Abstract
Higher economic development without urbanization is almost impossible. However, the magnitude of development can vary with the accuracy of the management of an urban area. Though several studies have established a positive effect of urbanization on economic growth, its impacts on the human development index (HDI) are unknown. In this context, we assessed the impacts of urbanization on the value of country-level HDI with a random effect Tobit and dynamic panel data estimations for 187 countries from 1990 to 2017. We found that overall, total urban populations, percentage of the urban populations, urban population growth rates, and percentage of the population living in million-plus agglomerations have a positive effect on the HDI values. The percentage of the urban population residing in the largest city of a country negatively affects the value of HDI. The analysis was also done by dividing countries based on their level of income. The percentage of urbanization is the most important measurement of urbanization having a positive impact on the HDI across countries separated by different income groups. The total urban population also has a positive effect on HDI except for upper-middle-income countries. However, all other measurements of urbanization have an ambiguous effect on HDI, suggesting the impacts of urbanization on HDI depend on different stages of development in a country. Among the control variables, higher emissions of carbon dioxide, fertility rate, GDP growth rate, level of inequality, and inflation rate negatively affect HDI, whereas higher foreign direct investment has a positive effect. Finally, policy options are prescribed to make an urban area more productive in higher economic development.

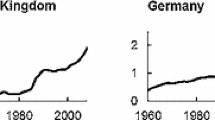
Source: the author’s calculation based on data from the World Bank


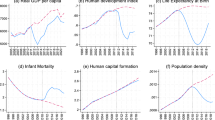
Source: author
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
More details explanation can be seen from Brülhart and Sbergami (2009).
As per-capita GDP, life expectancy at birth, and adult literacy rate are considered to construct HDI, we did not consider these variables in the regression analysis.
References
Ahmed Z, Le HP (2021) Linking information communication technology, trade globalization index, and CO 2 emissions: evidence from advanced panel techniques. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(7):8770–8781
Ahmed Z, Asghar MM, Malik MN, Nawaz K (2020) Moving towards a sustainable environment: the dynamic linkage between natural resources, human capital, urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint in China. Resour Policy 67:101677
Ahmed Z, Zafar MW, Ali S (2020) Linking urbanization, human capital, and the ecological footprint in G7 countries: an empirical analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 55:102064
Ahmed Z, Zhang B, Cary M (2021a) Linking economic globalization, economic growth, financial development, and ecological footprint: evidence from symmetric and asymmetric ARDL. Ecol Indic 121:107060
Ahmed Z, Cary M, Shahbaz M, Vo XV (2021b) Asymmetric nexus between economic policy uncertainty, renewable energy technology budgets, and environmental sustainability: Evidence from the United States. J Clean Prod 313:127723
Anisujjaman M (2015) Urbanisation and human development: a study of West Bengal. Int J Humanit Soc Sci Invent 4(7):2319–7722
Arcelus FJ, Sharma B, Srinivasan G (2005) Foreign capital flows and the efficiency of the HDI dimension. Glob Econ J 5(2):1–12
Arellano M, Bover O (1995) Another look at the instrumental variable estimation of error-components models. J Econom 68(1):29–52
Arisman A (2018) Determinant of human development index in ASEAN countries. Signifikan Jurnal Ilmu Ekonomi 7(1):113–122
Asmita, Fitrawaty, Ruslan D (2017) Analysis of factors affecting the human development index in North Sumatra Province. IOSR J Bus Manag 19(10):27–36. https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jbm/papers/Vol19-issue10/Version-7/D1910072736.pdf
Baldwin RE, Martin P (2004) Agglomeration and Regional Growth. In: Henderson JV, Thisse JF (eds) Handbook of regional and urban economics Vol. 4: cities and geography. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 2671–2711
Bedir S, Yilmaz VM (2016) CO2 emissions and human development in OECD countries: granger causality analysis with a panel data approach. Eurasian Econ Rev 6:97–110
Bergh A, Nilsson T (2010) Good for living? On the relationship between globalization and life expectancy. World Dev 38(9):1191–1203
Bertinelli L, Black D (2004) Urbanization and growth. J Urban Econ 56(1):80–96
Bhowmik D (2019) Nature of human development in SAARC region: a panel data analysis. J Quant Financ Econ 1(2):111–133
Binder M, Georgiadis G (2011) Determinants of human development: capturing the role of institutions, CESIFO working paper no. 3397.
