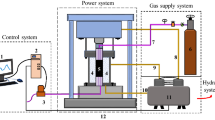
Abstract
The fluid–solid coupled with triaxial servo-controlled seepage experiments of coal containing gas was used to study coal samples from a coal mine in Sichuan Province, China. The mechanical characteristics, seepage laws, energy dissipation, and fracture evolution of raw coal under incremental tiered cyclic loading and different confining pressures were studied. The experimental results show that as the axial stress increases, the axial relative residual strain curve changes in an "N" shape, while the radial relative residual strain curve always increases. The change in the relative residual strain can be divided into three stages: compaction stage, elastic stage, and yield–failure stage. Except for in the last cycle, as the cycle number increases, the dissipated energy of coal increases linearly. With increasing cycle number, the difference in energy dissipation under different confining pressures gradually increases. During the yield–failure stage, some closed fractures inside the coal began to expand, and new fissures and cracks were generated, causing a large residual deformation and leading to a sharp increase in the dissipated energy and elastic modulus. Additionally, from the perspective of energy, a new method for calculating the elastic modulus (referred to as the equivalent elastic modulus) using the integral method was proposed.
Article Highlights
-
The geomechanical behavior of gas-containing coal under incremental tiered cyclic loading is investigated.
-
The failure mechanism of coal is analyzed based on dissipated energy analysis.
-
The equivalent elastic modulus is calculated from the perspective of energy.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Reference
Chang XC, Tian H (2018) Technical scheme and application of pressure-relief gas extraction in multi-coal seam mining region. Int J Min Sci Technol 28:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.03.010
Chu YP, Sun HT, Zhang DM (2019) Experimental study on evolution in the characteristics of permeability, deformation, and energy of coal containing gas under triaxial cyclic loading-unloading. Energy Sci Eng 7:2112–2123. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.417
Duan MK, Jiang CB, Gan Q, Li MH, Peng K, Zhang WZ (2020a) Experimental investigation on the permeability, acoustic emission and energy dissipation of coal under tiered cyclic unloading. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 73:103054. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2019.103054
Duan MK, Jiang CB, Gan Q, Zhao HB, Yang Y, Li ZK (2020) Study on permeability anisotropy of bedded coal under true triaxial stress and its application. Transport Porous Med 131:1007–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01375-y
Duan MK, Jiang CB, Xing HL, Zhang DM, Peng K, Zhang WZ (2020) Study on damage of coal based on permeability and load–unload response ratio under tiered cyclic loading Arabian. J Geosci 13:250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-5249-4
Dutta J, Bhardwaj N, Kumar A (2018) Integration of mini-frac stress results with core data to identify ductile behavior of overpressured sandstone reservoir in deep-water offshore Krishna-Godavari basin, India . Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 4:11–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-017-0071-5
Fan L, Liu SM (2019) Evaluation of permeability damage for stressed coal with cyclic loading: an experimental study. Int J Coal Geol 216:103338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2019.103338
Huang J, Song ZL, Liao ZW, Zhao WC, Wang D (2020) Quantification of cracks and the evolution of permeability for reservoir rock under coupled THM: equipment development and experimental research . Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 6:63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00187-5
Jiang CB et al (2017) Experimental study on seepage properties, AE characteristics and energy dissipation of coal under tiered cyclic loading. Eng Geol 221:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.005
Jiang CB, Liu XD, Wang WS, Wei WH, Duan MK (2021) Three-dimensional visualization of the evolution of pores and fractures in reservoir rocks under triaxial stress. Powder Technol 378:585–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.10.013
Jiang CB, Niu BW, Yin GZ, Zhang DM, Yu T, Wang P (2019) CT-based 3D reconstruction of the geometry and propagation of hydraulic fracturing in shale. J Petrol Sci Eng 179:899–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2019.04.103
Ju Y, Huang Y, Su S, Zheng J, Xie H, Chang C, Gao F (2018) Three-dimensional numerical reconstruction method for irregular structures of granular geomaterials . Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 4:327–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-018-0089-3
Kang H, Zhang X, Si L, Wu Y, Gao F (2010) In-situ stress measurements and stress distribution characteristics in underground coal mines in China. Eng Geol 116:333–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.09.015
Li DY, Sun Z, Xie T, Li XB, Ranjith PG (2017) Energy evolution characteristics of hard rock during triaxial failure with different loading and unloading paths. Eng Geol 228:270–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.08.006
Li QM, Liang YP, Zou QL, Li QG (2019) Acoustic emission and energy dissipation characteristics of gas-bearing coal samples under different cyclic loading paths. Nat Resour Res 29:1397–1412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09508-2
Li TT, Pei XJ, Wang DP, Huang RQ, Tang H (2019b) Nonlinear behavior and damage model for fractured rock under cyclic loading based on energy dissipation principle. Eng Fract Mech 206:330–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.12.010
Li ZL, He XQ, Dou LM, Song DZ, Wang GF, Xu XL (2019) Investigating the mechanism and prevention of coal mine dynamic disasters by using dynamic cyclic loading tests. Saf Sci 115:215–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2019.02.011
