-fat diet induced liver toxicity via attenuation of oxido-nitrosative stress and NF-κB activation. Pharmacol Rep 71:1235–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2019.07.002
Kurien BT, Scofield RH (2009) Introduction to protein blotting. Methods Mol Biol (clifton, NJ) 536:9–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-542-8_3
Li XC, Sun DL, Zhang YS, Zhang ZY (2011) Expression of PPAR-gamma in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Prog Mod Biomed 11:2620–2623
Lin D, Mao YQ, Cai FS (1990) Nutritional lipid liver disease of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Chin J Oceanol Limnol 8:363–373
Lin Y et al (2018) Effect of nitrite exposure on the antioxidant enzymes and glutathione system in the liver of bighead carp, Aristichthys nobilis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 76:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.02.015
Liu SH, Ma K, Xu XR, Xu B (2010) A single dose of carbon monoxide intraperitoneal administration protects rat intestine from injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Cell Stress Chaperones 15:717–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-010-0183-0
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods (san Diego, Calif) 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ma LX, Jia R (2020) Protective effect of polygonum cuspidatum extract on the fatty liver of Oreochromis niloticus. Freshw Fish 50(4):69–75. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2020.04.010
Ma MJ, Wu J (2017) Association between intestinal flora imbalance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi = Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi = Chin J Hepatol 25:789–793. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.10.017
Ma P, Peng Y, Yang JY, Li XB (2017) Mechanisms of PPARα, sterol regulatory element binding proteins and AMP-activated protein kinase in alcoholic fatty liver diseases: review. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol 31:900–906. https://doi.org/10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2017.09.006
Masarone M et al (2018) Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:9547613. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9547613
Nanji AA, Dannenberg AJ, Jokelainen K, Bass NM (2004) Alcoholic liver injury in the rat is associated with reduced expression of peroxisome proliferator-alpha (PPARalpha)-regulated genes and is ameliorated by PPARalpha activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:417–424. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.103.064717
Paradies G, Paradies V, Ruggiero FM, Petrosillo G (2014) Oxidative stress, cardiolipin and mitochondrial dysfunction in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 20:14205–14218. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14205
Peng HY, Yu HB, Zuo Z (2007) Development changes of oxidative and anti-oxidative indexes in establishment of steatohepatitis in rats fed by high-fat diets. Clin J Med Officers 35(5):677–679. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-3826.2007.05.012
Peng LL, Ding N, Zhao ZG, Li FH, Zhao ZJ (2020) Effects of high-fat diet on gut microbiota in male and female mice. Sci Technol Food Ind 41:86–90. https://doi.org/10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.01.015
Porras D et al (2017) Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radical Biol Med 102:188–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.037
Ren L et al (2019) Chronic treatment with the modified Longdan Xiegan Tang attenuates olanzapine-induced fatty liver in rats by regulating hepatic de novo lipogenesis and fatty acid beta-oxidation-associated gene expression mediated by SREBP-1c, PPAR-alpha and AMPK-alpha. J Ethnopharmacol 232:176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.12.034
Robertson DA, Morais S, Morris PC, Bell JG, Roy WJ (2001) Protein/lipid ratios in extruded diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.): effects on growth, feed utilisation, muscle composition and liver histology. Aquaculture 203:101–119
Sawada T, Konomi A, Yokoi K (2020) Serum lipid profiles of young Japanese women with iron deficiency without anemia. J Trace Elem Med Biol Organ Soc Miner Trace Elem (GMS) 57:126408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.126408
Shen BL, Han S, Yang ZN, Zou ZW, Liu J, Song SL (2018) Study Progress on the Function and Regulatory Mechanism of FASN Gene. J Heilongjiang August First Land Reclam Univ 30:27–34. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2018.03.006
Tan P et al (2017) Establishment of an alcoholic fatty liver disease model in mice. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 43:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/00952990.2016.1217539
Tuzcu Z, Orhan C, Sahin N, Juturu V, Sahin K (2017) Cinnamon polyphenol extract inhibits hyperlipidemia and inflammation by modulation of transcription factors in high-fat diet-fed rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:1583098. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1583098
