Abstract
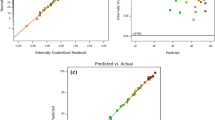
Developing affordable and efficient materials for the removal of arsenic from drinking water is crucial for human and environmental safety. In the present study, the adsorptive performance of magnetic GO/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposite and ZnFe2O4 nanospinel for arsenic removal from aqueous water was analyzed. The adsorbents were characterized using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray powder diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, selected area electron diffraction and vibrating sample magnetometer. The conditions were optimized by response surface methodology (RSM) by considering the main factors as adsorption time, arsenic concentration, dose of adsorbent and pH. The optimum condition for the removal of arsenic was observed at pH 9.76, 30 min of contact time, 13.4 mg L−1 of initial arsenic concentration and 0.048 g of adsorbent dosage. The predicted arsenic removal percent under optimized conditions was noted as 98%; on the other hand, the experimental values at optimized conditions were observed as 96%. The Pareto analysis predicted that pH of the polluted water is the major factor in adsorptive arsenic removal and the relative importance of the process factors was found in the following order: pH > arsenic concentration > contact time > adsorbent dosage. Thus, introduced compositions form a promising material for the decontamination of polluted water or using in environmental remediation programs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasian AR, Rahimipour MR, Hamnabard Z (2015) Hydrothermal synthesis of lithium meta titanate nanocrystallites. Proc Mater Sci 11:336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.110
Arabnezhad M, Shafieeafarani M, Jafari A (2017) Co-precipitation synthesis of ZnO–TiO2 nanostructure composites for arsenic photodegradation from industrial wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1585-7
Burton ED, Bush RT, Johnston SG, Watling KM, Hocking RK, Sullivan LA, Parker GK (2009) Sorption of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) to schwertmannite. Environ Sci Technol 43:9202–9207. https://doi.org/10.1021/es902461x
Chammui Y, Sooksamiti P, Naksata W, Thiansem S, Arqueropanyo O-A (2014) Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by adsorption on Leonardite. Chem Eng J 240:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.11.083
Chowdhury S, Mazumder MAJ, Al-Attas O, Husain T (2016) Heavy metals in drinking water: occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci Total Environ 569–570:476–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.166
Çiftçi TD, Henden E (2015) Nickel/nickel boride nanoparticles coated resin: a novel adsorbent for arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) removal. Powder Technol 269:470–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.09.041
Dhifaf AJ, Neus L, Kostas K (2016) Synthesis of few-layered, high-purity graphene oxide sheets from different graphite sources for biology. 2D Mater 3:014006
Dutta PK, Ray AK, Sharma VK, Millero FJ (2004) Adsorption of arsenate and arsenite on titanium dioxide suspensions. J Colloid Interface Sci 278:270–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.06.015
Flyunt R et al (2014) Mechanistic aspects of the radiation-chemical reduction of graphene oxide to graphene-like materials. Int J Radiat Biol 90:486–494. https://doi.org/10.3109/09553002.2014.907934
Hosseini SA, Babaei S (2017) Graphene oxide/zinc oxide (GO/ZnO) nanocomposite as a superior photocatalyst for degradation of methylene blue (MB)-process modeling by response surface methodology (RSM). J Braz Chem Soc 28:299–307
Hosseini SA, Davodian M, Abbasian AR (2017) Remediation of phenol and phenolic derivatives by catalytic wet peroxide oxidation over Co–Ni layered double nano hydroxides. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 75:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.03.001
Hosseini SA, Majidi V, Abbasian AR (2018) Photocatalytic desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by NiCo2O4 nanospinel obtained by an oxidative precipitation process modeling and optimization. J Sulfur Chem 39:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/17415993.2017.1369981
Hussein FB, Abu-Zahra NH (2016) Synthesis, characterization and performance of polyurethane foam nanocomposite for arsenic removal from drinking water. J Water Process Eng 13:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.07.005
Kapitanova OO, Panin GN, Baranov AN, Kang TW (2012) Synthesis and properties of graphene oxide/graphene nanostructures. J Korean Phys Soc 60:1789–1793. https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.60.1789
Lata S, Samadder SR (2016) Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: a review. J Environ Manag 166:387–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.039
Mandal P (2017) An insight of environmental contamination of arsenic on animal health. Emerg Contam 3:17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2017.01.004
Mandal S, Sahu MK, Patel RK (2013) Adsorption studies of arsenic(III) removal from water by zirconium polyacrylamide hybrid material (ZrPACM-43). Water Resour Ind 4:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2013.09.003
Mostaan H, Mehrizi MZ, Rafiei M, Beygi R, Abbasian AR (2017) Contribution of mechanical activation and annealing in the formation of nanopowders of Al(Cu)/TiC–Al2O3 hybrid nanocomposite. Ceram Int 43:2680–2685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.11.082
Pan B, Li Z, Zhang Y, Xu J, Chen L, Dong H, Zhang W (2014) Acid and organic resistant nano-hydrated zirconium oxide (HZO)/polystyrene hybrid adsorbent for arsenic removal from water. Chem Eng J 248:290–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.02.093
Pillai A, Sunita G, Gupta VK (2000) A new system for the spectrophotometric determination of arsenic in environmental and biological samples. Anal Chim Acta 408:111–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(99)00832-6
Qiao J, Jiang Z, Sun B, Sun Y, Wang Q, Guan X (2012) Arsenate and arsenite removal by FeCl3: effects of pH, As/Fe ratio, initial As concentration and co-existing solutes. Sep Purif Technol 92:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2012.03.023
Rahman MM, Adil M, Yusof AM, Kamaruzzaman YB, Ansary RH (2014) Removal of heavy metal ions with acid activated carbons derived from oil palm and coconut shells. Materials 7:3634–3650
Shokri E, Yegani R, Pourabbas B, Kazemian N (2016) Preparation and characterization of polysulfone/organoclay adsorptive nanocomposite membrane for arsenic removal from contaminated water. Appl Clay Sci 132–133:611–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.08.011
Tang X et al (2016) Chemical coagulation process for the removal of heavy metals from water: a review. Desalin Water Treat 57:1733–1748. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.977959
Wei J, Zhang X, Liu Q, Li Z, Liu L, Wang J (2014) Magnetic separation of uranium by CoFe2O4 hollow spheres. Chem Eng J 241:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.12.035
Wei Z et al (2016) The effect of pH on the adsorption of arsenic(III) and arsenic(V) at the TiO2 anatase [101] surface. J Colloid Interface Sci 462:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.10.018
Yazdani M, Tuutijärvi T, Bhatnagar A, Vahala R (2016) Adsorptive removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous phase by feldspars: kinetics, mechanism, and thermodynamic aspects of adsorption. J Mol Liq 214:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.12.002
Zamiri R et al (2017) Optical and magnetic properties of ZnO/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposite. Mater Chem Phys 192:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.01.066
Zhou Y et al (2017) Fabrication of novel ZnFe2O4/BiOI nanocomposites and its efficient photocatalytic activity under visible-light irradiation. J Alloys Compd 696:353–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.11.323
Zhu Y, Murali S, Cai W, Li X, Suk JW, Potts JR, Ruoff RS (2010) Graphene and graphene oxide: synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv Mater 22:3906–3924. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201001068
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge Iranian Nanotechnology Initiative Council and Urmia University for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, S.A., Abbasian, A.R., Gholipoor, O. et al. Adsorptive removal of arsenic from real sample of polluted water using magnetic GO/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposite and ZnFe2O4 nanospinel. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 16, 7455–7466 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2140-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2140-x