Abstract
Purpose
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) leads to decreased sole sensation and balance disorder, all of which increase the risk of falls and socioeconomic costs. Since the physiotherapists do not use the same manner to lessen the complications of this problem. Therefore, this review study was directed to appraise physiotherapy intervention efficiencies in diminishing DPN’s symptoms and complications.
Method
A database search of Pubmed, Elsevier, Google Scholar, and Embase was performed to determine DPN’s published documents. Finally, studies of DPN and treatments available in this field, particularly physiotherapy that included electrotherapy, exercise therapy, and other therapies, were identified.
Result
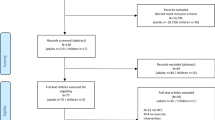
According to a database search on August 1, 2019, from 1989 to 2019, in the last 30 years, about 968 articles were found, 345 of which were free full text available, and finally, 19 articles were approved. These articles examined the effects of physiotherapy interventions, including exercise therapy, electrotherapy, and other treatment techniques on DPN patients.
Conclusions
The results showed that most diabetic peripheral neuropathy patients suffer from muscle weakness, pain, loss of balance, and lower limb dysfunction. As a result, their daily activity and Life satisfaction are gradually impaired. Exercise therapy, electrotherapy, and other physiotherapy methods have been used to reduce the mentioned cases. Among these interventions, exercise therapy has been the most effective. Although there was little evidence of aerobic exercise in these patients, further studies should be done on other therapies’ effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahbar S, Naimi SS, RezaSoltani A, Rahimi A, Baghban AA, Noori A, et al. Changes in vascular structure in diabetic patients after 8 weeks aerobic physical exercise: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Diabetes Dev Countries. 2017;38(2):202–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-017-0579-9.
Cade WT. Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular diseases in the physical therapy setting. Phys Ther. 2008;88(11):1322–35. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20080008.
Dyck PJ, Kratz K, Karnes J, Litchy WJ, Klein R, Pach J, et al. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology. 1993;43(4):817-. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.43.4.817.
BÖRü üT ALPR, SARGIN H, KOÇER A, Sargin M, LüLECI A, et al. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients attending a diabetes center in Turkey. Endocr J. 2005;51(6):563–7. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.51.563.
Feldman EL, Callaghan BC, Pop-Busui R, Zochodne DW, Wright DE, Bennett DL, et al. Diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0092-1.
Aghili R, Khamseh ME, Baradaran HR, Aghili SM, Malek M. Diabetic distal symmetric polyneuropathy: Role of physical examination in screening. Koomes. 2013;14(3):327–34.
Berger A, Dukes EM, Oster G. Clinical characteristics and economic costs of patients with painful neuropathic disorders. J Pain. 2004;5(3):143–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2003.12.004.
van Dijk M, Donga E, van Dijk JG, Lammers GJ, van Kralingen KW, Dekkers OM, et al. Disturbed subjective sleep characteristics in adult patients with long-standing type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2011;54(8):1967–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2184-7.
Chin YF, Liang J, Wang WS, Hsu BR, Huang TT. The role of foot self-care behavior on developing foot ulcers in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy: a prospective study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2014;51(12):1568–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.05.001.
Sartor CD, Watari R, Pássaro AC, Picon AP, Hasue RH, Sacco IC. Effects of a combined strengthening, stretching and functional training program versus usual-care on gait biomechanics and foot function for diabetic neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-13-36.
Najafi B, Talal TK, Grewal GS, Menzies R, Armstrong DG, Lavery LA. Using plantar electrical stimulation to improve postural balance and plantar sensation among patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a randomized double blinded study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017;11(4):693–701. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932296817695338.
Wilmot EG, Edwardson CL, Achana FA, Davies MJ, Gorely T, Gray LJ, et al. Sedentary time in adults and the association with diabetes, cardiovascular disease and death: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2012;55:2895–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-2842-z.
Francia P, Gulisano M, Anichini R, Seghieri G. Diabetic foot and exercise therapy: step by step the role of rigid posture and biomechanics treatment. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2014;10(2):86–99.