Wei SJ, Zan LS, Wang HB (2011) Advances in the research of animal fatty acid transport protein 1. China Cattle Sci 37:47–51. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-9111.2011.04.013
Wu ZN, Wang J (2013) Advances in lipid effects of total flavonoids of licorice. Med J Ind Enterp 26:69–70. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-814X.2013.01.054
Wu Q, Ortegon AM, Tsang B, Doege H, Feingold KR, Stahl A (2006) FATP1 is an insulin-sensitive fatty acid transporter involved in diet-induced obesity. Mol Cell Biol 26:3455–3467. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.26.9.3455-3467.2006
Wu YT, Sun Y, Liu GD (2013) Interention effect of total flavonoids of Gycyrrhiza on hyperlipidenia model mice. Heilongjiang Med J 774–776:777. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-2882.2013.05.015
Xia F, Zhou BJ (2018) Role of gut-liver axis dysfunction in pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Implications for treatment strategies. World Chin J Digestol 26:1439–1447. https://doi.org/10.11569/wcjd.v26.i24.1439
Xia ZL, Yu JH, Li HX, Li JL, Tang YK, Ren HT et al (2013) Sequences analysis of jlFABP2 and the correlation between polymorphisms and body weight gain in Cyprinus carpio var.jian. Hereditas 35(5):628–636. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1005.2013.00628
Xiao FX, Sun H, Chen LL (2008) Mechanism of skeletal muscle insulin resistance in rats induced by high fat diet. Acta Med Univ Sci Technol Huazhong 37:309–311. https://doi.org/10.3870/j.issn.1672-0741.2008.03.008
Xiong DD, Zhang M, Li N, Gai JF, Mao L, Li M (2017) Mediation of inflammation, obesity and fatty liver disease by advanced glycation endoproducts. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:5172–5178. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201711_13835
Yan H, Gao Y, Zhang Y (2017) Inhibition of JNK suppresses autophagy and attenuates insulin resistance in a rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Med Rep 15:180–186. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5966
Yan H, Gao YQ, Zhang Y, Wang H, Liu GS, Lei JY (2018) Chlorogenic acid alleviates autophagy and insulin resistance by suppressing JNK pathway in a rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Biosci 43:287–294
Yang YW, Yuan J (2016) Research progress on antioxidant stress of PPAR α. J Southeast Univ (med Sci Edition) 35:147–150
Yang CG, Wang XL, Tian J, Liu W, Wu F, Jiang M, Wen H (2013) Evaluation of reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of gene expression in nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Gene 527:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2013.06.013
Yang JM et al (2019) Regulatory effect of a Chinese herbal medicine formula on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 25:5105–5119. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5105
Zhang W (2017) Observation of liver function and blood lipid levels serological test in the diagnosis of fatty liver. J China Prescr Drug 15:141. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-945X.2017.11.100
Zhang R, Hu Y, Yuan J, Wu D (2009) Effects of Puerariae radix extract on the increasing intestinal permeability in rat with alcohol-induced liver injury. J Ethnopharmacol 126:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2009.08.044
Zhang Y et al (2015) Effects of electroacupunctrue combined with dietary control on peroxisome proliferator-activa- ted receptor-α, and liver fatty acid-binding protein levels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu = Acupunct Res 40:345–351
Zhao Y, Gui L, Chen LB (2020) Development status of tilapia industry. China Fish 539:54–56
Zhu M, Yan BL, Xu JH, Qin J, Luo G (2011) Effects of dietary lipid levels on growth performance, feed utilization and fatty acid composition of juvenile Japanese seabass (Lateolabrax japonicus) reared in seawater. Aquacult Int 19:79–89
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, CAFS (2019JBFM10); Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (NO.BK20201143); and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NO.31702318).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JD writing—original draft, methodology. LPC formal analysis, resources. RJ validation. ZG investigation. QH data curation. PX supervision, funding acquisition. GY writing—review and editing. YM conceptualization, project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Ethics approval
This experiments were approved by Freshwater Fisheries Research Center, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, J., Cao, Lp., Jia, R. et al. Alleviative effects of total flavones of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch on oxidative stress and lipid metabolism disorder induced by high-fat diet in intestines of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). 3 Biotech 11, 348 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02785-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02785-w