Abstract
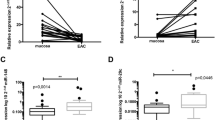
Esophageal cancer is a malignant disease with poor prognosis, increasing incidence, and ineffective treatment options. MicroRNAs are post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression involved in many biological processes including carcinogenesis. We determined miR-205 expression levels in tumor/non-tumor tissues of 45 esophageal cancer patients using qPCR and found that decreased level of miR-205 in tumor tissue correlates with poor overall survival in esophageal adenocarcinoma patients. Further, we observed significantly higher levels of miR-205 in tumor tissue of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ectopic overexpression of miR-205 in adenocarcinoma cell line SK-GT-4 led to decreased cell proliferation, cell cycle arrest in G1, and decreased migration ability. Conversely, in squamous cell line KYSE-150, same effects like inhibition of proliferation, migration, and colony-forming potential and cell cycle arrest in G2 were observed after silencing of miR-205. We performed global gene expression profiling and revealed that suppressive functioning of miR-205 in adenocarcinoma could be realized through regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), whereas oncogenic in squamous cell carcinoma by regulation of metalloproteinase 10. Our results suggest that miR-205 could serve as biomarker in esophageal cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor in esophageal adenocarcinoma and oncogene in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Shah MA, Kurtz RC. Upper gastrointestinal cancer predisposition syndromes. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2010;24:815–35.
Blot WJ. Esophageal cancer trends and risk factors. Semin Oncol. 1994;21:403–10.
Allum WH, Stenning SP, Bancewicz J, Clark PI, Langley RE. Long-term results of a randomized trial of surgery with or without preoperative chemotherapy in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5062–7.
Kelsen DP, Winter KA, Gunderson LL, Mortimer J, Estes NC, Haller DG, et al. Long-term results of RTOG trial 8911 (USA Intergroup 113): a random assignment trial comparison of chemotherapy followed by surgery compared with surgery alone for esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3719–25.
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ, Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2074–84.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:2257–61.
Orang AV, Safaralizadeh R, Hosseinpour Feizi MA. Insights into the diverse roles of mir-205 in human cancers. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP. 2014;15:577–83.
Zhao BS, Liu SG, Wang TY, Ji YH, Qi B, Tao YP, et al. Screening of microRNA in patients with esophageal cancer at same tumor node metastasis stage with different prognoses. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev APJCP. 2013;14:139–43.
Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, Inoue N, Machida H, Nakayama T, et al. Mirna-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Transl Med. 2011;9:30.
Fassan M, Volinia S, Palatini J, Pizzi M, Fernandez-Cymering C, Balistreri M, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in the histological subtypes of Barrett’s metaplasia. Clin Trans Gastro. 2013;4:e34.
Saad R, Chen Z, Zhu S, Jia P, Zhao Z, Washington MK, et al. Deciphering the unique microRNA signature in human esophageal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e64463.
Wu X, Ajani JA, Gu J, Chang DW, Tan W, Hildebrandt MA, et al. Microrna expression signatures during malignant progression from Barrett’s esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Prev Res. 2013;6:196–205.
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, et al. The mir-200 family and mir-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:593–601.
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjot L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, et al. Coordinated epigenetic repression of the mir-200 family and mir-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J J Int du cancer. 2011;128:1327–34.
Babak T, Zhang W, Morris Q, Blencowe BJ, Hughes TR. Probing micrornas with microarrays: tissue specificity and functional inference. RNA. 2004;10:1813–9.
Wang D, Qiu C, Zhang H, Wang J, Cui Q, Yin Y. Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show significantly different biological patterns: from functions to targets. PloS one. 2010;5.
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. Micrornas as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007;302:1–12.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microrna molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:189–98.
Berber U, Yilmaz I, Narli G, Haholu A, Kucukodaci Z, Demirel D. Mir-205 and mir-200c: predictive micro RNAs for lymph node metastasis in triple negative breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2014;17:143–8.
Chao CH, Chang CC, Wu MJ, Ko HW, Wang D, Hung MC, et al. Microrna-205 signaling regulates mammary stem cell fate and tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:3093–106.
Sun EH, Zhou Q, Liu KS, Wei W, Wang CM, Liu XF, et al. Screening miRNAs related to different subtypes of breast cancer with miRNAs microarray. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:2783–8.
Elgamal OA, Park JK, Gusev Y, Azevedo-Pouly AC, Jiang J, Roopra A, et al. Tumor suppressive function of mir-205 in breast cancer is linked to HMGB3 regulation. PLoS One. 2013;8:e76402.
Markou A, Yousef GM, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V, Lianidou E. Prognostic significance of metastasis-related microRNAs in early breast cancer patients with a long follow-up. Clin Chem. 2014;60:197–205.
Wang Z, Liao H, Deng Z, Yang P, Du N, Zhanng Y, et al. Mirna-205 affects infiltration and metastasis of breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;441:139–43.
