Abstract
Purpose
Increased oxidative stress and impaired antioxidant defense are important mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic myopathy. Since diabetes mellitus type 1 decreases muscle regeneration capacity the present study was designed to determine the influence of alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), a potent biological antioxidant, on the process of regeneration of diabetic rat skeletal muscles.
Methods
40 Wistar rats were divided into three groups: control (n = 8), untreated diabetic group (n = 16) and ALA treated diabetic group (n = 16). The regeneration process was provoked in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats in both slow (m.soleus, SOL) and fast (m.extensor digitorum longus, EDL) skeletal muscles by intramuscular injection of myotoxin bupivacaine. At intervals of 10 days and 4 weeks, muscle histochemical and morphometrical analysis (fiber cross areas and fiber type distribution) was performed.
Results
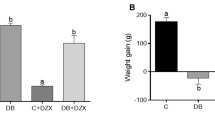
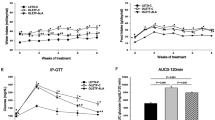
Changes induced by diabetes are evident in redistribution of muscle fibers and in significant level of atrophy. After 4 weeks of diabetes, glycolytic muscle fibers are dominant in both slow and fast muscles. Muscle atrophy is present in all fiber types except in type I of slow skeletal muscle. Treatment with ALA reduce changes in the morphological properties caused by diabetes mellitus type 1 in slow and fast rat skeletal muscles during the process of regeneration.
Conclusion
Treatment with lipoic acid during 4 weeks has shown effects on the redistribution of muscle fibers, and can prevent atrophy in slow and fast diabetic muscle.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414:813–820. doi:10.1038/414813a
Fahim MA, El-Sabban F, Davidson N (1998) Muscle contractility decrement and correlated morphology during the pathogenesis of streptozotocin-diabetic mice. Anat Rec 251:240–244
Jerkovic R, Bosnar A, Jurisic-Erzen D, Azman J, Starcevic-Klasan G, Peharec S, Coklo M (2009) The effects of long-term experimental diabetes mellitus type 1 on skeletal muscle regeneration capacity. Coll Antropol 33(4):1115–1119
Ozaki K, Matsuura T, Narama I (2001) Histochemical and morphometrical analysis of skeletal muscle in spontaneous diabetic WBN/Kob rat. Acta Neuropathol 102:264–270
Klueber KM, Feczko JD, Schmidt G, Watkins JB 3rd (1989) Skeletal muscle in the diabetic mouse: histochemical and morphometric analysis. Anat Rec 225:41–45. doi:10.1002/ar.1092250107
Rutschmann M, Dahlmann B, Reinauer H (1984) Loss of fast-twitch isomyosin in skeletal muscles of the diabetic rat. Biochem J 221:645–650
Jerkovic R, Argentini C, Serrano-Sanchez A, Cordonnier C, Schiaffino S (1997) Early myosin switching induced by nerve activity in regenerating slow skeletal muscle. Cell Struct Funct 22(1):147–153
Schiaffino S, Serrano AL, Jerkovic R, Di Lisi R, Murgia M (1998) Neural regulation of myosin gene expression in regenerating skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 163(3):S11–S15
Hall-Craggs EC (1974) Rapid degeneration and regeneration of a whole skeletal muscle following treatment with bupivacaine (Marcain). Exp Neurol 43:349–358
Barnard RJ, Youngren JF (1992) Regulation of glucose transport in skeletal muscle. FASEB J 6:3238–3244
Halseth AE, Bracy DP, Wasserman DH (2001) Functional limitations to glucose uptake in muscles comprised of different fiber types. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280:E994–E999
Packer L, Witt EH, Tritschler HJ (1995) alpha-Lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med 19:227–250
Yaworsky K, Somwar R, Ramlal T, Tritschler HJ, Klip A (2000) Engagement of the insulin-sensitive pathway in the stimulation of glucose transport by alpha-lipoic acid in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Diabetologia 43:294–303
Biewenga GP, Haenen GR, Bast A (1997) The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid. Gen Pharmacol 29(3):315–331
Estrada DE, Ewart HS, Tsakiridis T, Volchuk A, Ramlal T, Tritschler H, Klip A (1996) Stimulation of glucose uptake by the natural coenzyme alpha-lipoic acid/thioctic acid: participation of elements of the insulin signalling pathway. Diabetes 45(12):1798–1804
Khamaisi M, Potashnik R, Tirosh A, Demshchak E, Rudich A, Tritschler H, Wessel K, Bashan N (1999) Lipoic acid reduces glycemia and increases muscle GLUT4 content in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Metabolism 46(7):763–768