Liu YB, Yin GZ, Li MH, Zhang DM, Deng BZ, Liu C, Lu J (2019) Anisotropic mechanical properties and the permeability evolution of cubic coal under true triaxial stress paths. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:2505–2521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01748-1
Liu YB et al (2019) Mechanical properties and failure behavior of dry and water-saturated anisotropic coal under true-triaxial loading conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02035-9
Liu YJ, Li XL, Li ZH, Chen P, Yang T (2019c) Experimental study of the surface potential characteristics of coal containing gas under different loading modes (uniaxial, cyclic and graded). Eng Geol 249:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.013
Peng K, Shi SW, Zou QL, Zhang YJ, Tan GW (2020) Gas permeability characteristics and energy evolution laws of gas-bearing coal under multi-level stress paths. Nat Resour Res 29:3137–3158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09636-0
Peng RD, Ju Y, Wang JG, Xie HP, Gao F, Mao LT (2015) Energy dissipation and release during coal failure under conventional triaxial compression . Rock Mech Rock Eng 48:509–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0602-0
Perera MSA, Ranjith PG, Choi SK, Airey D (2012) Investigation of temperature effect on permeability of naturally fractured black coal for carbon dioxide movement: an experimental and numerical study. Fuel 94:596–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.10.026
Ranathunga AS, Perera MSA, Ranjith PG (2016) Influence of CO2 adsorption on the strength and elastic modulus of low rank Australian coal under confining pressure. Int J Coal Geol 167:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2016.08.027
Song Y, Jiang B, Qu MJ (2018) Molecular dynamic simulation of self- and transport diffusion for CO2/CH4/N-2 in Low-rank coal vitrinite. Energy Fuel 32:3085–3096. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03676
Song ZL, Yin GZ, Ranjith PG, Li MH, Huang J, Liu C (2019) Influence of the intermediate principal stress on sandstone failure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:3033–3046. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01756-1
Taheri A, Royle A, Yang Z, Zhao Y (2016) Study on variations of peak strength of a sandstone during cyclic loading. Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 2:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-015-0017-8
Tian WL, Yang SQ, Wang JG, Dong JP (2021) Failure behavior of the thermal treated granite under triaxial cyclic loading–unloading compression . Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 7:19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00218-9
Ulusay R (2015) The ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 2007–2014. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07713-0
Xie HP, Li LY, Ju Y, Peng RD, Yang YM (2011) Energy analysis for damage and catastrophic failure of rocks. Sci China Technol Sci 54:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-011-4639-y
Yang DS, Qi XY, Chen WZ, Wang SG, Yang JP (2018) Anisotropic permeability of coal subjected to cyclic loading and unloading. Int J Geomech 18:04018093. https://doi.org/10.1061/(Asce)Gm.1943-5622.0001229
Yang SQ, Yang J, Xu P (2020) Analysis on pre-peak deformation and energy dissipation characteristics of sandstone under triaxial cyclic loading. Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 6:24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00146-0
Yang YJ, Duan HQ, Xing LY, Deng L (2019) Fatigue characteristics of coal specimens under cyclic uniaxial loading. Geotech Test J 42:331–346. https://doi.org/10.1520/Gtj20170263
Yao YB, Liu DM, Che Y, Tang DZ, Tang SH, Huang WH (2010) Petrophysical characterization of coals by low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Fuel 89:1371–1380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2009.11.005
Zhang QG, Fan XY, Chen P, Ma TS, Zeng FT (2020) Geomechanical behaviors of shale after water absorption considering the combined effect of anisotropy and hydration. Eng Geol 269:105547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105547
Zhang R, Ai T, Li H, Zhang Z, Liu J (2013) 3D reconstruction method and connectivity rules of fracture networks generated under different mining layouts. Int J Min Sci Technol 23:863–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2013.10.013
Zhao HG, Song ZL, Liu C, Yu BC (2021) True triaxial experimental study on mechanical characteristics and energy evolution of sandstone under various loading and unloading rates . Geomech Geophys Geo-Energy Geo-Resour 7:22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00212-7
Zhong CL, Zhang ZY, Ranjith PG, Lu YY, Choi X (2019) The role of pore water plays in coal under uniaxial cyclic loading. Eng Geol 257:105125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.05.002
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52074044, 51674048), Scientific Research Foundation of Key Laboratory of Mining Disaster Prevention and Control (MDPC202012), and Postdoctoral Science Foundation of State Key Laboratory of the Coal Mine Disaster Dynamics and Control (2011DA105287–BH201905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: CJ, MD; Methodology: CJ, WW; Resources: CJ; Formal analysis and investigation: ZL, WW, MD, WG; Writing—original draft preparation: ZL, WW; Writing—review and editing: CJ, WW; Visualization: WW; Validation: ZW, MD; Funding acquisition: CJ, ZW, WW; Supervision: CJ, MD; Project administration: CJ.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, C., Li, Z., Wang, W. et al. Experimental investigation of the mechanical characteristics and energy dissipation of gas-containing coal under incremental tiered cyclic loading. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-energ. Geo-resour. 7, 75 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00274-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00274-1