Crews RT, Schneider KL, Yalla SV, Reeves ND, Vileikyte L. Physiological and psychological challenges of increasing physical activity and exercise in patients at risk of diabetic foot ulcers: a critical review. Diab/Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(8):791–804. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2817.
Barbosa AP, Medina JL, Ramos EP, Barros HP. Prevalence and risk factors of clinical diabetic polyneuropathy in a Portuguese primary health care population. Diabetes Metab. 2001;27(4 Pt 1):496–502.
Rahbar S, Naimi SS, Soltani AR, Rahimi A, Akbarzadeh Baghban A, Rashedi V, et al. Improvement in biochemical parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes after twenty-four sessions of aerobic exercise: A randomized controlled trial. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2017;19(7):e13931. https://doi.org/10.5812/ircmj.13931.
Lee S, Kim J-H, Shin K-M, Kim J-E, Kim T-H, Kang K-W, et al. Electroacupuncture to treat painful diabetic neuropathy: study protocol for a three-armed, randomized, controlled pilot trial. Trials. 2013;14(1):225. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6215-14-225.
Ahn S, Song R. Effects of tai chi exercise on glucose control, neuropathy scores, balance, and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes and neuropathy. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18(12):1172–8. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2011.0690.
Monteiro RL, Sartor CD, Ferreira JS, Dantas MG, Bus SA, Sacco IC. Protocol for evaluating the effects of a foot-ankle therapeutic exercise program on daily activity, foot-ankle functionality, and biomechanics in people with diabetic polyneuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):400. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2323-0.
Bus S, Van Netten J, Lavery L, Monteiro-Soares M, Rasmussen A, Jubiz Y, et al. IWGDF Guidance on the prevention of foot ulcers in at‐risk patients with diabetes. Diab/Metab Res Rev. 2016;32:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2696.
Maharaj SS, Nuhu JM. The effect of rebound exercise and treadmill walking on the quality of life for patients with non-insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes. Int J Diabetes Dev Countries. 2015;35(2):223–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-015-0350-z.
Cai H, Li G, Zhang P, Xu D, Chen L. Effect of exercise on the quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Qual Life Res. 2016;26(3):515–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-015-0350-z.
Xia TW, Yang Y, Li WH, Tang ZH, Li ZR, Qiao LJ. Different training durations and styles of tai chi for glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled trials. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2475-y.
Kavookjian J, Elswick BM, Whetsel T. Interventions for being active among individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2007;33(6):962–88. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145721707308411.
Wayne PM, Walsh JN, Taylor-Piliae RE, Wells RE, Papp KV, Donovan NJ, et al. Effect of Tai Chi on cognitive performance in older adults: Systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(1):25–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.12611.
Lee MS, Choi T-Y, Lim H-J, Ernst E. Tai chi for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Chin J Integr Med. 2011;17(10):789–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0812-1.
Wang J-S, Lan C, Wong M-K. Tai Chi Chuan training to enhance microcirculatory function in healthy elderly men. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;82(9):1176–80. https://doi.org/10.1053/apmr.2001.24305.
Latey PJ, Burns J, Hiller CE, Nightingale EJ. Relationship between foot pain, muscle strength and size: a systematic review. Physiotherapy. 2017;103(1):13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physio.2016.07.006.
Richardson JK, Sandman D, Vela S. A focused exercise regimen improves clinical measures of balance in patients with peripheral neuropathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82(2):205–9. https://doi.org/10.1053/apmr.2001.19742.
Madruga M, Prieto J, Rohlfs P, Gusi N. Cost-effectiveness and effects of a home-based exercise intervention for female caregivers of relatives with dementia: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. March. 2020;6(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8010054 (Healthcare (Basel, Switzerland)).
Allet L, Armand S, De Bie R, Golay A, Monnin D, Aminian K, et al. The gait and balance of patients with diabetes can be improved: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2009;53(3):458–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-009-1592-4.
Goldsmith JR, Lidtke RH, Shott S. The effects of range-of-motion therapy on the plantar pressures of patients with diabetes mellitus. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2020;92(9):483–90. https://doi.org/10.7547/87507315-92-9-483.
