Abstract
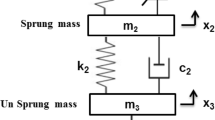
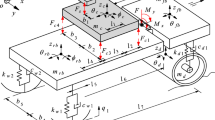
Control polices with semi-active and active devices such as magnetorheological (MR) damper, magnetorheological isolator, magnetorheological mount, electrorheological dampers, actuators and pneumatics are integrated with automotive seating system (ASS) for seating and ride comfort. Semi-active device has been developed to replace the traditional static spring and damper system for reducing the acceleration of the human body. The current work reviews various control policies like PID, GA-PID, PSO-PID, MR on–off, FLC, Skyhook, etc., used for controlling the vibration level of ASS. This review study finds that adoption of cost effective intelligent vibration control policies with adoptive solutions will improve the ride comfort and will be made available in all ASS in the near future.






























Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Organization for Standardization (1997) Mechanical vibration and shock-evaluation of human exposure to whole-body vibration-part 1: general requirements
Griffin MJ (1996) Handbook of human vibration. Academic Press, London
Hiemstravan Mastrigt S, Groenesteijn L, Vink P, Kuijt-Evers LF (2017) Predicting passenger seat comfort and discomfort on the basis of human, context and seat characteristics: a literature review. Ergonomics 60(7):889–911
Fischer D, Kaus E, Isermann R (2003) Fault detection for an active vehicle suspension. In: Proceedings of the American control conference, 2003, vol 5. IEEE, pp 4377–4382
Ning D, Sun S, Du H, Li W (2017) Integrated active and semi-active control for seat suspension of a heavy duty vehicle. J of Intell Mater Syst Struct. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X17721032
Sahin I, Engin T, Cesmeci S (2010) Comparison of some existing parametric models for magnetorheological fluid dampers. Smart Mater Struct 19(3):035012
Nieto AJ, Morales AL, Chicharro JM, Pintado P (2016) An adaptive pneumatic suspension system for improving ride comfort and handling. J Vib Control 22(6):1492–1503
Crivellaro C, Alves SJ (2006) Phenomenological model of a magneto-rheological damper for semi-active suspension control design and simulation (no. 2006-01-2520). SAE technical paper
Ahn KK (2014) Active pneumatic vibration isolation system using negative stiffness structures for a vehicle seat. J Sound Vib 333(5):1245–1268
Maciejewski I, Meyer L, Krzyzynski T (2010) The vibration damping effectiveness of an active seat suspension system and its robustness to varying mass loading. J Sound Vib 329(19):3898–3914
Choi SB, Nam MH, Lee BK (2000) Vibration control of a MR seat damper for commercial vehicles. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 11(12):936–944
Lee HS, Choi SB (2000) Control and response characteristics of a magneto-rheological fluid damper for passenger vehicles. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 11(1):80–87
Lai CY, Liao WH (2002) Vibration control of a suspension system via a magnetorheological fluid damper. Modal Anal 8(4):527–547
Cao J, Liu H, Li P, Brown DJ (2008) State of the art in vehicle active suspension adaptive control systems based on intelligent methodologies. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 9(3):392–405
Du H, Sze KY, Lam J (2005) Semi-active H∞ control of vehicle suspension with magneto-rheological dampers. J Sound Vib 283(3):981–996
Nusantoro GD, Priyandoko G (2011) PID state feedback controller of a quarter car active suspension system. J Basic Appl Sci Res 1(11):2304–2309
Ahmadian M, Pare CA (2000) A quarter-car experimental analysis of alternative semiactive control methods. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 11(8):604–612
Maciejewski I (2012) Control system design of active seat suspensions. J Sound Vib 331(6):1291–1309
Choi SB, Sung KG (2008) Vibration control of magnetorheological damper system subjected to parameter variations. Int J Veh Des 46(1):94–110
Zribi M, Karkoub M (2004) Robust control of a car suspension system using magnetorheological dampers. Modal Anal 10(4):507–524
Guo DL, Hu HY, Yi JQ (2004) Neural network control for a semi-active vehicle suspension with a magnetorheologicaldamper. J Vib Control 10(3):461–471
