Abstract
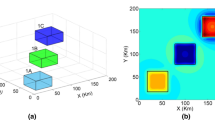
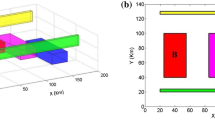
Edge detection is a requisite task in the interpretation of potential field data. The existed edge detectors have the disadvantages that they cannot balance the edges of strong and weak amplitude anomalies simultaneously, or the identified edges of deep geological bodies are divergence and fuzzy. In order to overcome this problem, this paper presents the normalized enhanced analytic signal detectors to extract the edges, which can improve the disadvantages effectively. The normalized enhanced analytic signal detectors use different orders vertical derivatives of potential field data to normalize the different orders enhanced analytic signals. The new detectors are tested on synthetic gravity data, which can not only display the edges of shallow and deep geological bodies clearly at the same time, also can identify the edges more precisely and clearly. Finally, these detectors are demonstrated on real gravity and magnetic data from China, which can bring out more edge information.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blakely RJ (1995) Potential theroy in gravity and magnetic applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Cooper G (2009) Balancing images of potential-field data. Geophysics 74:L17–L20
Cooper GRJ (2014) The automatic determination of the location and depth of contacts and dykes from aeromagnetic data. Pure Appl Geophys 171:2417–2423
Cooper GRJ (2015) Using the analytic signal amplitude to determine the location and depth of thin dikes from magnetic data. Geophysics 80(1):J1–J6
Cooper G, Cowan D (2006) Enhancing potential field data using filters based on the local phase. Comput Geosci 32:1585–1591
Cooper G, Cowan D (2008) Edge enhancement of potential-field data using normalized statistics. Geophysics 73:H1–H4
Cordell L (1979) Gravimetric expression of graben faulting in Santa Fe Country and the Espanola Basin. 30th Field conference New Mexico. New Mexico Geological Society Guidebook, 59–64
Cordell L, Grauch VJS (1985) Mapping basement magnetization zones from aeromagnetic data in the San Juan basin, New Mexico. In: Hinze WJ (ed) The utility of regional gravity and magnetic anomaly society of exploration geophysics, p 181–197
Evjen HM (1936) The place of the vertical gradient in gravitational interpretations. Geophysics 1:127–136
Ferreira FJF, Douza J, Bongiolo ABS, Castro LG (2013) Enhancement of the total horizontal gradient of magnetic anomalies using the tilt angle. Geophysics 78(3):J33–J41
Hsu SH, Sibuet JC, Shyu CT (1996) High-resolution detection of geologic boundaries from potential-field anomalies: an enhanced analytic signal technique. Geophysics 61:373–386
Li X (2006) Understanding 3D analytic signal amplitude. Geophysics 71(2):L13–L16
Ma G, Du X (2012) An improved analytic signal technique for the depth and structural index from 2D magnetic anomaly data. Pure Appl Geophys 169:2193–2200
Ma G, Li L (2012) Edge detection in potential fields with the normalized total horizontal derivative. Comput Geosci 41:83–87
Miller HG, Singh V (1994) Potential field tilt—a new concept for location of potential field sources. J Appl Geophys 32:213–217
Nabighian MN (1972) The analytic signal of two-dimensional magnetic bodies with polygonal cross-section: its properties and use for automated anomaly interpretation. Geophysics 37:507–517
Nabighian MN (1974) Additional comments on the analytic signal of two-dimensional magnetic bodies with polygonal cross-section. Geophysics 39:85–92
Nabighian MN (1984) Toward a three-dimensional automatic interpretation of potential field data via generalized Hilbert transforms: fundamental relations. Geophysics 49:780–786
Roest WR, Verhoef J, Pilkington M (1992) Magnetic interpretation using the 3-D analytic signal. Geophysics 57:116–125
Verduzco B, Fairhead JD (2004) New insights into magnetic derivatives for structural mapping. Lead Edge 23:116–119
Wijns C, Perez C, Kowalczyk P (2005) Theta map: edge detection in magnetic data. Geophysics 70:L39–L43
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the National High Technology Research and Development 863 Program of China (Grant No. 2013AA063930) for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Huang, D., Yu, X. et al. Edge interpretation of potential field data with the normalized enhanced analytic signal. Acta Geod Geophys 51, 125–136 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-015-0120-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-015-0120-x