Abstract
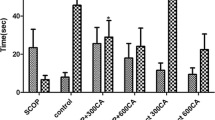
Mesua ferrea Linn. flowers have been used in Ayurveda as a brain tonic and as an ingredient in memory-enhancing formulations such as Brahma Rasayan and Chyawanprash. However, this ethnomedicinal use has not been investigated scientifically. This study evaluated the effect of the ethanolic extract of Mesua ferrea flowers (MFE) on memory in scopolamine-induced models of cognitive dysfunction. MFE was administered to rats (100, 200 and 400 mg/kg, p.o) for a period of 14 days, after which amnesia was induced by giving scopolamine (1 mg/kg, s.c) on the 14th day. Piracetam (200 mg/kg, p.o) was given as a positive control. The models employed to assess memory in the rats were the T-maze continuous alternation task (T-CAT) and novel object recognition test (NORT). Pretreatment with MFE ameliorated the memory deficit caused by scopolamine; which was evidenced by a significantly greater relative proportion of spontaneous alternation percentage in the T-CAT, and a significant increase of discrimination index in the NORT. Further, MFE significantly inhibited anticholinesterase activity in the brain, elevated the levels of reduced glutathione and catalase, and decreased malondialdehyde and nitrite levels in the brain. The results of this study show that MFE exhibited significant anticholinesterase and antioxidant activities in scopolamine treated rats, which could be the possible underlying mechanism of its memory-enhancing activity and of its ethnomedicinal use as a brain tonic.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
To be made available on request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ABTS:
-
2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)
- ACh:
-
Acetylcholine
- AChE:
-
Acetylcholinesterase
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ATC:
-
Acetylthiocholine iodide
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- CPCSEA:
-
Committee for purpose of control and supervision of experiments on animals
- DI:
-
Discrimination Index
- DPPH:
-
2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
- DTNB:
-
5,5’-dithio-bis (2-nitrobenzoic acid)
- GAE:
-
Gallic acid equivalents
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- IAEC:
-
Institutional Animal Ethics Committee
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MFE:
-
Mesua ferrea flowers ethanolic extract
- NORT:
-
Novel object recognition test
- PIR:
-
Piracetam
- RE:
-
Rutin equivalents
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SEM:
-
Standard error of mean
- SCOP:
-
Scopolamine
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- T-CAT:
-
T-maze continuous alternation task
- TFC:
-
Total flavonoid content
- TPC:
-
Total phenolic content
References
Abozed SS, El-kalyoubi M, Abdelrashid A, Salama MF (2014) Total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of various solvent extracts from whole wheat and bran. Ann Agric Sci 59(1):63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2014.06.009
Alibabaei Z, Rabiei Z, Rahnama S, Mokhtari S, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2014) Matricaria chamomilla extract demonstrates antioxidant properties against elevated rat brain oxidative status induced by amnestic dose of scopolamine. Biomed Aging Pathol 4(4):355–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomag.2014.07.003
Anandakumar A, Balasubramanian M, Muralidharan R (1986) Nagakesara - a comparative pharmacognosy. Anc Sci Life 5(4):263–268
Andriambeloson E, Huyard B, Poiraud E, Wagner S (2014) Methyllycaconitine- and scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunction: differential reversal effect by cognition-enhancing drugs. Pharmacol Res Perspect 2(4):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/prp2.48
Baliga SM, Sharake M, Vaishnav LK, Rao S, Palatty PL (2013) Rasayana drugs from the ayurvedic system of medicine as possible radioprotective agents in cancer treatment. Integr Cancer Ther 12(6):455–463. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534735413490233
Barai P, Raval N, Acharya S, Acharya N (2018) Bergenia ciliata ameliorates streptozotocin-induced spatial memory deficits through dual cholinesterase inhibition and attenuation of oxidative stress in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 102:966–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.115