Metered H, Bonello P, Oyadiji SO (2010) An investigation into the use of neural networks for the semi-active control of a magnetorheologically damped vehicle suspension. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part D J Automob Eng 224(7):829–848
Ning D, Sun S, Wei L, Zhang B, Du H, Li W (2017) Vibration reduction of seat suspension using observer based terminal sliding mode control with acceleration data fusion. Mechatronics 44:71–83
Nagarkar MP, Vikhe GJ, Borole KR, Nandedkar VM (2011) Active control of quarter-car suspension system using linear quadratic regulator. Int J Automot Mech Eng 3(1):364–372
Gad S, Metered H, Bassuiny A, Abdel Ghany AM (2015) Vibration control of semi-active MR seat suspension for commercial vehicles using genetic PID controller. In: Sinha J (ed) Vibration engineering and technology of machinery. Mechanisms and machine science, vol 23. Springer, Cham, pp 721–732
Rashid MM, Rahim NA, Hussain MA, Rahman MA (2011) Analysis and experimental study of magnetorheological-based damper for semiactive suspension system using fuzzy hybrids. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 47(2):1051–1059
Aggarwal ML (2015) Fuzzy control of passenger ride performance using MR shock absorber suspension in quarter car model. Int J Dyn Control 3(4):463–469
Singh D (2018) Modeling and control of passenger body vibrations in active quarter car system: a hybrid ANFIS PID approach. Int J Dyn Control. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-018-0409-z
Karnopp D, Crosby MJ, Harwood RA (1974) Vibration control using semi-active force generators. J Eng Ind 96(2):619–626
Segla S, Orecny M (2014) Balance control of semi-active seat suspension with elimination of dynamic jerk. Procedia Eng 96:419–427
Segla S, Reich S (2007) Optimization and comparison of passive, active, and semi-active vehicle suspension systems. In: 12th IFToMM world congress, Besancon, France
Yi K, Song BS (1999) A new adaptive skyhook control of vehicle semi-active suspensions. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part D J Autom Eng 213(3):293–303
Kafafy El, Mahmoud El-Demerdash S M, Rabeih AAM (2012) Automotive ride comfort control using MR fluid damper. Engineering 4(4):179–187
Balamurugan L, Jancirani J, Eltantawie MA (2014) Generalized magnetorheological (MR) damper model and its application in semi-active control of vehicle suspension system. Int J Automot Technol 15(3):419–427
Huang W, Xu J, Zhu DY, Wu YL, Lu JW, Lu KL (2015) Semi-active vibration control using a magneto rheological (MR) damper with particle swarm optimization. Arab J Sci Eng 40(3):747–762
Dong XM, Yu M, Liao CR, Chen WM (2010) Comparative research on semi-active control strategies for magneto-rheological suspension. Nonlinear Dyn 59(3):433–453
Shiao Y, Lai CC, Nguyen QA (2010) The analysis of a semi-active suspension system. In: Proceedings of SICE annual conference 2010. IEEE, pp 2070–2082
Liu Y, Matsuhisa H, Utsuno H (2008) Semi-active vibration isolation system with variable stiffness and damping control. J Sound Vib 313(1–2):16–28
Lajqi S, Pehan S (2012) Designs and optimizations of active and semi-active non-linear suspension systems for a terrain vehicle. Stroj vestn J Mech Eng 58(12):732–743
El Majdoub K, Ghani D, Giri F, Chaoui FZ (2015) Adaptive semi-active suspension of quarter-vehicle with magnetorheological damper. J Dyn Syst Meas Control 137(2):021010
Babak Assadsangabi, Eghtesad M, Daneshmand F, Vahdati N (2009) Hybrid sliding mode control of semi-active suspension systems. Smart Mater Struct 18(12):125027
Ahmadian M, Song X, Southward SC (2004) No-jerk skyhook control methods for semiactive suspensions. J Vib Acoust 126(4):580–584
Aly AA, Salem FA (2013) Vehicle suspension systems control: a review. Int J Control Autom Syst 2(2):46–54
Kasemi B, Muthalif AG, Rashid MM, Fathima S (2012) Fuzzy-PID controller for semi-active vibration control using magnetorheological fluid damper. Procedia Eng 41:1221–1227
Wu JD, Chen RJ (2004) Application of an active controller for reducing small-amplitude vertical vibration in a vehicle seat. J Sound Vib 274(3–5):939–951
Lam AHF, Liao WH (2003) Semi-active control of automotive suspension systems with magneto-rheological dampers. Int J Veh Des 33(1–3):50–75
Choi SB, Han YM (2003) MR seat suspension for vibration control of a commercial vehicle. Int J Veh Des 31(2):202–215
Du H, Li W, Zhang N (2011) Semi-active variable stiffness vibration control of vehicle seat suspension using an MR elastomer isolator. Smart Mater Struct 20(10):105003
