Abstract
Introduction
Immunotherapy [(specifically, antibodies blocking programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1)] is a valuable option in cancer treatment because it leads to durable tumour regression and improves survival in several cancers. Patients with PD-L1 expressing tumours benefit from this therapy, but currently it can only be determined through biopsy, which may be inconclusive or impossible due to lesion location, associated risks, intratumoral and interlesional heterogeneity. Therefore, radio-immune-imaging with a specific radiopharmaceutical is ideally placed to play an important role when performing real-time, in vivo, whole-body and non-invasive PD-L1 expression mapping.
Purpose
To describe and summarise published scientific data on imaging PD-L1 expression using radiopharmaceuticals and discuss future directions in this research field.
Methods
A summary review of the literature was done through PubMed to search papers that described and included radiopharmaceuticals to image PD-L1 expression. Only English papers published until April 2018 that detailed laboratorial and animal procedures were selected.
Results
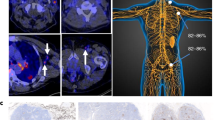
Eleven pre-clinical papers published between 2015 and 2018 were included. Four studies used anti-PD-L1 radiopharmaceuticals labelled with Indium-111, 4 with Copper-64, 2 with Fluoride-18 and 1 with both Copper-64 and Gallium-68. All of them had identical protocols and showed similar radiopharmaceutical biodistribution. They reported successful anti-PD-L1 labelling, with high tumour–background ratio (mainly when spleen uptake was saturated with unlabelled/cold antibody).
Conclusions
All reported radiopharmaceuticals had high sensitivity and specificity to identify tumours with PD-L1 expression in animal model. Clinical experiments appear to be now justifiable.

These results are presented with permission from the Journal of Nuclear Medicine and were originally published in [30] © SNMMI

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatterjee S, Lesniak WG, Gabrielson M, Lisok A, Wharram B, Sysa-Shah P, Azad BB, Pomper MG, Nimmagadda S (2016) A humanized antibody for imaging immune checkpoint ligand PD-L1 expression in tumors. Oncotarget 7(9):10215–10227. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7143
Lesniak WG, Chatterjee S, Gabrielson M, Lisok A, Wharram B, Pomper MG, Nimmagadda S (2016) PD-L1 detection in tumors using [(64)Cu]Atezolizumab with PET. Bioconjug Chem 27(9):2103–2110. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.6b00348
Ehlerding EB, England CG, McNeel DG, Cai W (2016) Molecular imaging of immunotherapy targets in cancer. J Nucl Med 57(10):1487–1492. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.177493
Chen L, Han X (2015) Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy of human cancer: past, present, and future. J Clin Invest 125(9):3384–3391. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI80011
Chen DS, Mellman I (2013) Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 39(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012
Zhang T, Xie J, Arai S, Wang L, Shi X, Shi N, Ma F, Chen S, Huang L, Yang L, Ma W, Zhang B, Han W, Xia J, Chen H, Zhang Y (2016) The efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies for treatment of advanced or refractory cancers: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 7(45):73068–73079. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12230
Huang G, Sun X, Liu D, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Xiao G, Li X, Gao X, Hu C, Wang M, Ren H, Qin S (2017) The efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody therapy versus docetaxel for pretreated advanced NSCLC: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 9(3):4239–4248. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23279
Santarpia M, González-Cao M, Viteri S, Karachaliou N, Altavilla G, Rosell R (2015) Programmed cell death protein-1/programmed cell death ligand-1 pathway inhibition and predictive biomarkers: understanding transforming growth factor-beta role. Transl Lung Cancer Res 4(6):728–742. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.12.04
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD, Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger SN, Kohrt HE, Horn L, Lawrence DP, Rost S, Leabman M, Xiao Y, Mokatrin A, Koeppen H, Hegde PS, Mellman I, Chen DS, Hodi FS (2014) Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 515(7529):563–567. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14011
