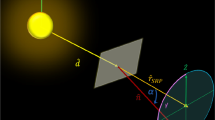
Abstract
The Sun-Earth triangular Lagrange point, L5, offers an ideal location to monitor the space weather. Furthermore, L4, L5 may harbor Earth ‘Trojan’ asteroids and space dust that are of significant interest to the scientific community. No spacecraft has, thus far, entered an orbit in the vicinity of Sun-Earth triangular points in part because of high propellant costs. By incorporating solar sail dynamics in the model representing CR3BP, the concept of a mission to L4, L5 can be re-evaluated and the total ΔV can be reconsidered. A solar sail is employed to increase the energy of the spacecraft and deliver the spacecraft to an orbit about an artificial Lagrange point by leveraging solar radiation pressure and, potentially, without any insertion ΔV.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baoyin, H., Mcinnes, C.R.: Solar sail halo orbits at the Sun–Earth artificial L 1 point. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 94(2), 155–171 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-005-4626-3
Barden, B.T., Howell, K.C.: Fundamental motions near collinear libration points and their transitions. J. Astronaut. Sci. 46(4), 361–378 (1998)
Biddy, C., Svitek, T.: Lightsail-1 solar sail design and qualification. In: Proceedings of the 41st aerospace mechanisms symposium, pp. 451-463. Jet Propulsion Lab., National Aeronautics and Space Administration Pasadena, CA (2012)
Christou, A.A., Asher, D.J.: A long-lived horseshoe companion to the earth. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 414(4), 2965–2969 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.18595.x
Connors, M., Wiegert, P., Veillet, C.: Earth’s Trojan asteroid. Nature 475(7357), 481 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10233
Davis, J.: Lightsail test mission declared success; first image complete, the planetary society (2015)
Dvorak, R., Lhotka, C., Zhou, L.: The orbit of 2010 TK7: possible regions of stability for other Earth Trojan asteroids. Astron. Astrophys. 541, A127 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201118374
Gerard, G., Jaume, L., Martínez, R.: Dynamics and mission design near libration points-vol I: fundamentals: the case of collinear libration points, vol. 2 world scientific (2001)
Goodrich, E.F.: Numerical determination of short-period Trojan orbits in the restricted three-body problem. Astron. J. 71, 88 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1086/109860
Gopalswamy, N., Davila, J., Cyr, O.S., Sittler, E., Auchère, F., Duvall, T., Hoeksema, J., Maksimovic, M., MacDowall, R., Szabo, A., Collier, M.: Earth-affecting solar causes observatory (EASCO): A potential international living with a star mission from sun-earth L5. J. Atmos. Solar-Terrestrial Phys. 73(5-6), 658–663 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2011.01.013
Gopalswamy, N., Davila, J.M., Auchère, F., Schou, J., Korendyke, C.M., Shih, A., Johnston, J.C., MacDowall, R.J., Maksimovic, M., Sittler, E., Szabo, A., Wesenberg, R., Vennerstrom, S., Heber, B.: Earth-affecting solar causes observatory (EASCO): a mission at the Sun-Earth L5. In: Fineschi, S., Fennelly, J. (eds.) Solar Physics and Space Weather Instrumentation IV. SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.901538 (2011)
Grebow, D.: Generating periodic orbits in the circular restricted three-body problem with applications to lunar south pole coverage. MSAA Thesis, School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Purdue University (2006)
Heiligers, J., Hiddink, S., Noomen, R., McInnes, C.R.: Solar sail lyapunov and halo orbits in the earth–moon three-body problem. Acta Astronaut. 116, 25–35 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.05.034
Heiligers, J., McInnes, C.: Novel Solar Sail Mission Concepts for Space Weather Forecasting. In: 24Th AAS/AIAA space flight mechanics meeting 2014, pp. AAS–14 (2014)
Howell, K.C.: Three-dimensional, periodic, ‘halo’ orbits. Celest. Mech. 32(1), 53–71 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01358403
John, K., Graham, L., Abell, P.: Investigating Trojan Asteroids at the L4/L5 sun-earth lagrange points. In: Lunar and planetary science conference, vol. 46, p. 2845 (2015)
Llanos, P., Miller, J., Hintz, G.: Mission and navigation design of integrated trajectories to L4,5 in the Sun-Earth system. In: AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics specialist conference. American institute of aeronautics and astronautics (2012), https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2012-4668
Llanos, P.J., Hintz, G.R., Lo, M.W., Miller, J.K.: Powered Heteroclinic and Homoclinic Connections between the Sun-Earth Triangular Points and Quasi-Satellite Orbits for Solar Observations. In: AAS/AIAA astrodynamics specialist conference, AAS, pp. 13–786 (2013)
