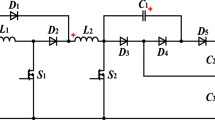
Abstract
High voltage conversion with a continuous input and output current is the prime requirement for electric vehicles and renewable energy applications. In this paper, a new topology based on the Cuk converter is proposed to meet the high step-up gain, reduced switch stress, and continuous input current requirements. The topology is derived from the Cuk converter by using two switches, three inductors, a voltage-lift capacitor, and switched-capacitors. When compared to conventional converters, the proposed converter achieves a high step-up gain with reduced switch stress. Since the topology does not consist of a coupled inductor or transformer structure, voltage spikes during the turnoff process are eliminated. In addition, by simply varying the duty ratio of the two switches, a wide output voltage range is possible. The duty cycle and the switching pulses for the two switches are identical. Hence, the operation and control are simple. To analyze the topology, the continuous conduction mode of operation, voltage, and current stress of the devices, as well as an efficiency analysis are discussed. Finally, a 690 W prototype is implemented to experimentally examine and investigate the proposed converter.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larminie, J., Lowry, J.: Electric Vehicle Technology Explained: Second Edition. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118361146
Lukic, S.M., Cao, J., Bansal, R.C., Rodriguez, F., Emadi, A.: Energy storage systems for automotive applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 55, 2258–2267 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2008.918390
Hart Danial, W.: Commonly Used Power and Converter Equations. McGraw Hill, New York (2010)
Bellur, D.M., Kazimierczuk, M.K.: DC–DC converters for electric vehicle applications. In: 2007 Electr. Insul. Conf. Electr. Manuf. Expo, EEIC 2007, pp 286–293 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/EEIC.2007.4562633
Ellis, M.W., Von Spakovsky, M.R., Nelson, D.J.: Fuel cell systems: efficient, flexible energy conversion for the 21st century. Proc. IEEE. 89, 1808–1817 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1109/5.975914
Richardson, D.B.: Electric vehicles and the electric grid: a review of modeling approaches, impacts, and renewable energy integration. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 19, 247–254 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.11.042
Luthander, R., Shepero, M., Munkhammar, J., Widén, J.: Photovoltaics and opportunistic electric vehicle charging in the power system—a case study on a Swedish distribution grid. IET Renew. Power Gener. 13, 710–716 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-rpg.2018.5082
Amir, A., Amir, A., Che, H.S., Elkhateb, A., Rahim, N.A.: Comparative analysis of high voltage gain DC–DC converter topologies for photovoltaic systems. Renew. Energy. 136, 1147–1163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.09.089
Cardoso, V., Brockveld, S.L., Lazzarin, T.B., Waltrich, G.: Double boost-flyback converter. IET Power Electron. 13, 1163–1171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2019.1073
Park, K.B., Moon, G.W., Youn, M.J.: High step-up boost converter integrated with voltage-doubler. In: 2010 IEEE Energy Convers. Congr. Expo. ECCE 2010—Proc., vol. 25, pp. 810–816 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/ECCE.2010.5617916
Maheswari, L., Sivakumaran, N.: An isolated single-switch high step-up DC/DC converter with three-winding transformer for solar photovoltaic applications. Electr. Eng. 102, 1383–1392 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-020-00959-y
Hu, X., Gao, B., Huang, Y., Chen, H.: Novel single switch DC–DC converter for high step-up conversion ratio. J. Power Electron. 18, 662–671 (2018). https://doi.org/10.6113/JPE.2018.18.3.662
Subramanian, V., Manimaran, S.: Design of parallel-operated SEPIC converters using coupled inductor for load-sharing. J. Power Electron. 15, 327–337 (2015). https://doi.org/10.6113/JPE.2015.15.2.327
Premkumar, M., Kumar, C., Anbarasan, A., Sowmya, R.: A novel non-isolated high step-up DC–DC boost converter using single switch for renewable energy systems. Electr. Eng. 102, 811–829 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-019-00904-8
Ding, X., Zhao, D., Liu, Y., Li, K., Hao, Y.: High step-up three-level DC–DC converter with three-winding coupled-inductor. J. Power Electron. 20, 53–64 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-019-00006-5
Yang, L.S.: Novel dual DC–DC flyback converter with leakage-energy recycling. J. Power Electron. 18, 1007–1014 (2018). https://doi.org/10.6113/JPE.2018.18.4.1007
Raja, R., Jagadeesan, A., Princelynjebakiruba, R., Navabalachandru, C.: An efficient high-step-up interleaved with a common active clamp DC–DC converter for electric vehicle. In: 2013 Int. Conf. Energy Effic. Technol. Sustain. ICEETS 2013, vol. 26, pp. 760–764 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEETS.2013.6533480
Luo, Q., Zhang, Y., Sun, P., Zhou, L.: An active clamp high step-up boost converter with a coupled inductor. J. Power Electron. 15, 86–95 (2014). https://doi.org/10.6113/JPE.2015.15.1.86
