Abstract
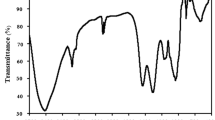
Biomass of the invasive seaweed Sargassum muticum harvested from the Atlantic coast of Morocco was investigated as a natural biosorbent for the removal of methylene blue (MB) dye from aqueous solutions. FTIR spectroscopy was used to examine the variability of functional groups participating in the interaction between MB and biosorbent. The zero point charge (pHZPC) of the biomass was about 5.45. The factors affecting the efficiency of the biosorption process such as the biosorbent dose, the initial solution pH, the initial dye concentration and the contact time were investigated. The theoretical monolayer saturation capacity was estimated to be 191.38 mg/g. The biosorption process was generally not dependent on pH for values ranging from 2 to 10. The biosorption occurs very fast in the first 5 min and reaches the equilibrium within 60–90 min. The pseudo-second-order model was found to explain the adsorption kinetics most effectively. Four conventional isotherm models were applied to describe the biosorption equilibrium data and classified according to their correlation coefficients in the following order: Temkin model (R2 = 0.989) > Dubinin–Radushkevich (R2 = 0.982) > Langmuir (R2 = 0.938) > Freundlich (R2 = 0.934). The Temkin constants (KT = 0.825 L/g, bT = 43.165 J/mol) and the Dubinin–Radushkevich mean free energy (ED= 0.731 kJ/mol) indicated that the adsorption of MB onto the biomass of the invasive seaweed could be a physisorption process. The values of the thermodynamic parameters showed that adsorption is a spontaneous and exothermic process. This study suggests that biomass of the invasive seaweed Sargassum muticum has a good potential capacity to remove MB dye and it could offer promising opportunity, as a low-cost biosorbent for the treatment of cationic dye industrial wastewaters.
Article Highlights
-
Removal potential of methylene blue by biomass of the invasive seaweed Sargassum muticum was evaluated.
-
The theoretical monolayer saturation capacity was estimated to be 191.38 mg/g.
-
The adsorption process was better described by the pseudo-second-order model.
-
Among isotherm models tested, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich described better methylene blue adsorption.
-
Considering their low cost and abundance, the biomass of Sargassum muticum can be used as a promising biosorbent for the decolorization of cationic dyes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Degs YS, El-Barghouthi MI, El-Sheikh AH, Walker GM (2008) Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dyes Pigm 77:16–23
Allen SJ, Koumanova B (2005) Decolourisation of water/wastewater using adsorption. J Univ Chem Technol Metall 40:175–192
Aravindhan R, Rao JR, Nair BU (2007) Kinetic and equilibrium studies on biosorption of basic blue dye by green macro algae Caulerpa scalpelliformis. J Environ Sci Health A 42:621–631
Argun ME, Dursun S, Ozdemir C, Karatas M (2007) Heavy metal adsorption by modified oak sawdust: thermodynamics and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 141:77–85
Arivoli S, Hema M, Parthasarathy S, Manju N (2010) Adsorption dynamics of methylene blue by acid activated carbon. J Chem Pharm Res 2:626–641
Asgari G, Roshani B, Ghanizadeh G (2012) The investigation of kinetic and isotherm of fluoride adsorption onto functionalize pumice stone. J Hazard Mater 217–218:23–132
Attouti S, Bestani B, Benderdouche N, Laurent D (2013) Application of Ulva lactuca and Cystoceira stricta algae-based activated carbons to hazardous cationic dyes removal from industrial effluents. Water Res 47:3375–3388
Banat IM, Nigam P, Singh D, Marchant R (1996) Microbial decolorization of textile-dye-containing effluents: a review. Bioresour Technol 58:217–227
Caparkaya D, Cavas L (2008) Biosorption of Methylene blue by a Brown Alga Cystoseira Barbatula Kützing. Acta Chim Slov 55:547–553
Cardoso NF, Lima EC, Royer B, Bach MV, Dotto GL, Pinto LAA, Calvete T (2012) Comparison of Spirulina platensis microalgae and commercial activated carbon as adsorbents for the removal of reactive Red 120 dye from aqueous effluents. J Hazard Mater 241–242:146–153
Cengiz S, Cavas L (2008) Removal of methylene blue by invasive marine seaweed: caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea. Bioresour Technol 99:2357–2363
Chia CH, Duong TD, Nguyen KL, Zakaria S (2007) Thermodynamics aspects of sorption of Fe2+ onto unbleached kraft fibres. J Colloid Interface Sci 307:29–33
Chowdhury S, Saha PD (2012) Biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions by a Waste biomaterial: hen feathers. Appl Water Sci 2:209–219
Cragan DJ (1999) Teratogen update: methylene blue. Teratology 60:42–48