Jacob S, Henriksen EJ, Schiemann AL, Simon I, Clancy DE, Tritschler HJ, Jung WI, Augustin HJ, Dietze GJ (1995) Enhancement of glucose disposal in patients with type 2 diabetes by alpha-lipoic acid. Arzneimittelforschung 45(8):872–874
Papanas N, Ziegler D (2014) Efficacy of Alpha-lipoic acid in diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin Pharmacother 15(18):2721–2731. doi:10.1517/14656566.2014.972935
Golbidi S, Badran M, Laher I (2011) Diabetes and alpha lipoic acid. Front Pharmacol 2(69):1–15. doi:10.3389/fphar.2011.00069
Coleman SK, Rebalka IA, D’Souza DM, Hawke TJ (2015) Skeletal muscle as a therapeutic target for delaying type 1 diabetic complications. World J Diabetes 6(17):1323–1336. doi:10.4239/wjd.v6.i17.1323
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, Grodsky GM (2002) Oxidative stress and stress-activated signalling pathways: a unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 23(5):599–622. doi:10.1210/er.2001-0039
Saltiel AR, Kahn CR (2001) Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414(6865):799–806. doi:10.1038/414799a
Wieteska-Skrzeczynska W, Grzelkowska-Kowalczyk K, Jank M, Maciejewski H (2009) Transcriptional dysregulation of skeletal muscle protein metabolism in streptozotocin-diabetic mice. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(Suppl 1):29–36
Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Bastard JP, Jaudon MC, Delattre J (2000) Consequences of the diabetic status on the oxidant/antioxidant balance. Diabetes Metab 26(3):163–176
Cariello A (2003) New insights on oxidative stress and diabetic complications may lead to a “causal” antioxidant therapy. Diabetes Care 26(5):1589–1596
Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, Hasche H, Lobisch M, Schütte K, Kerum G, Malessa R (1999) Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a 7-month multicenter randomized controlled trial (ALADIN III Study). ALADIN III Study Group. Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 22(8):1296–1301
Panigrahi M, Sadguna Y, Shivakumar BR, Kolluri SV, Roy S, Packer L, Ravindranath V (1996) Alpha lipoic protects against reperfusion injury following cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res 717(1–2):79–101
Koçak G, Aktan F, Canbolat O, Ozoğul C, Elbeğ S, Yildizoglu-Ari N, Karasu C, ADIC Study Group-Antioxidants in Diabetes-Induced Complications (2000) Alpha-lipoic acid treatment ameliorates metabolic parameters, blood pressure, vascular reactivity and morphology of vessels already damaged by streptozotocin-diabetes. Diabetes Nutr Metab 13(6):308–318
Konrad D, Somwar R, Sweeney G, Yaworsky K, Hayashi M, Ramlal T, Klip A (2001) The antihyperglycemic drug alpha-lipoic acid stimulates glucose uptake via both GLUT4 translocation and GLUT4 activation: potential role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in GLUT4 activation. Diabetes 50(6):1464–1470
Shen QW, Jones CS, Kalchayanand N, Zhu MJ, Du M (2005) Effect of dietary alpha-lipoic acid on growth, body composition, muscle pH, and AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in mice. J Anim Sci 83(11):2611–2617
Lee WJ, Song KH, Koh EH, Won JC, Kim HS, Park HS, Kim MS, Kim SW, Lee KU, Park JY (2005) Alpha-lipoic acid increases insulin sensitivity by activating AMPK in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 332(3):885–891. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.05.035
Acknowledgements
We specially thank Prof. Stefano Sciaffino from the Department of Biomedical Sciences, Padua, Italy for supplying us with monoclonal antibodies for slow and fast myosin heavy chain isoforms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: SKG, ID, JED, JR. Performed experiments: SKG, ID, JR, JED. Analysed the data: JR, JED, PS, GD. Contributed reagents/analysis tools: JR, JED, PS, GD. Wrote the paper: SKG, JR, JED. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data and manuscript writing of the study was supported by a Grant from the University of Rijeka, Croatia No. 848-10-1348.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures using animals in this investigation were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, University of Rijeka and are in accordance with the Law on the implementation of European Union Regulations on animal welfare 2013.
Informed consent
No informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jurisic-Erzen, D., Starcevic-Klasan, G., Ivanac, D. et al. The effects of alpha-lipoic acid on diabetic myopathy. J Endocrinol Invest 41, 203–209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0720-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0720-0