Abstract
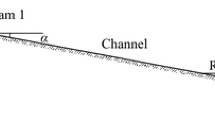
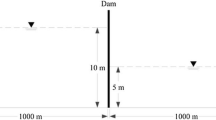
A two-dimensional flow model based on shallow water equations is developed for modeling dam-break flows. The spatial discretization is obtained by the finite volume cell centered type method. The numerical system is solved in explicit way. The flux modeling has been deployed by TVD WAF scheme with a second-order accuracy in both time and space. The local Riemann problem is solved by the HLLC method in the interface of the cells. The numerical model is verified by comparison of model results and analytical solutions. Then the results of numerical model are compared with available experimental data of dam-break waves in a channel with 90° and 180° deviation angle and in a straight channel over a triangular bottom sill. The results confirm the reasonable performance of the present model in predicting dam-break waves.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ata R, Pavan S, Khelladi S, Toro EF (2013) A Weighted Average Flux (WAF) scheme applied to shallow water equations for real-life applications. Adv Water Resour 62:155–172
Aureli F, Maranzoni A, Mignosa P, Ziveri C (2008) A weighted surface-depth gradient method for the numerical integration of the 2D shallow water equations with topography. Adv Water Resour 31(7):962–974
Bell SW, Elliot RC, Hanif Chaudhry M (1992) Experimental results of two-dimensional dam-break flows. J Hydraul Res 30(2):225–252
Benkhaldoun F, Sari S, Seaid M (2015) Projection finite volume method for shallow water flows. Math Comput Simul 118:87–101
Chung TJ (2010) Computational fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press
Einfeldt B, Munz CD, Roe PL, Sjögreen B (1991) On Godunov-type methods near low densities. J Comput Phys 92(2):273–295
Erduran KS, Kutija V, Hewett CJM (2002) Performance of finite volume solutions to the shallow water equations with shock-capturing schemes. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 40(10):1237–1273
Gallardo JM, Schneider KA, Castro MJ (2019) On a class of two-dimensional incomplete Riemann solvers. J Comput Phys 386:541–567
Fraccarollo L, Toro EF (1995) Experimental and numerical assessment of the shallow water model for two-dimensional dam-break type problems. J Hydraul Res 33(6):843–864
Gupta SC (2019) Numerical grid generation and parallel computations. J Aerosp Eng Technol 5(1):11–22
Hosseinzadeh-Tabrizi A, Ghaeini-Hessaroeyeh M (2015) Coupled dam-break flow and bed load modelling using HLLC-WAF scheme. Water Sci Technol 72(7):1155–1167
Kocaman S, Ozmen-Cagatay H (2015) Investigation of dam-break induced shock waves impact on a vertical wall. J Hydrol 525:1–12
Liang Q, Borthwick AGL, Stelling G (2004) Simulation of dam-and dyke-break hydrodynamics on dynamically adaptive quadtree grids. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 46(2):127–162
Liang D, Lin B, Falconer RA (2007) Simulation of rapidly varying flow using an efficient TVD–MacCormack scheme. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 53(5):811–826
Munoz DH, Constantinescu G (2020) 3-D dam break flow simulations in simplified and complex domains. Adv Water Resour 103510
Muscat L, Puigt G, Montagnac M, Brenner P (2019) A coupled implicit-explicit time integration method for compressible unsteady flows. J Comput Phys 398:183
Ozmen-Cagatay H, Kocaman S (2010) Dam-break flows during initial stage using SWE and RANS approaches. J Hydraul Res 48(5):603–611
Ozmen-Cagatay H, Kocaman S, Guzel H (2014) Investigation of dam-break flood waves in a dry channel with a hump. J Hydro Environ Res 8(3):304–315
Pongsanguansin T, Maleewong M, Mekchay K (2015) Consistent weighted average flux of well-balanced TVD-RK discontinuous galerkin method for shallow water flows. Modelling and simulation in Engineering, pp. 591282
Pongsanguansin T, Maleewong M, Mekchay K (2016) Shallow-water simulations by a well-balanced WAF finite volume method: a case study to the great flood in 2011. Thailand Comput Geosci 20(6):1269–1285
Soares-Frazão S (2007) Experiments of dam-break wave over a triangular bottom sill. J Hydraul Res 45(sup1):19–26
Soares Frazao S, Abbeels S, Messens M (2019) Dam-break flow in a channel with a 90° bend and mobile bed: experimental and numerical simulations. In: 38th IAHR world congress
Toro EF (1992) Riemann problems and the WAF method for solving the two-dimensional shallow water equations. Philos Trans Roy Soc Lond Ser A Phys Eng Sci 338(1649):43–68
Toro EF, Spruce M, Speares W (1994) Restoration of the contact surface in the HLL-Riemann solver. Shock Waves 4(1):25–34
Toro EF (2001) Shock-capturing methods for free-surface shallow flows, vol 868. Wiley, New York
Toro EF, Garcia-Navarro P (2007) Godunov-type methods for free-surface shallow flows: a review. J Hydraul Res 45(6):736–751
Toro, E.F., 2013. Riemann solvers and numerical methods for fluid dynamics: a practical introduction. Springer Science & Business Media.
Valiani A, Caleffi V, Zanni A (2002) Case study: Malpasset dam-break simulation using a two-dimensional finite volume method. J Hydraul Eng 128(5):460–472
Xia J, Lin B, Falconer RA, Wang G (2010) Modelling dam-break flows over mobile beds using a 2-D coupled approach. Adv Water Resour 33(2):171–183
Zia A, Banihashemi MA (2008) Simple efficient algorithm (SEA) for shallow flows with shock wave on dry and irregular beds. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 56(11):2021–2043
Zoppou C, Roberts S (2003) Explicit schemes for dam-break simulations. J Hydraul Eng 129(1):11–34
Zhou JG, Causon DM, Ingram DM, Mingham CG (2002) Numerical solutions of the shallow water equations with discontinuous bed topography. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 38(8):769–788
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaeini-Hessaroeyeh, M., Namin, M.M. & Fadaei-Kermani, E. 2-D Dam-Break Flow Modeling Based on Weighted Average Flux Method. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 46, 1515–1525 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00708-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00708-6