Dahri MK, Kooh MRR, Lim LBL (2015) Application of Casuarina equisetifolia needle for the removal of methylene blue and malachite green dyes from aqueous solution. Alex Eng J 54:1253–1263
Daneshvar E, Kousha M, Jokar M, Koutahzadeh N, Guibal E (2012) Acidic dye biosorption onto marine brown macroalgae: isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 204–206:225–234
de Oliveira Brito SM, Andrade HMC, Soares LF, de Azevedo RP (2010) Brazil nut shells as a new biosorbent to remove methylene blue and indigo carmine from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 174:84–92
El Atouani S, Bentiss F, Reani A, Zrid R, Belattmania Z, Pereira L, Mortadi A, Cherkaoui O, Sabour B (2016) The invasive brown seaweed Sargassum muticum as new resource for alginate in Morocco: spectroscopic and rheological characterization. Phycol Res 64:185–193
El Sikaily A, Khaled A, El Nemr A, Abdelwahab O (2006) Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solution by marine green alga Ulva lactuca. Chem Ecol 22:149–157
Fiol N, Villaescusa I (2009) Determination of sorbent point zero charge: usefulness in sorption studies. Environ Chem Lett 7:79–84
Freundlich HMF (1906) Uber die adsorption in losungen. J Phys Chem 57:385–470
Fu YZ, Viraraghavan T (2001) Fungal decolorization of dye wastewaters: a review. Bioresour Technol 79:251–262
Fu L, Wang T, Lu H, Su Y, Ren A (2008) Comment on “The removal of phenolic compounds from aqueous solutions by organophilic bentonite”. J Hazard Mater 151:851–854
Ghosh D, Bhattacharyya KG (2002) Adsorption of methylene blue on kaolinite. Appl Clay Sci 20:295–300
Gong R, Li M, Yang C, Sun Y, Chen J (2005) Removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on peanut hull. J Hazard Mater 121:247–250
Gouamid M, Ouahrani MR, Bensaci MB (2013) Adsorption Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using Date Palm Leaves. Energy Procedia 36:898–907
Guechi EK, Hamdaoui O (2016) Biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by potato (Solanum tuberosum) peel: equilibrium modelling, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin Water Treat 57:10270–10285
Guibal E, Roulph C, Le Cloirec P (1995) Infrared spectroscopic study of biomass and materials of biological origin. Environ Sci Technol 29:2496–2503
Hamdaoui O (2006) Batch study of liquid-phase adsorption of methylene blue using cedar sawdust and crushed brick. J Hazard Mater 135:264–273
Hameed BH (2009) Evaluation of papaya seeds as a novel non-conventional low-cost adsorbent for removal of methylene blue. J Hazard Mater 162:939–944
Han RP, Zhang LJ, Song C, Zhang MM, Zhu HM, Zhang LJ (2010) Characterization of modified wheat straw, kinetic and equilibrium study about copper ion and methylene blue adsorption in batch mode. Carbohydr Polym 79:1140–1149
Han X, Wang W, Ma X (2011) Adsorption characteristics of methylene blue onto low cost biomass material lotus leaf. Chem Eng J 171:1–8
Horsfall M, Spiff AI (2005) Equilibrium sorption study of Al(III), Co(II) and Ag(I) in aqueous solutions by Fluted Pumpkin (Telfairia Occidentalis HOOK f) waste Biomass. Acta Chim Slov 52:174–181
Jalali R, Ghafourian H, Asef Y, Davarpanah SJ, Sepehr S (2002) Removal and recovery of lead using nonliving biomass of marine algae. J Hazard Mater 92:253–262
Khattri SD, Singh MK (2000) Colour removal from synthetic dye wastewater using a bioadsorbent. Water Air Soil Pollut 120:283–294
Kousha M, Daneshvar E, Sohrabi MS, Jokar M, Bhatnagar A (2012) Adsorption of acid orange II dye by raw and chemically modified brown macroalga Stoechospermum marginatum. Chem Eng J 192:67–76
Kumar PS, Pavithra J, Suriya S, Ramesh M, Kumar KA (2014) Sargassum wightii, a marine alga is the source for the production of algal oil, bio-oil, and application in the dye wastewater treatment. Desalin Water Treat 55:1–17
Lagergren S (1898) Zurtheorie der sogenannten adsorption gelsterstoffe, Kungliga SvenskaVetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24:1–39
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295
Lodeiro P, Cordero B, Grille Z, Herrero R, Sastre de Vicente ME (2004) Physicochemical studies of cadmium(II) biosorption by the invasive alga in Europe, Sargassum muticum. Biotechnol Bioeng 88:237–247
Marungrueng K, Pavasant P (2007) High performance biosorbent (Caulerpa lentillifera) for basic dye removal. Bioresour Technol 98:1567–1572
Mitrogiannis D, Markou G, Çalekli A, Bozkurt H (2015) Biosorption of methylene blue onto Arthrospira platensis biomass: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Chem Eng 3:670–680
Nady AF, Ola IE, Laila BK (2013). Effectiveness of alkali-acid treatment in enhancement the adsorption capacity for rice straw: the removal of methylene bluedye. ISRN Phys Chem (Article ID 208087)