Brülhart M, Sbergami F (2009) Agglomeration and growth: cross-country evidence. J Urban Econ 65(1):48–63
Castells-Quintana D, Wenban-Smith H (2020) Population dynamics, urbanisation without growth, and the rise of megacities. J Dev Stud 56(9):1–20
Connoly A, Leoz CMD, Gorospe M, Sebastian M (2014) Determinants of Having a High Human Development Index, Technical Report, 1–29
Crafts NFR (1997) The Human development index and changes in standards of living: some historical comparisons. Eur Rev Econ Hist 1(2):1–5
Cutler D, Deaton A, Lleras-Muney A (2005) The Determinants of Mortality, NBER working paper no. 11963. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge
Deb S (2015) Gap between GDP and HDI: Are the rich country experiences different from the poor? In Proceedings of the IARIW-OECD Special Conference, Paris, France, 16–17 August
Dunning J (1977) Trade, location of economic activity and the multinational enterprise: a search for an eclectic approach. In: Ohlin B, Hesselborn P, Wijkman P (eds) The international allocation of economic activity. Macmillan, London, pp 395–418
Dunning J (1993) Multinational enterprises and the global economy. Addison-Wesley, Wokingham
Duranton G (2008) Viewpoint: from cities to productivity and growth in developing countries. Can J Econ 41(3):689–736
Duranton G, Puga D (2004) Micro-foundation of urban agglomeration economies. In: Henderson JV, Thisse J-F (eds) Handbook of regional and urban economics, Vol. 4: cities and geography. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 2063–2117
Fadillah N, Setiartiti L (2021) Analysis of factors affecting human development index in special regional of Yogyakarta. J Econo Res Soc Sci 5(1):88–104
Fei J, Ranis G (1964) Development of the labor surplus economy: theory and policy. Irwin, Homewood
Fossaceca A (2019) Assessing the determinants of the human development index in oil-dependent nations. Undergrad Econ Rev 16(1):1–14
Fujita M, Thisse J-F (2002) Economics of agglomeration: cities, industrial location, and regional growth. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gökmenoğlu KK, Apinran MO, Taşpınar N (2018) Impact of foreign direct investment on human development index in Nigeria. Bus Econ Res J 9(1):1–14
Ha NM, Le ND, Trung-Kien P (2019) The impact of urbanization on income inequality: a study in Vietnam. J Risk Financ Manag 12:146
Henderson JV (2003) The urbanization process and economic growth: the so-what question. J Econ Growth 8:47–71
Hofmann A, Wan G (2013) Determinants of Urbanization, ADB Economics Working Paper Series No. #355. Manila, Philippines: Asian Development Bank
Huang G, Jiang Y (2017) Urbanization and socioeconomic development in inner Mongolia in 2000 and 2010: a GIS analysis. Sustainability 9(2):235
Jayasuriya R, Wodon Q (2003) Measuring and Explaining Country Efficiency in Improving Health and Education Indicators. Published in: Efficiency in Reaching the Millennium Development Goals (World Bank Working Paper) No. 9 (June 2003): pp. 5–16.