Llanos, P.J., Miller, J.K., Hintz, G.R.: Navigation Analysis for an L5 Mission in the Sun-Earth System. In: AAS/AIAA Astrodynamicist specialist conference, Girdwood, vol. 142, pp. 11–503 (2011)
Lo, M.W., Llanos, P.J., Hintz, G.R.: An L5 Mission to Observe the Sun and Space Weather, Part I. In: AAS/AIAA Astrodynamicist Specialist Conference, San Diego, vol. 136, pp. 10–121 (2010)
Macdonald, M., McInnes, C.: Solar sail science mission applications and advancement. Adv. Space Res. 48(11), 1702–1716 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2011.03.018
Markellos, V.V.: Asymmetric periodic orbits in three dimensions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 184(2), 273–281 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/184.2.273
McInnes, C.: Solar Sailing. Technology dynamics and mission applications, vol. 1. Springer, London (1999)
McInnes, C.R., McDonald, A.J.C., Simmons, J.F.L., MacDonald, E.W.: Solar sail parking in restricted three-body systems. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 17(2), 399–406 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.21211
Mori, O., Tsuda, Y., Sawada, H., Funase, R., Saiki, T., Yonekura, K., Hoshino, H., Minamino, H., Endo, T., Kawaguchi, J., et al.: World’s first demonstration of solar power sailing by IKAROS. In: Proceedings of 2nd International symposium on solar sailing (2010)
Ozimek, M.T., Grebow, D.J., Howell, K.C.: Design of solar sail trajectories with applications to lunar south pole coverage. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 32(6), 1884–1897 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.41963
Pavlak, T.A.: Trajectory design and orbit maintenance strategies in multi-body dynamical regimes. Ph.D. thesis, School of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Purdue University, West Lafayette IN (2013)
Pezent, J.B., Sood, R., Heaton, A.: Near Earth Asteroid (NEA) Scout Solar Sail Contingency Trajectory Design and Analysis. In: 2018 space flight mechanics meeting. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2018-0199 (2018)
Prado, A.F.: Orbital maneuvers between the lagrangian points and the primaries in the earth-sun system. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 28(2), 131–139 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1590/s1678-58782006000200001
Simo, J., McInnes, C.R.: Solar Sail Trajectories at the Earth-Moon Lagrange Points. In: 59Th International astronautical congress (2008)
Sood, R.: Solar sail applications for mission design in sun-planet systems from the perspective of the circular restricted three-body problem. Master’s thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN. ProQuest: AAI1535164 (2012)
Szebehely, V., Geyling, F.T.: Theory of orbits: The restricted problem of three bodies. J. Appl. Mech. 35(3), 624 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3601280
Tsuda, Y., Mori, O., Funase, R., Sawada, H., Yamamoto, T., Saiki, T., Endo, T., Yonekura, K., Hoshino, H., Kawaguchi, J.: Achievement of IKAROS — Japanese deep space solar sail demonstration mission. Acta Astronaut. 82(2), 183–188 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2012.03.032
Vourlidas, A.: Mission to the sun-earth l5lagrangian point: an optimal platform for space weather research. Space Weather 13(4), 197–201 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/2015sw001173
Waters, T.J., McInnes, C.R.: Periodic orbits above the ecliptic in the solar-sail restricted three-body problem. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 30(3), 687–693 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.26232
Wawrzyniak, G.G., Howell, K.C.: Generating solar sail trajectories in the Earth-Moon system using augmented finite-difference methods. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2011, 1–13 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/476197
Wie, B.: Solar sail attitude control and dynamics, part two. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 27(4), 536–544 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.11133
Wright, J.L., Kantrowitz, A.: Space sailing. Phys. Today 45(12), 85–85 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2809919
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
An earlier version was presented as a conference paper AAS 16-467 at the 26th AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Napa, CA, February 14-18, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sood, R., Howell, K. Solar Sail Transfers and Trajectory Design to Sun-Earth L4, L5: Solar Observations and Potential Earth Trojan Exploration. J of Astronaut Sci 66, 247–281 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-018-00141-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-018-00141-4