Nassar MM, Magdy YH (1997) Removal of different basic dyes from aqueous solution by adsorption on palm-fruit bunch particles. Chem Eng J 66:223–226
Ncibi MC, Mahjoub B, Seffen M (2007) Kinetic and equilibrium studies of methylene blue biosorption by Posidonia oceanica (L.) fibres. J Hazard Mater 139:280–285
Ncibi MC, Ben Hamissa AM, Fathallah A, Kortas MH, Baklouti T, Mahjoub B, Seffen M (2009) Biosorptive uptake of methylene blue using Mediterranean green alga Enteromorpha spp. J Hazard Mater 170:1050–1055
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80
Rajeshwari S, Subburam V (2002) Activated parthenium carbon as an adsorbent for the removal of dyes and heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Bioresour Technol 85:205–206
Royer B, Cardoso NF, Lima EC, Vaghetti JC, Simon NM, Calvete T, Veses RC (2009) Applications of Brazilian pine-fruit shell in natural and carbonized forms as adsorbents to removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions—Kinetic and equilibrium study. J Hazard Mater 164:1213–1222
Rubin E, Rodriguez P, Herrero R, Cremades J, Barbara I, Sastre de Vicente ME (2005) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using as biosorbent Sargassum muticum: an invasive macroalga in Europe. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:291–298
Sabour B, Reani A, El Magouri H, Haroun R (2013) Sargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt (Fucales, Phaeophyta) in Morocco, an invasive marine species new to the Atlantic Coast of Africa. Aquat Invasions 8:97–102
Safa Y, Bhatti HN (2011) Kinetic and thermodynamique modeling for the removal of Direct Red-31 and Direct Orange-26 dyes from aqueous solutions by rice husk. Desalination 272:313–322
Sarici-Özdemir Ç, Önal Y (2013) Error analysis studies of dye adsorption onto activated carbon from aqueous solutions. Part Sci Technol 32:20–27
Sarma GK, Sen Gupta S, Bhattacharyya KG (2011) Methylene blue adsorption on natural and modified clays. Sep Sci Technol 46:1602–1614
Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2011) Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism of removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto pine cone biomass of Pinus radiata. Water Air Poll 218:499–515
Shahryari Z, Goharrizi AS, Azadi M (2010) Experimental study of methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solutions onto carbon nano tubes. Int J Water Res Environ Eng 2:016–028
Shih MC (2012) Kinetics of the batch adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions onto rice husk: effect of acid-modified process and dye concentration. Desalin Water Treat 37:200–214
Temkin MI (1941) Adsorption equilibrium and kinetics of processes on non-homogeneous surfaces and the interaction between adsorbed molecules. J Phys Chem 15:296–332
Tichaona N, Viola S, Olindah H, Munyaradzi S (2013) Exploring the biosorption of methylene blue dye onto acid treated sugarcane bagasse. Int J Curr Res 5:2169–2175
Uddin MT, Islam MA, Mahmud S, Rukanuzzaman M (2009) Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by tea waste. J Hazard Mater 164:53–60
Vilar VJP, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2007) Methylene blue adsorption by algal biomass based Materials: biosorbent characterisation and process behaviour. J Hazard Mater 147:120–132
Wang SB, Zhu ZH (2006) Characterization and environmental application an Australian natural zeolite for basic dye removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 136:946–952
Weng CH, Lin YT, Tzeng TW (2009) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto pineapple leaf powder. J Hazard Mater 170:417–424
Xu SM, Wang JL, Wu RL, Wang JD, Li H (2006) Adsorption behaviors of acid and basic dyes on crosslinked amphoteric starch. Chem Eng J 117:161–167
Yu JX, Wang LY, Chi RA, Zhang YF, Xu ZG, Guo J (2013) Removal of cationic dyes: basic magenta and methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption on modified loofah. Res Chem Intermediat 39:3775–3790
Zhang J, Ping Q, Niu M, Shi H, Li N (2013) Kinetics and equilibrium studies from the methylene blue adsorption on diatomite treated with sodium hydroxide. Appl Clay Sci 83–84:1–16
Zhou Q, Gong WQ, Li YB, Chen SH, Yang DJ, Bai CP, Liu XF, Xu N (2011) Biosorption of Methylene Blue onto spent corncob substrate: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Desalin Water Treat 29:317–325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Atouani, S., Belattmania, Z., Reani, A. et al. Brown Seaweed Sargassum muticum as Low-Cost Biosorbent of Methylene Blue. Int J Environ Res 13, 131–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-018-0161-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-018-0161-4