Abstract
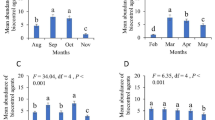
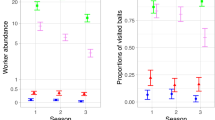
To examine the effects of pesticides on insect biodiversity, a population survey was conducted in conventionally managed, low-input, and organic peach orchards. Pitfall traps were used to sample a total of 6489 insects representing 151 species at seven study sites. Results of a population survey suggest that pesticide application adversely affected insect biodiversity in peach orchards and that the magnitude of the adverse effect might be greater for herbicide application than for insecticide application. The usefulness of carabids and ants as biological indicators of the effects of pesticides was also evaluated. Results suggest that the ant species Tetramorium tsushimae is a good indicator in peach orchards. In contrast, carabids are not suitable indicators.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen AN (1997) Using ants as bioindicators: multiscale issues in ant community ecology. Conserv Ecol 1: article 8
Begon M, Harper JL, Townsend CR (1996) Ecology. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Benton TG, Vickery JA, Wilson JD (2003) Farmland biodiversity: is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol Evol 18:182–188
Bolton B (1994) Identification guide to the ant genera of the world. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Brooks DR, Clark SJ, Perry JN, Bohan DA, Champion GT, Firbank LG, Haughton AJ, Hawes C, Heard MS, Woiwod IP (2005) Invertebrate biodiversity in maize following withdrawal of triazine herbicides. Proc R Soc B 272:1497–1502
Chiverton PA, Sotherton NW (1991) The effects on beneficial arthropods of the exclusion of herbicides from cereal crop edges. J Appl Ecol 28:1027–1039
Döring TF, Kromp B (2003) Which carabid species benefit from organic agriculture?—a review of comparative studies in winter cereals from Germany and Switzerland. Agric Ecosyst Environ 8:153–161
Dritschilo W, Wanner D (1980) Ground beetle abundance in organic and conventional corn fields. Environ Entomol 9:629–631
Ervin TL (1991) How many species are there? Revisit Conserv Biol 5:330–333
Ewald JA, Aebischer NJ (2000) Trends in pesticide use and efficacy during 26 years of changing agriculture in southern England. Environ Monit Assess 64:493–529
Folgarait PJ (1998) Ant biodiversity and its relationship to ecosystem functioning: a review. Biodivers Conserv 7:1221–1244
Gaston KJ (1991) The magnitude of global insect species richness. Conserv Biol 5:283–296
Geiger F, Bengtsson J, Berendse F, Weisser WW, Emmerson M, Morales MB, Ceryngier P, Liira J, Tscharntke T, Winqvist C, Eggers S, Bommarco R, Pärt T, Bretagnolle V, Plantegenest M, Clement LW, Dennis C, Palmer C, Oñate JJ, Guerrero I, Hawro V, Aavik T, Thies C, Flohre A, Hänke S, Fischer C, Goedhart PW, Inchausti P (2010) Persistent negative effects of pesticides on biodiversity and biological control potential on European farmland. Basic Appl Ecol 11:97–105
Groombridge B (ed) (1992) Global biodiversity, status of the earth’s living resources. Chapman and Hall, London
Hole DG, Perkins AJ, Wilson JD, Alexander IH, Grice F, Evans AD (2005) Does organic farming benefit biodiversity? Biol Conserv 122:113–130
Honek A (1988) The effect of crop density and microclimate on pitfall trap catches of Carabidae, Staphylinidae (Coleoptera) and Lycodidae (Araneae) in cereal fields. Pedobiologia 32:233–234
Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setälä H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecol Monogr 75:3–35
Ito M, Itou K, Ito K (2010) Are carabid beetles suitable biotic indicators of insecticide impact in potato fields? Appl Entomol Zool 45:435–447
Lawton JH, Bifnel DE, Bolton B, Blowmers GF, Eggleton P, Hammond PM, Hodda M, Holt RD, Larsen TN, Mawdsley NA, Stork NE, Srivastava DS, Watt AD (1998) Biodiversity inventories, indicator taxa and effects of habitat modification in tropical forest. Nature 391:72–76
Majer JD (1983) Ants: bioindicators of minesite rehabilitation, land-use, and land conservation. Environ Manage 7:375–383
Matlock RB Jr, De La Cruz R (2002) An inventory of parasitic Hymenoptera in banana plantations under two pesticide regimes. Agric Ecosyst Environ 93:147–164
McGeoch MA (1998) The selection testing and application of terrestrial insects as bioindicators. Biol Rev 73:181–210
Menge BA, Sutherland JP (1987) Community regulation: variation in disturbance, competition, and predation in relation to environmental stress and recruitment. Am Nat 130:730–757
Norton L, Johnson P, Joys A, Stuart R, Chamberlain D, Firbank RFL, Manley W, Wolfe M, Hart B, Mathews F, Macdonald D, Fuller RJ (2009) Consequences of organic and non-organic farming practices for field, farm and landscape complexity. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129:221–227
Perfecto I, Snelling R (1995) Biodiversity and the transformation of a tropical agroecosystem: ants in coffee plantations. Ecol Appl 5:1084–1097
Rainio J, Niemelä J (2003) Ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) as bioindicators. Biodivers Conserv 12:487–506
Sonoda S, Yamashita J, Kohara Y, Izumi Y, Yoshida H, Enomoto T (2011) Population survey of spiders using mt-DNA (COI) sequences in Japanese peach orchards. Appl Entomol Zool 46:81–86
Thiele HU (1977) Carabid beetles in their environments. Springer, Berlin
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan through the research project “Selection of functional biodiversity indicators and development of the assessment methods” and the Ohara Foundation for Agricultural Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below are the links to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonoda, S., Izumi, Y., Kohara, Y. et al. Effects of pesticide practices on insect biodiversity in peach orchards. Appl Entomol Zool 46, 335–342 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-011-0041-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-011-0041-2