Spector TD, Harris PA, Hart DJ, Cicuttini FM, Nandra D, Etherington J, et al. Risk of osteoarthritis associated with long-term weight‐bearing sports: a radiologic survey of the hips and knees in female ex‐athletes and population controls. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(6):988–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780390616.
Tuttle LJ, Hastings MK, Mueller MJ. A moderate-intensity weight-bearing exercise program for a person with type 2 diabetes and peripheral neuropathy. Phys Ther. 2012;92(1):133–41. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20110048.
Mueller MJ, Tuttle LJ, LeMaster JW, Strube MJ, McGill JB, Hastings MK, et al. Weight-bearing versus nonweight-bearing exercise for persons with diabetes and peripheral neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;94(5):829–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2012.12.015.
Billinger SA, Sisante J-FV, Alqahtani AS, Pasnoor M, Kluding PM. Aerobic exercise improves measures of vascular health in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Int J Neurosci. 2017;127(1):80–5. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2016.1144056.
Kluding PM, Pasnoor M, Singh R, D’Silva LJ, Yoo M, Billinger SA, et al. Safety of aerobic exercise in people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: single-group clinical trial. Phys Ther. 2015;95(2):223–34. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20140108.
Chen Y-W, Hsieh P-L, Chen Y-C, Hung C-H, Cheng J-T. Physical exercise induces excess hsp72 expression and delays the development of hyperalgesia and allodynia in painful diabetic neuropathy rats. Anesth Analg. 2013;116(2):482–90. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e318274e4a0.
LeMaster JW, Mueller MJ, Reiber GE, Mehr DR, Madsen RW, Conn VS. Effect of weight-bearing activity on foot ulcer incidence in people with diabeic peripheral neuropathy: feet first randomized controlled trial. Phys Ther. 2008;88(11):1385–98. https://doi.org/10.2522/ptj.20080019.
Toth C, Brady S, Gagnon F, Wigglesworth K. A randomized, single-blind, controlled, parallel assignment study of exercise versus education as adjuvant in the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain. Clin J Pain. 2014;30(2):111–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/AJP.0b013e31828ccd0f.
Yoo M, D’Silva LJ, Martin K, Sharma NK, Pasnoor M, LeMaster JW, et al. Pilot study of exercise therapy on painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pain Med. 2015;16(8):1482–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12743.
Malik R, Newrick P, Sharma A, Jennings A, Ah-See A, Mayhew T, et al. Microangiopathy in human diabetic neuropathy: relationship between capillary abnormalities and the severity of neuropathy. Diabetologia. 1989;32(2):92–102.
Kanno S, Oda N, Abe M, Saito S, Hori K, Handa Y, et al. Establishment of a simple and practical procedure applicable to therapeutic angiogenesis. Circulation. 1999;9(20):2682–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.99.20.2682.
Grewal GS, Schwenk M, Lee-Eng J, Parvaneh S, Bharara M, Menzies RA, et al. Sensor-based interactive balance training with visual joint movement feedback for improving postural stability in diabetics with peripheral neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. Gerontology. 2015;61(6):567–74. https://doi.org/10.1159/000371846.
Dhruv NT, Niemi JB, Harry JD, Lipsitz LA, Collins JJ. Enhancing tactile sensation in older adults with electrical noise stimulation. Neuroreport. 2002;13(5):597–600.
Thiagarajah AG. How effective is acupuncture for reducing pain due to plantar fasciitis? Singap Med J. 2017;58(2):92. https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2016143.
Hamza MA, White PF, Craig WF, Ghoname E-S, Ahmed HE, Proctor TJ, et al. Percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: a novel analgesic therapy for diabetic neuropathic pain. Diabetes Care. 2002;23(3):365–70. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.23.3.365.
Mo X, Chen D, Ji C, Zhang J, Liu C, Zhu L. Effect of electro-acupuncture and transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation on experimental diabetes and its neuropathy. Zhen ci yan jiu = Acupunct Res. 1996;21(3):55–9.