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N, Pennati M, Binda M, Colecchia M, et al. Mir-205 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase Cepsilon. Cancer Res. 2009;69:2287–95.
Hagman Z, Haflidadottir BS, Ceder JA, Larne O, Bjartell A, Lilja H, et al. Mir-205 negatively regulates the androgen receptor and is associated with adverse outcome of prostate cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:1668–76.
Chen Z, Tang ZY, He Y, Liu LF, Li DJ, Chen X. Mirna-205 is a candidate tumor suppressor that targets ZEB2 in renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Res Treat. 2014;37:658–64.
Majid S, Saini S, Dar AA, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Tanaka Y, et al. MicroRNA-205 inhibits SRC-mediated oncogenic pathways in renal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2611–21.
Dar AA, Majid S, de Semir D, Nosrati M, Bezrookove V, Kashani-Sabet M. Mirna-205 suppresses melanoma cell proliferation and induces senescence via regulation of E2F1 protein. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:16606–14.
Xu Y, Brenn T, Brown ER, Doherty V, Melton DW. Differential expression of micrornas during melanoma progression: mir-200c, mir-205 and mir-211 are downregulated in melanoma and act as tumour suppressors. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:553–61.
Lei L, Huang Y, Gong W. Mir-205 promotes the growth, metastasis and chemoresistance of NSCLC cells by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:2897–902.
Cai J, Fang L, Huang Y, Li R, Yuan J, Yang Y, et al. Mir-205 targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5402–15.
Vosa U, Vooder T, Kolde R, Vilo J, Metspalu A, Annilo T. Meta-analysis of microRNA expression in lung cancer. Int J Cancer J Int du cancer. 2013;132:2884–93.
Chung TK, Cheung TH, Huen NY, Wong KW, Lo KW, Yim SF, et al. Dysregulated microRNAs and their predicted targets associated with endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma in Hong Kong women. Int J Cancer J Int du cancer. 2009;124:1358–65.
Su N, Qiu H, Chen Y, Yang T, Yan Q, Wan X. Mir-205 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion through targeting ESRRG in endometrial carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:2297–302.
Tian L, Zhang J, Ge J, Xiao H, Lu J, Fu S, et al. Microrna-205 suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2014;31:785.
Yu J, Ryan DG, Getsios S, Oliveira-Fernandes M, Fatima A, Lavker RM. MicroRNA-184 antagonizes microRNA-205 to maintain SHIP2 levels in epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:19300–5.
Redova M, Poprach A, Besse A, Iliev R, Nekvindova J, Lakomy R, et al. Mir-210 expression in tumor tissue and in vitro effects of its silencing in renal cell carcinoma. Tum Biology J Int Soc Oncod Biol Med. 2013;34:481–91.
Carvalho BS, Irizarry RA. A framework for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:2363–7.
Team RC. A language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing, vienna, austria; 2013. Url http://www.R-project.Org/.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. Microrna expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8.
Kimura S, Naganuma S, Susuki D, Hirono Y, Yamaguchi A, Fujieda S, et al. Expression of microRNAs in squamous cell carcinoma of human head and neck and the esophagus: miR-205 and miR-21 are specific markers for HNSCC and ESCC. Oncol Rep. 2010;23:1625–33.
Li K, Yao L, Chen L, Cao ZG, Yu SJ, Kuang XY, et al. Id2 predicts poor prognosis in breast cancer, especially in triple-negative breast cancer, and inhibits e-cadherin expression. OncoTargets Ther. 2014;7:1083–94.
Allegra M, Zaragkoulias A, Vorgia E, Ioannou M, Litos G, Beug H, et al. Semaphorin-7a reverses the ERF-induced inhibition of EMT in Ras-dependent mouse mammary epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23:3873–81.
Nam EJ, Lee M, Yim GW, Kim JH, Kim S, Kim SW, et al. Microrna profiling of a cd133(+) spheroid-forming subpopulation of the ovcar3 human ovarian cancer cell line. BMC Med Genet. 2012;5:18.
Greene SB, Gunaratne PH, Hammond SM, Rosen JM. A putative role for microrna-205 in mammary epithelial cell progenitors. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:606–18.
Du X, Lin BC, Wang QR, Li H, Ingalla E, Tien J, et al. Mmp-1 and pro-mmp-10 as potential urinary pharmacodynamic biomarkers of fgfr3-targeted therapy in patients with bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2014;20:6324–35.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by grants of Czech Ministry of Health NT/13547-4/2012, NV15-34678A, CEITEC Central European Institute of Technology (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0068), the Project RVO (MOU,00209805), and The Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports for the Project BBMRI CZ (LM2010004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hezova, R., Kovarikova, A., Srovnal, J. et al. MiR-205 functions as a tumor suppressor in adenocarcinoma and an oncogene in squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Tumor Biol. 37, 8007–8018 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4656-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4656-8