Abstract
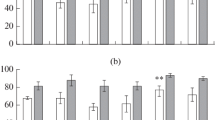
The seed germination of Helichrysum microphyllum subsp. tyrrhenicum, an endemic species of Sardinia and Corsica with metal tolerance capability, was evaluated against zinc (Zn; 0, 250, 500 and 1000 mg/L) and lead (Pb; 0, 25, 50 and 100 mg/L) stress. Seeds were collected in three localities: (a) inside a mine dump highly polluted with these metals, (b) outside but close to this area and (c) far from the metal-polluted site. Germination responses were assessed at 10, 15 and 20 °C, and the percentage, time of germination and mortality of seedlings were evaluated. The taxon showed a high capacity to germinate under Zn and Pb stress, and the germination was never completely inhibited; however, the germination decreased with increasing Zn concentrations, but not under Pb stress. Moreover, the seeds from specimens growing in mining sites appeared to be less affected by Zn stress than seeds coming from the other localities. A successful survival of seedlings during the first days of their development under metal stress and under controlled conditions was detected. Our study suggests that this species may give an important contribution to future phytoremediation programs on mining sites, in which it could be spread by seeds in order to form a vegetation cover.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angiolini C, Bacchetta G, Brullo S, Casti M, Giusso Del Galdo G (2005) The vegetation of mining dumps in SW-Sardinia. Feddes Repert 116(3–4):243–276
Antunes Viegas D, Palmeira-de-Oliveira A, Salgueiro L, Martinez-de-Oliveira J, Palmeira-de-Oliveira R (2014) Helichrysum italicum: from traditional use to scientific data. J Ethnopharmacol 151(1):54–65
Aversa G, Balassone G, Boni M, Amalfitano G (2002) The mineralogy of the “calamine” ores in SW Sardinia (Italy): preliminary results. Period Mineral 71(3):201–218
Bacchetta G, Brullo S, Mossa L (2003) Note sul genere Helichrysum Miller (Asteraceae) in Sardegna. Ital Bot 35(1):217–225
Bacchetta G, Casti M, Zavattero L (2007) Analisi della vegetazione del distretto minerario di Montevecchio (Sardegna sud-occidentale). Fitosociologia 44(2):83–108
Bacchetta G, Cao A, Cappai G, Carucci A, Casti M, Fercia ML, Lonis R, Mola F (2012) A field experiment on the use of Pistacia lentiscus L. and Scrophularia canina L. subsp. bicolor (Sm.) Greuter for the phytoremediation of abandoned mining areas. Plant Biosyst 146(4):1054–1063
Bacchetta G, Cappai G, Carucci A, Tamburini E (2015) Use of native plants for the remediation of abandoned mine sites in mediterranean semiarid environments. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94(3):326–333
Bacchetta G, Boi ME, Cappai G, De Giudici G, Piredda M (2017) Phytoremediation of Sardinian abandoned mine site: a preliminary study on the use of Helichrysum microphyllum Cambess. subsp. tyrrhenicum Bacch., Brullo & Giusso. Proceedings of the 15th international conference on environmental science and technology. Rhodes, Greece. https://cest2017.gnest.org/sites/default/files/presentation_file_list/cest2017_01066_oral_paper.pdf. Accessed 13 July 2017
Bacchetta G, Boi ME, Cappai G, De Giudici G, Piredda M, Porceddu M (2018) Metal tolerance capability of Helichrysum microphyllum Cambess. subsp. tyrrhenicum Bacch., Brullo & Giusso: a candidate for phytostabilization in abandoned mine sites. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101(6):758–765
Barbafieri M, Dadea C, Tassi E, Bretzel F, Fanfani L (2011) Uptake of heavy metals by native species growing in a mining area in Sardinia, Italy: discovering native flora for phytoremediation. Int J Phytorem 13(10):985–997
Baskin CC, Baskin JM (2014) Seeds: ecology, biogeography, and evolution of dormancy and germination. Academic Press, San Diego
Bechstädt T, Boni M (1994) Sedimentological, stratigraphical and ore deposits field guide of the autochthonous Cambro–Ordovician of Southwestern Sardinia, Italy. Servizio Geologico d’Italia, Rome
Boni M, Costabile S, De Vivo B, Gasparrini M (1999) Potential environmental hazard in the mining district of southern Iglesiente (SW Sardinia, Italy). J Geochem Explor 67(1):417–430
Cao A, Cappai G, Carucci A, Muntoni A (2004) Selection of plants for zinc and lead phytoremediation. J Environ Sci Health 39(4):1011–1024