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, Honjo T (1992) Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J 11(11):3887–3895
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L (1999) B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med 5:1365. https://doi.org/10.1038/70932
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne MC, Horton HF, Fouser L, Carter L, Ling V, Bowman MR, Carreno BM, Collins M, Wood CR, Honjo T (2000) Engagement of the Pd-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med 192(7):1027–1034
Maute RL, Gordon SR, Mayer AT, McCracken MN, Natarajan A, Ring NG, Kimura R, Tsai JM, Manglik A, Kruse AC, Gambhir SS, Weissman IL, Ring AM (2015) Engineering high-affinity PD-1 variants for optimized immunotherapy and immuno-PET imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(47):E6506–E6514. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1519623112
Josefsson A, Nedrow JR, Park S, Banerjee SR, Rittenbach A, Jammes F, Tsui B, Sgouros G (2016) Imaging, biodistribution, and dosimetry of radionuclide-labeled PD-L1 antibody in an immunocompetent mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer Res 76(2):472–479. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2141
Natarajan A, Mayer AT, Xu L, Reeves RE, Gano J, Gambhir SS (2015) Novel radiotracer for immunoPET imaging of PD-1 checkpoint expression on tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. Bioconjug Chem 26(10):2062–2069. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00318
Mayer AT, Natarajan A, Gordon SR, Maute RL, McCracken MN, Ring AM, Weissman IL, Gambhir SS (2017) Practical immuno-PET radiotracer design considerations for human immune checkpoint imaging. J Nucl Med 58(4):538–546. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.177659
Trotter DEG, Meng X, McQuade P, Rubins D, Klimas M, Zeng Z, Connolly BM, Miller PJ, O’Malley SS, Lin S-A, Getty KL, Fayadat-Dilman L, Liang L, Wahlberg E, Widmark O, Ekblad C, Frejd FY, Hostetler ED, Evelhoch JL (2017) In vivo imaging of the programmed death ligand 1 by 18F PET. J Nucl Med 58(11):1852–1857. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.117.191718
Cole EL, Kim J, Donnelly DJ, Smith RA, Cohen D, Lafont V, Morin PE, Huang RY-C, Chow PL, Hayes W Jr (2017) Radiosynthesis and preclinical PET evaluation of 89Zr-nivolumab (BMS-936558) in healthy non-human primates. Bioorg Med Chem 25(20):5407–5414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.07.066
England CG, Ehlerding EB, Hernandez R, Rekoske BT, Graves SA, Sun H, Liu G, McNeel DG, Barnhart TE, Cai W (2017) Preclinical pharmacokinetics and biodistribution studies of 89Zr-labeled Pembrolizumab. J Nucl Med 58(1):162–168. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.177857
Mahmoudi M, Farokhzad OC (2017) Cancer immunotherapy: wound-bound checkpoint blockade. Nat Biomed Eng 1:0031. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-017-0031
Gong J, Chehrazi-Raffle A, Reddi S, Salgia R (2018) Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy: a comprehensive review of registration trials and future considerations. J Immunother Cancer 6(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0316-z
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ, Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, Pitot HC, Hamid O, Bhatia S, Martins R, Eaton K, Chen S, Salay TM, Alaparthy S, Grosso JF, Korman AJ, Parker SM, Agrawal S, Goldberg SM, Pardoll DM, Gupta A, Wigginton JM (2012) Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N Engl J Med 366(26):2455–2465. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1200694
Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS, Loriot Y, Cruz C, Bellmunt J, Burris HA, Petrylak DP, S-l Teng, Shen X, Boyd Z, Hegde PS, Chen DS, Vogelzang NJ (2014) MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature 515:558. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13904
Hettich M, Braun F, Bartholomä MD, Schirmbeck R, Niedermann G (2016) High-resolution PET imaging with therapeutic antibody-based PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint tracers. Theranostics 6(10):1629–1640. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.15253
Frederick DT, Piris A, Cogdill AP, Cooper ZA, Lezcano C, Ferrone CR, Mitra D, Boni A, Newton LP, Liu C, Peng W, Sullivan RJ, Lawrence DP, Hodi FS, Overwijk WW, Lizée G, Murphy GF, Hwu P, Flaherty KT, Fisher DE, Wargo JA (2013) BRAF inhibition is associated with enhanced melanoma antigen expression and a more favorable tumor microenvironment in patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 19(5):1225–1231. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-1630