Bhattamisra SK, Singh PN, Singh SK (2012) Effect of standardized extract of Marsilea minuta on learning and memory performance in rat amnesic models. Pharm Biol 50(6):766–772. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2011.632421
Chahar MK, Sanjaya Kumar DS, Lokesh T, Manohara KP (2012) In-vivo antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity of mesuol isolated from Mesua ferrea L. seed oil. Int Immunopharmacol 13(4):386–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2012.05.006
Dennis TJ, Akshaya Kumar K (1998) Constituents of Mesua ferrea. Fitoterapia 69:291–304
Dey A, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee A, Pandey DK (2017) Natural products against Alzheimer’s disease: pharmaco-therapeutics and biotechnological interventions. Biotechnol Adv 35(2):178–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.12.005
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Foyet HS, Ngatanko Abaïssou HH, Wado E, Asongalem Acha E, Alin C (2015) Emilia coccinae (SIMS) G Extract improves memory impairment, cholinergic dysfunction, and oxidative stress damage in scopolamine-treated rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 15(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0864-4
Garg S, Sharma K, Ranjan R, Attri P, Mishra P (2009) In vivo Antioxidant activity and hepatoprotective effects of methanolic extract of Mesua ferrea linn. Int J PharmTech Res 1(4):1692–1696
Gerlai R (1998) A new continuous alternation task in T-maze detects hippocampal dysfunction in mice: a strain comparison and lesion study. Behav Brain Res 95(1):91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(97)00214-3
Ghumatkar PJ, Patil SP, Jain PD, Tambe RM, Sathaye S (2015) Nootropic, neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects of phloretin in scopolamine induced amnesia in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 135:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2015.06.005
Habu JB, Ibeh BO (2015) In vitro antioxidant capacity and free radical scavenging evaluation of active metabolite constituents of Newbouldia laevis ethanolic leaf extract. Biol Res 48:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-015-0007-x
Hitzenberger G (1998) Pharmacological properties of piracetam: rationale for use in stroke patients. CNS Drugs 9(SUPPL. 1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.2165/00023210-199809001-00003
Ishola IO, Tota S, Adeyemi OO, Agbaje EO, Narender T, Shukla R (2013) Protective effect of Cnestis ferruginea and its active constituent on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice: a behavioral and biochemical study. Pharm Biol 51(7):825–835. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2013.767360
Ishola IO, Awoyemi AA, Afolayan GO (2016) Involvement of antioxidant system in the amelioration of scopolamine-induced memory impairment by grains of paradise (Aframomum melegueta KSchum.) extract. Drug Res (Stuttg) 66(9):455–463. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-109391
Ishola IO, Ikuomola BO, Adeyemi OO (2018) Protective role of Spondias mombin leaf and Cola acuminata seed extracts against scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunction. Alexandria J Med 54(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2016.08.001
Jeong EJ, Ma CJ, Lee KY, Kim SH, Sung SH, Kim YC (2009) KD-501, a standardized extract of Scrophularia buergeriana has both cognitive-enhancing and antioxidant activities in mice given scopolamine. J Ethnopharmacol 121(1):98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2008.10.006
Keller JN, Schmitt FA, Scheff SW, Ding Q, Chen Q, Butterfield DA, Markesbery WR (2005) Evidence of increased oxidative damage in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 64(7):1152–1156. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000156156.13641.BA
Khan RA (2012) Effects of Launaea procumbens on brain antioxidant enzymes and cognitive performance of rat. BMC Complement Altern Med 12(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-12-219
Khandelwal KR (2008) Preliminary Phytochemical Screening. In: Practical pharmacognosy. Nirali Prakashan, Pune, India, pp. 149-157.