Cao A, Carucci A, Lai T, Bacchetta G, Casti M (2009) Use of native species and biodegradable chelating agent in phytoremediation of abandoned mining area. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84(6):884–889
Cidu R, Frau F, Da Pelo S (2011) Drainage at abandoned mine sites: natural attenuation of contaminants in different seasons. Mine Water Environ 30(2):113–126
Concas S, Lattanzi P, Bacchetta G, Babafieri M, Vacca A (2015) Zn, Pb and Hg contents of Pistacia lentiscus L. grown on heavy metal-rich soils: implications for phytostabilization. Water Air Soil Pollut 226(10):340–355
De Giudici G, Medas D, Meneghini C, Casu MA, Giannoncelli A, Iadecola A, Podda S, Lattanzi P (2015) Microscopic bio mineralization processes and Zn bioavailability: a synchrotron-based investigation of Pistacia lentiscus L. root. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(24):19352–19361
De Giudici G, Pusceddu C, Medas D, Meneghini C, Giannoncelli A, Rimondi V, Podda F, Cidu R, Lattanzi P, Wanty RB, Kimball BA (2017) The role of natural biogeochemical barriers in limiting metal loading to a stream affected by mine drainage. Appl Geochem 76:124–135
Di Salvatore M, Carafa AM, Carratù G (2008) Assessment of heavy metals phytotoxicity using seed germination and root elongation tests: a comparison of two growth substrates. Chemosphere 73(9):1461–1464
Doumas P, Munoz M, Banni M, Becerra S, Bruneel O, Casiot C, Cleyet-Marel JC, Gardon J, Noack Y, Sappin-Didier V (2018) Polymetallic pollution from abandoned mines in Mediterranean regions: a multidisciplinary approach to environmental risks. Reg Environ Change 18(3):677–692
Frau F, Medas D, Da Pelo S, Wanty RB, Cidu R (2015) Environmental effects on the aquatic system and metal discharge to the mediterranean sea from a near-neutral zinc-ferrous sulfate mine drainage. Water Air Soil Pollut 226(3):1–17
Ginocchio R, León-Lobos P, Arellano EC, Anic V, Ovalle JF, Baker AJM (2017) Soil physicochemical factors as environmental filters for spontaneous plant colonization of abandoned tailing dumps. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(15):13484–13496
Jadia CD, Fulekar MH (2008) Phytoremediation: the application of vermicompost to remove zinc, cadmium, copper, nickel and lead by sunflower plant. Environ Eng Manag J 7(5):547–558
Jiménez MN, Fernandez E, Navarro EB, Contini E, Casti M, Bacchetta G (2005) Livelli di metalli pesanti in Dittrichia viscosa (L.) Greuter, Cistus salviifolius L. e Euphorbia cupanii Bertol. ex Moris su suoli contaminati e non contaminati dalle attività estrattive nell’Iglesiente (Sardegna sudoccidentale). Ital Bot 37(1):794–795
Jiménez MN, Bacchetta G, Casti M, Navarro FB, Lallena AM, Fernandèz-Ondono E (2011) Potential use in phytoremediation of three plant species growing on contaminated mine-tailing soils in Sardinia. Ecol Eng 37(2):392–398
Jiménez MN, Bacchetta G, Casti M, Navarro FB, Lallena AM, Fernandèz-Ondono E (2014) Study of Zn, Cu and Pb content in plants and contaminated soils in Sardinia. Plant Biosyst 148(3):419–428
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kranner I, Colville L (2011) Metals and seeds: biochemical and molecular implications and their significance for seed germination. Environ Exp Bot 72(1):93–105
Krichen K, Ben Mariem H, Chaieb M (2014) Ecophysiological requirements on seed germination of a Mediterranean perennial grass (Stipa tenacissima L.) under controlled temperatures and water stress. S Afr J Bot 94:210–217
Lefèvre I, Marchal G, Corréal E, Zanuzzi A, Lutts S (2009) Variation in response to heavy metals during vegetative growth in Dorycnium pentaphyllum Scop. Plant Growth Regul 59(1):1–11
Leonardi M, Ambryszewska KE, Melai B, Flamini G, Cioni PL, Parri F, Pistelli L (2013) Essential-oil composition of Helichrysum italicum (Roth) G. Don ssp. italicum from Elba Island (Tuscany, Italy). Chem Biodivers 10(3):343–355
Madzhugina YG, Kuzetsov V, Shevyakova NI (2008) Plants inhabiting polygons formegapolis waste as promising species for phytoremediation. Russ J Plant Physiol 55(3):410–419
Maheshwari R, Dubey R (2008) Inhibition of ribonuclease and protease activities in germinating rice seeds exposed to nickel. Acta Physiol Plant 30(6):863–872