Kokkonda, K., Kulkarni, P.S.: A high gain soft-switching active-clamped coupled-inductor-based converter for grid-tied photovoltaic applications. Electr. Eng. 103, 2783–2797 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01250-4
Tseng, K.C., Chen, J.Z., Lin, J.T., Huang, C.C., Yen, T.H.: High step-up interleaved forward-flyback boost converter with three-winding coupled inductors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 30, 4696–4703 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2014.2364292
Leão e Silva Aquino, R.N.A., Tofoli, F.L., Praca, P.P., de Souza Oliveira, D., Barreto, L.H.S.C.: Soft switching high-voltage gain dc-dc interleaved boost converter. IET Power Electron. 8, 120–129 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2014.0275
Joseph, P.K., Devaraj, E.: Design of hybrid forward boost converter for renewable energy powered electric vehicle charging applications. IET Power Electron. 12, 2015–2021 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2019.0151
Tofoli, F.L., de Pereira, D.C., de Paula, W.J., de Oliveira Júnior, D.S.: Survey on non-isolated high-voltage step-up DC–DC topologies based on the boost converter. IET Power Electron. 8, 2044–2057 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2014.0605
Axelrod, B., Berkovich, Y., Ioinovici, A.: Switched-capacitor/switched-inductor structures for getting transformerless hybrid DC–DC PWM converters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 55, 687–696 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSI.2008.916403
Yang, L.S., Liang, T.J., Chen, J.F.: Transformerless DC–DC converters with high step-up voltage gain. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56, 3144–3152 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2009.2022512
Lakshmi, M., Hemamalini, S.: Nonisolated high gain DC–DC converter for DC microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65, 1205–1212 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2733463
Ye, H., Jin, G., Fei, W., Ghadimi, N.: High step-up interleaved DC/DC converter with high efficiency. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1716111
Vafa, M., Ershadi, M.H., Khodadadi, H., Baharizadeh, M.: An interleaved high step-up DC–DC converter with low voltage stress. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40998-020-00366-w
Lopez-Santos, O., Mayo-Maldonado, J.C., Rosas-Caro, J.C., Valdez-Resendiz, J.E., Zambrano-Prada, D.A., Ruiz-Martinez, O.F.: Quadratic boost converter with low-output-voltage ripple. IET Power Electron. 13, 1605–1612 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2019.0472
Valdez-Resendiz, J.E., Rosas-Caro, J.C., Mayo-Maldonado, J.C., Llamas-Terres, A.: Quadratic boost converter based on stackable switching stages. IET Power Electron. 11, 1373–1381 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2017.0278
Marimuthu, M., Vijayalakshmi, S., Shenbagalakshmi, R.: A novel non-isolated single switch multilevel cascaded DC–DC boost converter for multilevel inverter application. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 15, 2157–2166 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-020-00494-7
Lotfi Nejad, M., Poorali, B., Adib, E., Birjandi, A.A.M.: New cascade boost converter with reduced losses. IET Power Electron. 9, 1213–1219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel.2015.0240
de Bento, A.A.M.: Hybrid operational high step-up DC–DC converter. J. Control. Autom. Electr. Syst. 31, 350–359 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40313-019-00548-w
Zhang, N., Zhang, G., See, K.W., Zhang, B.: A single-switch quadratic buck-boost converter with continuous input port current and continuous output port current. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33, 4157–4166 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2017.2717462
Banaei, M.R., Sani, S.G.: Analysis and implementation of a new SEPIC-based single-switch buck-boost DC–DC converter with continuous input current. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 33, 10317–10325 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2018.2799876
Ansari, S.A., Moghani, J.S.: A novel high voltage gain noncoupled inductor SEPIC converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66, 7099–7108 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2018.2878127
Salvador, M.A., Lazzarin, T.B., Coelho, R.F.: High step-up DC–DC converter with active switched-inductor and passive switched-capacitor networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65, 5644–5654 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2782239
Zhu, M., Luo, F.L.: Voltage-lift-type Cûk converters: Topology and analysis. IET Power Electron. 2, 178–191 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-pel:20070023
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sivaraj, G., Karpagavalli, P. Novel double switch voltage-lift Cuk converter. J. Power Electron. 23, 23–34 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-022-00509-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43236-022-00509-8