Klinkenberg I, Blokland A (2010) The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: a review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34(8):1307–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.04.001
Kumar V, Singh PN, Muruganandam AV, Bhattacharya SK (2000) Effect of Indian Hypericum perforatum Linn on animal models of cognitive dysfunction. J Ethnopharmacol 72(1–2):119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00216-6
Kumaran A, Joel Karunakaran R (2007) In vitro antioxidant activities of methanol extracts of five Phyllanthus species from India. LWT Food Sci Technol 40(2):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.09.011
Lim TK (2016) Mesua ferrea, In: Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants. Volume 7, Flowers. Springer, Netherlands, pp: 641-652. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-7276-1
Lima JA, Costa RS, Epifânio RA, Castro NG, Rocha MS, Pinto AC (2009) Geissospermum vellosii stembark. Anticholinesterase activity and improvement of scopolamine-induced memory deficits. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92(3):508–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2009.01.024
Ma N, Sasoh M, Kawanishi S, Sugiura H, Piao F (2010) Protection effect of taurine on nitrosative stress in the mice brain with chronic exposure to arsenic. J Biomed Sci 17(SUPPL. 1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S7
Makchuchit S, Itharat A, Tewtrakul S (2010) Antioxidant and nitric oxide inhibition activities of thai medicinal plants. J Med Assoc Thai 93(7):S227–S235
Mathuranath PS, George A, Ranjith N, Justus S, Kumar MS, Menon R, Sarma PS, Varghese J (2012) Incidence of Alzheimer’s disease in India: A 10 years follow-up study. Neurol India 60(6):625–630. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.105198
Naik B, Nirwane A, Majumdar A (2017) Pterostilbene ameliorates intracerebroventricular streptozotocin induced memory decline in rats. Cogn Neurodyn 11(1):35–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-016-9413-1
Ngoupaye GT, Pahaye DB, Ngondi J, Moto FCO, Bum EN (2017) Gladiolus dalenii lyophilisate reverses scopolamine-induced amnesia and reduces oxidative stress in rat brain. Biomed Pharmacother 91:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.061
Odubanjo VO, Ibukun EO, Oboh G, Adefegha SA (2018) Aqueous extracts of two tropical ethnobotanicals (Tetrapleura tetraptera and Quassia undulata) improved spatial and non-spatial working memories in scopolamine-induced amnesic rats: Influence of neuronal cholinergic and antioxidant systems. Biomed Pharmacother 99:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.043
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2000) Guidance document on acute oral toxicity. Environmental Health and Safety Monograph Series on Testing and Assessment No.24. Paris, France: OECD.
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2001) Draft updated test guidelines 420: Acute Oral toxicity – Fixed Dose Procedure. OECD, Paris
Ozarowski M, Mikolajczak PL, Bogacz A, Gryszczynska A, Kujawska M, Jodynis-Liebert J, Piasecka A, Napieczynska H, Szulc M, Kujawski R, Bartkowiak-Wieczorek J, Cichocka J, Bobkiewicz-Kozlowska T, Czerny B, Mrozikiewicz PM (2013) Rosmarinus officinalis L. leaf extract improves memory impairment and affects acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activities in rat brain. Fitoterapia 91:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2013.09.012
Pahwa P, Goel RK (2016) Asparagus adscendens root extract enhances cognition and protects against scopolamine induced amnesia: an in-silico and in-vivo studies. Chem Biol Interact 260:208–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.10.007
Pitsikas N (2015) The role of nitric oxide in the object recognition memory. Behav Brain Res 285:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.06.008
Rabiei Z, Mokhtari S, Asgharzade S, Gholami M, Rahnama S, Rafieian-kopaei M (2015) Inhibitory effect of Thymus vulgaris extract on memory impairment induced by scopolamine in rat. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 5(10):845–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.07.006
Rahman I, Kode A, Biswas SK (2007) Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat Protoc 1(6):3159–3165. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.378
Rajput PV (2018) Mode of action of Kalyanak Ghrita. World J Pharm Res 7(13):1273–1277
Raju MS, Srimannarayana G, Pa NVS (2016) Tetrahedron Letters NO. 49, DP 4509 - 4512, 1976. (49):6–9
Rendeiro C, Guerreiro JDT, Williams CM, Spencer JPE (2012) Postgraduate symposium: flavonoids as modulators of memory and learning: molecular interactions resulting in behavioural effects. Proc Nutr Soc 71(2):246–262. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665112000146
Rubio J, Dang H, Gong M, Liu X, Chen S, lin, Gonzales GF, (2007) Aqueous and hydroalcoholic extracts of Black Maca (Lepidium meyenii) improve scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 45(10):1882–1890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.04.002