Kalediene R, Petrauskiene J (2000) Regional life expectancy patterns in Lithuania. Eur J Pub Health 10(2):101–104
Kanbur R, Zhuang J (2013) Urbanization and inequality in Asia. Asian Dev Rev 30(1):131–147
Khan NH, Ju Y, Hassan ST (2018) Modeling the impact of economic growth and terrorism on the human development index: collecting evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:34661–34673
Khan NH, Yanbing J, Hassan ST (2019) Investigating the determinants of human development index in Pakistan: an empirical analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:19294–19304
Khodabakshi A (2011) Relationship between GDP and human development indices in India. Int J Trade Econ Financ 2(3):251–253
Krugman P (1991) Increasing returns and economic geography. J Polit Econ 99(3):483–499
Lewis A (1954) Economic development with unlimited supplies of labor. Manch Sch 22(2):139–191
Li X, Wang C, Zhang G, Xiao L, Dixon J (2012) Urbanisation and human health in china: spatial features and a systemic perspective. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1375–1384
Linn JF (1982) The costs of urbanization in developing countries. Econ Dev Cult Change 30(3):625–648
Maiti M (2017) Urbanisation and inequalities in China and India overview and comparative study. Theor Appl Econ 4(613):121–136
Malik UA (2014) Urbanization and Human Development: A New Look, Briefing paper, Mahbub ul Haq Human Development Centre, Lahore. Web address https://mhrc.lums.edu.pk/sites/default/files/user376/urbanization_and_human_development_0.pdf, Accessed 15 November 2019
Marshall A (1890) Principles of economics. Macmillan, London
Martin P, Ottaviano GIP (1999) Growing localizations: industry localization in a model of endogenous growth. Eur Econ Rev 43:281–302
Muhammad Shahbaz M, Loganathan N, Mujahid N, Ali A, Nawaz A (2016) Determinants of life expectancy and its prospects under the role of economic misery: a case of Pakistan. Soc Indic Res 126:1299–1316
Nguyen HM, Nguyen LD (2018) The relationship between urbanization and economic growth: an empirical study on ASEAN countries. Int J Soc Econ 45(2):316–339
Ranis G, Stewart F, Ramirez A (2000) Economic growth and human development. World Dev 28(2):197–219
Richardson HW (1987) The costs of urbanization: a four-country study. Econ Dev Cult Change 33:561–580
Rumney E, Binnie I (2021) 25 cities are driving urban greenhouse gas emissions worldwide, Reuters - UK Online Report World News . Available from https://www.euronews.com/green/2021/07/12/25-cities-are-driving-urban-greenhouse-gas-emissions-worldwide-says-new-stsudy. Accessed on 25/07/2021
Sangaji J (2016) The determinants of human development index in several Buddhist countries. J Buddh Edu Res 2(1):48–60
Shah S (2016) Determinant of Huan Development Index: A Cross-Country Empirical Analysis, Munich Personal RePEc Archive (MRPA) Paper No. 73759. Retrieved from https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/73759/1/MPRA_paper_73759.pdf
Smith A (1976) An inquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of nations. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Suri T, Boozer MA, Ranis G, Stewart F (2011) Paths to success: the relationship between human development and economic growth. World Dev 39(4):506–522
Tripathi S (2013) Do large agglomerations lead to economic growth? Evidence from urban India. Rev Urban Reg Dev Stud 25(3):176–200
Tudorache MD (2020) Examining the Drivers of Human Development in European Union, In: Proceedings of 35th IBIMA Conference, Seville, Spain, ISBN 978-0-9998551-4-0. IBIMA Publishing. King of Prussia
Turok I (2014) The urbanization-development Nexus in the BRICS. In: Parnell S, Oldfield S (eds) Handbook on cities in the global south. Routledge, London, pp 122–138
UN-Habitat (2016) Urbanization and Structural Transformation. United Nations Human Settlements Programme, Series 2, Nairobi GPO Kenya. Web address http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/content/427863/urbanization-and-structural-transformation/. Accessed 11 November 2019
Viddy A, Rafiqoh RT, Asniwati B (2019) The determinants of human development index and economic growth in Indonesia. Int J Sci Technol Res 8(12):661–665
Wang Z, Ahmed Z, Zhang B, Wang B, Wang B (2019) The nexus between urbanization, road infrastructure, and transport energy demand: empirical evidence from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:34884–34895
Williamson JG (1965) Regional inequality and the process of national development: a description of the patterns. Econ Dev Cult Change 13(4):1–84
World Bank (2009) Systems of Cities: Harnessing Urbanization for Growth and Poverty Alleviation-World Bank Urban and Local Government Strategy. World Bank, Washington, DC
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to the three anonymous referees and to the editor of this journal for their detailed and constructive comments that have significantly improved the quality of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, S. How does urbanization affect the human development index? A cross-country analysis. Asia-Pac J Reg Sci 5, 1053–1080 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-021-00211-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41685-021-00211-w