Watkins E, Koeze T. Spinal cord stimulation and pain relief. BMJ. 1993;307(6902):462. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.307.6902.462.
Cameron NE, Cotter MA, Robertson S, Maxfield EK. Nerve function in experimental diabetes in rats: effects of electrical stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1993;264(2 Pt 1):E161-6.
Walsh DM, Foster NE, Baxter GD, Allen JM. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Relevance of stimulation parameters to neurophysiological and hypoalgesic effects. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1995;74(3):199–206.
Khaodhiar L, Niemi JB, Earnest R, Lima C, Harry JD, Veves A. Enhancing sensation in diabetic neuropathic foot with mechanical noise. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(12):3280–3. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.12.3280.
Najafi B, Crews RT, Wrobel JS. A novel plantar stimulation technology for improving protective sensation and postural control in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a double-blinded, randomized study. Gerontology. 2013;59(5):473–80. https://doi.org/10.1159/000352072.
Singh B, Xu Q-g, Franz CK, Zhang R, Dalton C, Gordon T, et al. Accelerated axon outgrowth, guidance, and target reinnervation across nerve transection gaps following a brief electrical stimulation paradigm. J Neurosurg. 2012;116(3):498–512. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.10.JNS11612.
Slangen R, Pluijms W, Faber C, Dirksen C, Kessels A, Van Kleef M. Sustained effect of spinal cord stimulation on pain and quality of life in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Br J Anaesth. 2013;111(6):1030–1. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aet397.
Anders JJ, Borke RC, Woolery SK, Van De Merwe WP. Low power laser irradiation alters the rate of regeneration of the rat facial nerve. Lasers Surg Med. 1993;13(1):72–82. https://doi.org/10.1002/lsm.1900130113.
Li Z-J, Wang Y, Zhang H-F, Ma X-L, Tian P, Huang Y. Effectiveness of low-level laser on carpal tunnel syndrome: a meta-analysis of previously reported randomized trials. Medicine. 2016;95(31):e4424. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000004424.
CG SK, Maiya AG, Hande HM, Vidyasagar S, Rao K, KV R. Efficacy of low level laser therapy on painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Laser Ther. 2015;24(3):195–200. https://doi.org/10.5978/islsm.15-OR-12.
Güngörmüş M, Akyol UK. Effect of biostimulation on wound healing in diabetic rats. Photomed Laser Surg. 2009;27(4):607–10. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2008.2349.
Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, Xu Q, Peng W, Liu W, et al. Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(7):883. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2562.
Lai Z, Lee S, Hu X, Wang L. Effect of adding whole-body vibration training to squat training on physical function and muscle strength in individuals with knee osteoarthritis. J Musculoskel Neuronal Interact. 2019;19(3):333–41.
Lee K, Lee S, Song C. Whole-body vibration training improves balance, muscle strength and glycosylated hemoglobin in elderly patients with diabetic neuropathy. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2013;231(4):305–14. https://doi.org/10.1620/tjem.231.305.
Chatchawan U, Eungpinichpong W, Plandee P, Yamauchi J. Effects of thai foot massage on balance performance in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathy: a randomized parallel-controlled trial. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2015;21:68. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSMBR.894163.
Song R, Ahn S, Roberts BL, Lee EO, Ahn YH. Adhering to a t’ai chi program to improve glucose control and quality of life for individuals with type 2 diabetes. J Altern Complement Med. 2009;15(6):627–32. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2008.0330.
Park IS, Song R, Oh KO, So HY, Kim DS, Kim JI, et al. Managing cardiovascular risks with Tai Chi in people with coronary artery disease. J Adv Nurs. 2016;66(2):282–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2009.05134.x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the responsible author declares that there is no conflict of interest. This research has not received any assistance from the financial support center.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahantigh Akbari, N., Hosseinifar, M., Naimi, S.S. et al. The efficacy of physiotherapy interventions in mitigating the symptoms and complications of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. J Diabetes Metab Disord 19, 1995–2004 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00652-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00652-8