Kasprzyk J, Wyrwal J, Krauze P (2014) Automotive MR damper modeling for semi-active vibration control. In: 2014 IEEE/ASME international conference on advanced intelligent mechatronics (AIM). IEEE, pp 500–505
Du H, Li W, Zhang N (2012) Integrated seat and suspension control for a quarter car with driver model. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 61(9):3893–3908
Chen YW, Zhao Q (2012) Sliding mode variable structure control for semi-active seat suspension in vehicles. J Harbin Eng Univ 33(6):775–781
Yao HJ, Fu J, Yu M, Peng YX (2013) Semi-active control of seat suspension with MR damper. In: Journal of physics: conference series, vol 412, no 1. IOP Publishing, IOP Publishing, p 012054
Maciejewski I, Glowinski S, Krzyzynski T (2014) Active control of a seat suspension with the system adaptation to varying load mass. Mechatronics 24(8):1242–1253
Sathishkumar P, Jancirani J, John D (2014) Reducing the seat vibration of vehicle by semi active force control technique. J Mech Sci Technol 28(2):473–479
Attia EM, FZ A, El Gamal HA, El Souhily BM (2014) Effect of irregular road on dynamic response of car seat suspended by a magneto-rheological (MR) damper. Int J Appl Sci Technol 4(5):39–54
Metered H, Sika Z (2014) Vibration control of a semi-active seat suspension system using magnetorheological damper. In: 2014 IEEE/ASME 10th international conference on mechatronic and embedded systems and applications (MESA). IEEE, pp 1–7
Gan Z, Hillis AJ, Darling J (2015) Adaptive control of an active seat for occupant vibration reduction. J Sound Vib 349:39–55
Shin DK, Choi SB (2015) Design of a new adaptive fuzzy controller and its application to vibration control of a vehicle seat installed with an MR damper. Smart Mater Struct 24(8):085012
Ghany GHMABAA (2015) Ride comfort enhancement of heavy vehicles using magnetorheological seat suspension. Int J Heavy Veh Syst 22(2):93–113
Phu DX, Choi SM, Choi SB (2017) A new adaptive hybrid controller for vibration control of a vehicle seat suspension featuring MR damper. J Vib Control 23(20):3392–3413
Rajendiran S, Lakshmi P (2016) Simulation of PID and fuzzy logic controller for integrated seat suspension of a quarter car with driver model for different road profiles. J Mech Sci Technol 30(10):4565–4570
Sun SS, Ning DH, Yang J, Du H, Zhang SW, Li WH (2016) A seat suspension with a rotary magnetorheological damper for heavy duty vehicles. Smart Mater Struct 25(10):105032
Bai XX, Jiang P, Qian LJ (2016) Integrated semi-active seat suspension for both longitudinal and vertical vibration isolation. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 28(8):1036–1049
Singh D, Aggarwal ML (2017) Passenger seat vibration control of a semi-active quarter car system with hybrid Fuzzy–PID approach. Int J Dyn Control 5(2):287–296
Alfadhli A, Darling J, Hillis AJ (2017) The control of an active seat with vehicle suspension preview information. J Vib Control. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546317698285
Gad S, Metered H, Bassuiny A, Abdel Ghany AM (2017) Multi-objective genetic algorithm fractional-order PID controller for semi-active magneto-rheologically damped seat suspension. J Vib Control 23(8):1248–1266
Zhang N, Zhao Q (2017) Fuzzy sliding mode controller design for semi-active seat suspension with neuro-inverse dynamics approximation for MR damper. J Vib Eng 19(5):3488–3511
Hu G, Liu Q, Ding R, Li G (2017) Vibration control of semi-active suspension system with magneto-rheological damper based on hyperbolic tangent model. Adv Mech Eng 9(5):1687814017694581
Phu DX, An JH, Choi SB (2017) A novel adaptive PID controller with application to vibration control of a semi-active vehicle seat suspension. Appl Sci 7(10):1055
Metered H, Elsawaf A, Vampola T, Sika Z (2015) Vibration control of MR-damped vehicle suspension system using PID controller tuned by particle swarm optimization. SAE Int J Passeng Cars-Mech Syst 8(2015-01-0622):426–435
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramalingam, M., Patel, R., Thirumurugan, M.A. et al. Control policies used for semi-active damper for automotive seating system: a review. Int. J. Dynam. Control 7, 1135–1148 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-018-0460-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-018-0460-9