Saxena G, Singh SP, Pal R, Singh S, Pratap R, Nath C (2007) Gugulipid, an extract of Commiphora whighitii with lipid-lowering properties, has protective effects against streptozotocin-induced memory deficits in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86(4):797–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2007.03.010
Schulz JB, Lindenau J, Seyfried J, Dichgans J (2000) Glutathione, oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Eur J Biochem 267:4904–4911
Shin CY, Kim HS, Cha KH, Won DH, Lee JY, Jang SW, Sohn UD (2018) The effects of donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, on impaired learning and memory in rodents. Biomol Ther 26(3):274–281. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2017.189
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47(2):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(72)90132-7
Spowart-Manning L, Van Der Staay FJ (2004) The T-maze continuous alternation task for assessing the effects of putative cognition enhancers in the mouse. Behav Brain Res 151(1–2):37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2003.08.004
Sulaiman CT, Balachandran I (2012) Total phenolics and total flavonoids in selected indian medicinal plants. Indian J Pharm Sci 74(3):258–260. https://doi.org/10.4103/0250-474X.106069
Sultana R, Cenini G, Butterfield DA (2013) Biomarkers of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. In: Villamena FA (ed) Molecular basis of oxidative stress: chemistry, mechanisms, and disease pathogenesis. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York. pp 359–376. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118355886.ch14
Thouvarecq R, Protais P, Jouen F, Caston J (2001) Influence of cholinergic system on motor learning during aging in mice. Behav Brain Res 118(2):209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(00)00330-2
Vasileva LV, Getova DP, Doncheva ND, Marchev AS, Georgiev MI (2016) Beneficial effect of commercial Rhodiola extract in rats with scopolamine-induced memory impairment on active avoidance. J Ethnopharmacol 193:586–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.011
Vasudevan M, Parle M (2007) Memory enhancing activity of Anwala churna (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.): an Ayurvedic preparation. Physiol Behav 91(1):46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.01.016
Verotta L, Lovaglio E, Vidari G, Finzi PV, Neri MG, Raimondi A, Parapini S, Taramelli D, Riva A, Bombardelli E (2004) 4-Alkyl- and 4-phenylcoumarins from Mesua ferrea as promising multidrug resistant antibacterials. Phytochemistry 65:2867–2879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.07.001
Wessapan C, Charoenteeraboon J, Wetwitayaklung P, Limmatvapirat C, Phaechamud T (2007) Antimicrobial activity of some edible flowers in Thailand. Planta Med 73(09):P_201. doi: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-986982
Wu CYC, Lerner FM (2018) e Silva AC, Possoit HE, Hsieh TH, Neumann JT, Minagar A, Lin HW, Lee RHC (2018) Utilizing the modified T-maze to assess functional memory outcomes after cardiac arrest. J Vis Exp 131:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3791/56694
Yassin NAZ, El-Shenawy MA, Mahdy KA, Gouda NAM, Razik A, Marrie H, Farrag H, Ibrahim BMM (2013) Effect of Boswellia serrata on Alzheimer’s disease induced in rats. J Arab Soc Med Res 8:1–11. https://doi.org/10.7123/01.JASMR.0000429323.25743.cc
Acknowledgements
The authors would wish to thank the Principal and the administration of AISSMS College of Pharmacy, Pune, Maharashtra for providing the necessary facilities and equipment for the conduction of the studies.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pallavi Shirsat-John – planned and performed experiments and biochemical analysis, data collection, statistical analysis, and drafting of the article; Tina Saldanha – data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article; Swati Kolhe – project planning and supervision; Ziyaurrahman A.R. – supervision of the research work and in-charge of overall direction and planning.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
The guidelines established by the CPCSEA (Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals), Govt. of India, were followed for the animal experiments. The protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of AISSMS College of Pharmacy, Pune (Reg. No. – 257/PO/ReBi/S/2000/CPCSEA).
Conflict of interest
Shirsat‑John Pallavi has no conflict of interest. Tina Saldanha has no conflict of interest. Swati Kolhe has no conflict of interest. A. R. Ziyaurrahman has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirsat-John, P., Saldanha, T., Kolhe, S. et al. Antiamnesic effect of Mesua ferrea (L.) flowers on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and oxidative stress in rats. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 23, 1109–1121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-022-00654-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-022-00654-2