Márquez-García B, Márquez C, Sanjosé I, Nieva FJJ, Rodríguez-Rubio P, Muñoz-Rodríguez AF (2013) The effects of heavy metals on germination and seedling characteristics in two halophyte species in Mediterranean marshes. Mar Poll Bull 70(1–2):119–124
Martínez-Fernández D, Walkera DJ, Romero-Espinara P, Flores P, del Río JA (2011) Physiological responses of Bituminaria bituminosa to heavy metals. J Plant Physiol 168(18):2206–2211
Medas D, De Giudici G, Casu MA, Musu E, Giannoncelli A, Iadecola A, Meneghini C, Tamburini E, Sprocati AR, Turnau K, Lattanzi P (2015) Microscopic processes ruling the bioavailability of Zn to roots of Euphorbia pithyusa L. pioneer plant. Environ Sci Technol 49(3):1400–1408
Medas D, De Giudici G, Pusceddu C, Casu MA, Birarda G, Vaccari L, Giannoncelli A, Meneghini C (2017) Impact of Zn excess on biomineralization processes in Juncus acutus grown in mine polluted sites. J Hazard Mater 370:98–107
Medas D, Boi ME, Bacchetta G, Cappai G, Carlomagno I, Casu MA, De Giudici G, Gianoncelli A, Meneghini C, Piredda M, Podda F, Porceddu M (2018) Mineral evolution at geosphere–biosphere interface: investigation on the endemic shrub Helichrysum microphyllum Cambess. subsp. tyrrhenicum Bacch., Brullo & Giusso growing in abandoned mining area. In: Geosciences for the environment, natural hazard and cultural heritage-Congress SGI-SIMP 2018, pp 545–545
Mendez MO, Maier RM (2008) Phytostabilization of mine tailings in arid and semiarid environments—an emerging remediation technology. Environ Health Perspect 116(3):278–283
Monaci F, Trigueros D, Dingorance MD, Rossini-Oliva S (2019) Phytostabilization potential of Erica australis L. and Nerium oleander L.: a comparative study in the Riotinto mining area (SW Spain). Environ Geochem Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00391-7
Picciau R, Serra S, Porceddu M, Bacchetta G (2019) Seed traits and germination behaviour of four Sardinian populations of Helichrysum microphyllum ssp. tyrrhenicum (Asteraceae) along an altitudinal gradient. Plant Biol 21(3):498–506
Porceddu M, Mattana E, Pritchard HW, Bacchetta G (2013) Thermal niche for in situ seed germination by Mediterranean mountain streams: model prediction and validation for Rhamnus persicifolia seeds. Ann Bot 112(9):1887–1897
R Development Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org
RAS - Regione Autonoma della Sardegna (2003) Assessorato della Difesa dell’Ambiente. Piano regionale di gestione dei rifiuti. Piano di bonifica siti inquinati. http://www.regione.sardegna.it/documenti/1_39_20051011121758.pdf
Seregin IV, Kozhevnikova AD (2005) Distribution of cadmium, lead, nickel, and strontium in imbibing maize caryopses. Russ J Plant Physiol 52(4):565–569
Wierzbicka M, Obidzinska J (1998) The effect of lead on seed imbibition and germination in different plant species. Plant Sci 137(2):155–171
Wong MH (2003) Ecological restoration of mine degraded soils, with emphasis on metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere 50(6):775–780
Yang Y, Wei X, Lu J, You J, Wang W, Shi R (2010) Lead-induced phytotoxicity mechanism involved in seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73(8):1982–1987
Zavattero L, Casti M, Bacchetta G, Di Pietro R (2006) Analisi multi temporale del paesaggio del distretto minerario di Monteponi (Sardegna sud-occidentale). Rivista Italiana di telerilevamento 37:137–146
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the research project REMINE-REstoration and remediation of abandoned MINE sites, funded by the Fondazione di Sardegna and Regional Sardinian Government (Grant CUP F72F16003160002). We gratefully acknowledge the University of Cagliari for the financial support of the PhD scholarship of Maria Enrica Boi (years 2015–2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by MEB and MP. All authors wrote the original manuscript and contributed substantially to the manuscript improvement and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Mehmet Salih Nas.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boi, M.E., Porceddu, M., Cappai, G. et al. Effects of zinc and lead on seed germination of Helichrysum microphyllum subsp. tyrrhenicum, a metal-tolerant plant. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 17, 1917–1928 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02589-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02589-9