Abstract
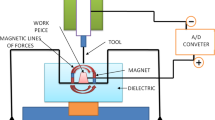
Micro-electrodischarge machining (micro-EDM) is one of the most sustainable processes used to machine 3D features on metallic surfaces. It is an effective method of machining extremely hard and difficult to cut materials. Material is removed from anode surface, primarily, by heat generated due to controlled sparking. Size and shape of electrodes play significant role in the stability of the micro-EDM process by governing the debris flushing out of inter-electrode gap. The present study addresses the effect of geometries on the performance of the micro-EDM process. Designed experiments have been conducted by using solid, single-channel and multichannel electrodes. Material removal rate (MRR) and tool wear rate (TWR) being the important indicators of micro-EDM process, effect of different process parameters on MRR and TWR have been evaluated for different set of experiments on solid rod, single-channel and multichannel electrodes. From the analysis, a solid electrode has been found to provide a better performance than the other two type of electrodes. Highest MRR and lowest TWR is observed for the solid electrode. A 16.63% of maximum increment was found in MRR with the use of solid electrode.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raju L, Hiremath SS (2016) A state-of-the-art review on micro electro-discharge machining. ProcTechnol 25:1281–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.08.222
Meshram DB, Puri YM (2017) Review of research work in die sinking EDM for machining curved hole. J BrazSocMechSciEng 39(7):2593–2605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-016-0622-7
Bozdana AT, Ulutas T (2016) The effectiveness of multichannel electrodes on drilling blind holes on Inconel 718 by EDM process. Mater Manuf Processes 31(4):504–513. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1059451
Bozdana AT, Yilmaz O, Okka MA, Filiz IH (2009, June) A comparative experimental study on fast hole EDM of Inconel 718 and Ti-6Al-4V. In: Proceeding of 5th international conference and exhibition on design and production of machines and dies/molds.
Opoz TT, Ekmekci B, Erden A (2009) An experimental study on the geometry of microholes in microelectric discharge machining. Mater Manuf Processes 24(12):1236–1241. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910903129422
Yilmaz O, Okka MA (2010) Effect of single and multi-channel electrodes application on EDM fast hole drilling performance. Int J AdvManufTechnol 51(1–4):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-010-2625-3
Janmanee P, Muttamara A (2011) A study of hole drilling on stainless steel AISI 431 by EDM using brass tube electrode. Int Trans J EngManagApplSciTechnol 2(4):471–481
Plaza S, Sanchez JA, Perez E, Gil R, Izquierdo B, Ortega N, Pombo I (2014) Experimental study on micro EDM-drilling of Ti6Al4V using helical electrode. PrecisEng 38(4):821–827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.04.010
Ferraris E, Castiglioni V, Ceyssens F, Annoni M, Lauwers B, Reynaerts D (2013) EDM drilling of ultra-high aspect ratio micro holes with insulated tools. CIRP Ann 62(1):191–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2013.03.115
Kursad GOV (2017) Experimental investigation of the effects of electrodes on EDM hole drilling process. J Polytechnic 20(2):377–382. https://doi.org/10.2339/2017.20.2377-382
Sharma P, Singh S, Mishra DR (2014) Electrical discharge machining of AISI 329 stainless steel using copper and brass rotary tubular electrode. Proc Mater Sci 5:1771–1780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.367
Vincent N, Kumar AB (2016) Experimental investigations into EDM behaviours of En41b using copper and brass rotary tubular electrode. ProcTechnol 25:877–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2016.08.196
Wang K, Zhang Q, Zhu G, Huang Y, Zhang J (2018) Influence of tool size on machining characteristics of micro-EDM. Proc CIRP 68:604–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.122
Zhu G, Zhang Q, Wang K, Huang Y, Zhang J (2018) Effects of different electrode materials on high-speed electrical discharge machining of W9Mo3Cr4V. Proc CIRP 68:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2017.12.023
Risto M, Haas R, Munz M (2016) Optimization of the EDM drilling process to increase the productivity and geometrical accuracy. ProcCirp 42(1):537–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.247
Munz M, Risto M, Haas R (2013) Specifics of flushing in electrical discharge drilling. Proc CIRP 6:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2013.03.024
Fu Y, Miyamoto T, Natsu W, Zhao W, Yu Z (2016) Study on influence of electrode material on hole drilling in micro-EDM. Proc CIRP 42(1):516–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.02.243
Kumar R, Thakur S, Pandey AK (2017) Modelling and optimization of hole circularity and hole dilation in electrical discharge drilling. Mater Today Proc 4(8):8706–8716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.07.219
Jadam T, Datta S, Mahapatra SS (2019) Electro-discharge Machining (EDM) of superalloyinconel 718 using triangular cross-sectioned copper tool electrode: emphasis on topography and metallurgical characteristics of the EDMed work surface. ProcNatlAcadSci India Sect A. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-019-00642-3
Fu J, Qiu M, Shen L, Kong L, Ma J (2020) On processing of Inconel718 through multi-channel discharge ablation. J Manuf Processes 57:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.07.014
Kumar S, Dhanabalan S (2019) Influence on machinability and form tolerance of Inconel 718 in Edm using different diameter multi hole Cu electrodes. SN ApplSci 1(5):396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0403-x
Kuppan P, Rajadurai A, Narayanan S (2008) Influence of EDM process parameters in deep hole drilling of Inconel 718. Int J AdvManufTechnol 38(1–2):74–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1084-y
Nagrale M, Mastud S (2018) Micro electrical discharge machining for machining micro holes. Trends Manuf Processes 32(1–3):23–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9099-0_3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest from author’s side.
Additional information
Technical Editor: Adriano Fagali de Souza.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagrale, M.S., Mastud, S.A. An experimental study to investigate the effect of solid, single-channel and multichannel electrodes in micro-electrodischarge drilling process. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 43, 88 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-02815-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-021-02815-x