Heskamp S, Hobo W, Molkenboer-Kuenen JDM, Olive D, Oyen WJG, Dolstra H, Boerman OC (2015) Noninvasive imaging of tumor PD-L1 xxpression using radiolabeled anti-PD-L1 antibodies. Cancer Res 75(14):2928–2936. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-14-3477
Kraeber-Bodere F, Bailly C, Chérel M, Chatal J-F (2016) ImmunoPET to help stratify patients for targeted therapies and to improve drug development. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43(12):2166–2168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3458-6
Aguiar JPN, Perry LA, Penny-Dimri J, Babiker H, Tadokoro H, de Mello RA, Lopes JGL (2017) The effect of PD-L1 testing on the cost-effectiveness and economic impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors for the second-line treatment of NSCLC. Ann Oncol 28(9):2256–2263. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx305
Donnelly DJ, Smith RA, Morin P, Lipovšek D, Gokemeijer J, Cohen D, Lafont V, Tran T, Cole EL, Wright M, Kim J, Pena A, Kukral D, Dischino DD, Chow P, Gan J, Adelakun O, Wang X-T, Cao K, Leung D, Bonacorsi SJ, Hayes W (2018) Synthesis and biologic evaluation of a novel 18F-labeled adnectin as a PET radioligand for imaging PD-L1 expression. J Nucl Med 59(3):529–535. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.117.199596
Nedrow JR, Josefsson A, Park S, Ranka S, Roy S, Sgouros G (2017) Imaging of programmed cell death ligand 1: impact of protein concentration on distribution of anti-PD-L1 SPECT agents in an immunocompetent murine model of melanoma. J Nucl Med 58(10):1560–1566. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.117.193268
Truillet C, Oh HLJ, Yeo SP, Lee C-Y, Huynh LT, Wei J, Parker MFL, Blakely C, Sevillano N, Wang Y-H, Shen YS, Olivas V, Jami KM, Moroz A, Jego B, Jaumain E, Fong L, Craik CS, Chang AJ, Bivona TG, Wang C-I, Evans MJ (2018) Imaging PD-L1 expression with immunoPET. Bioconjug Chem 29(1):96–103. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00631
Chatterjee S, Lesniak WG, Miller MS, Lisok A, Sikorska E, Wharram B, Kumar D, Gabrielson M, Pomper MG, Gabelli SB, Nimmagadda S (2017) Rapid PD-L1 detection in tumors with PET using a highly specific peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483(1):258–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.12.156
Niemeijer A-LN, Smit EF, GaMSv Dongen, Windhorst AD, Huisman MC, Hendrikse NH, Leung DK, Smith RA, Hayes W, Velasquez LM, Bonacorsi SJ, Donnelly DJ, Morin PE, Thunnissen E, Poot AJ, Vugts DJ, Langen JD (2017) Whole body PD-1 and PD-L1 PET with 89Zr-nivolumab and 18F-BMS-986192 in pts with NSCLC. J Clin Oncol 35(15_suppl):e20047. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2017.35.15_suppl.e20047
England CG, Rui L, Cai W (2017) Lymphoma: current status of clinical and preclinical imaging with radiolabeled antibodies. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 44(3):517–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-016-3560-9
Josefsson A, Nedrow J, Park S, Ranka S, Sgouros G (2016) Dosimetric analysis of Actinium-225 labeled anti-PD-L1 alpha particle radioimmunotherapy of melanoma cancer in an immunocompetent mouse model. J Nucl Med 57(Supplement 2):635
Kwak JJ, Tirumani SH, Abbeele ADVd, Koo PJ, Jacene HA (2015) Cancer immunotherapy: imaging assessment of novel treatment response patterns and immune-related adverse events. Radiographics 35(2):424–437. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.352140121
Funding
S. C. Vaz, A. S. Capacho and D. C. Costa received antibody anti-PDL1 [clone 6E11] through a MTA from Genentech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SCV: Literature Search and Review; Manuscript Writing, Editing and Content Planning. ASC: Literature Review; Manuscript Writing, Editing and Content Planning. FPO: Literature Review; Manuscript Writing, Editing and Content Planning. NG: Editing and Content Planning. CB: Editing and Content Planning. AP: Editing and Content Planning. DCC: Manuscript Writing, Editing and Content Planning.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
F. P. Oliveira, N. Gil, C. Barros and A. Parreira declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable. This is a literature review. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaz, S.C., Capacho, A.S., Oliveira, F.P. et al. Radiopharmacology and molecular imaging of PD-L1 expression in cancer. Clin Transl Imaging 6, 429–439 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-018-0303-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40336-018-0303-x