Abstract
Background
Type 2 diabetes is a major health problem affecting millions of people. Controlled eating and regular physical activity are important for the management of type 2 diabetes. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme (DPP-4) inhibitor sitagliptin is a potent agent for the treatment of type-2 diabetes. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of sitagliptin on the liver of rats with streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, in terms of (i) the expression levels of the cannabinoid 1 receptor (CB-1R) and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R), (ii) alterations in the number and localization of these peptides, and (iii) changes in histological and oxidative damage.
Methods
Thirty-two neonatal (two-day-old) rats, which were divided into four groups, were treated with saline (control), sitagliptin (control; 1.5 mg/kg/day for 15 days starting from day 5 of the experimental period), STZ (diabetes; 100 mg/kg single dose), STZ + sitagliptin (diabetes + sitagliptin). After 20 days, hepatic tissues were obtained from rats.
Results
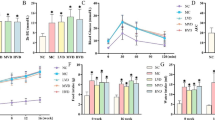
The expressions of GLP-1R and CB-1R mRNA increased approximately 1.89- and 2.94-fold, respectively, in the diabetes + sitagliptin group as compared to the diabetic group. Additionally the number of GLP-1R immunopositive cells decreased and CB-1R immunopositive cells increased in comparison to the diabetic group; however, this was not statistically significant. Glutathione levels increased, but malondialdehyde and protein carbonyl levels decreased in the diabetes + sitagliptin group more than the diabetic group.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that sitagliptin treatment regulates GLP-1R and CB-1R gene expressions, which are associated with appetite regulation in diabetic rat, and may decrease oxidative stress and liver tissue damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verspohl EJ. Novel therapeutics for type 2 diabetes: incretin hormone mimetics (glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther 2009;124(1):113–38.
Ahrén B. Islet G protein-coupled receptors as potential targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009;8(5):369–85.
Szayna M, Doyle ME, Betkey JA, Holloway HW, Spencer RG, Greig NH, et al. Exendin-4 decelerates food intake, weight gain, and fat deposition in Zucker rats. Endocrinology 2000;141(6):1936–41.
Tang-Christensen M, Larsen PJ, Göke R, Fink-Jensen A, Jessop DS, Møller M, et al. Central administration of GLP-1-(7-36) amide inhibits food and water intake in rats. Am J Physiol 1996;271(4 Pt 2):R848–56.
Turton MD, O’Shea D, Gunn I, Beak SA, Edwards CM, Meeran K, et al. A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 1996;379 (6560):69–72.
van Bloemendaal L, Ten Kulve JS, la Fleur SE, Ijzerman RG, Diamant M. Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 on appetite and body weight: focus on the CNS. J Endocrinol 2014;221(1):T1–T16.
Soria-Gómez E, Bellocchio L, Reguero L, Lepousez G, Martin C, Bendahmane M, et al. The endocannabinoid system controls food intake via olfactory processes. Nat Neurosci 2014;17(3):407–15.
Jamshidi N, Taylor DA. Anandamide administration into the ventromedial hypothalamus stimulates appetite in rats. Br J Pharmacol 2001; 134(6): 1151–4.
Schiöth HB. G protein-coupled receptors in regulation of body weight. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2006;5(3):241–9.
Cable JC, Tan GD, Alexander SP, O’Sullivan SE. The effects of obesity, diabetes and metabolic syndrome on the hydrolytic enzymes of the endocannabinoid system in animal and human adipocytes. Lipids Health Dis 2014;13:43.
Vilches-Flores A, Delgado-Buenrostro NL, Navarrete-Vázquez G, Villalobos-Molina R. CB1 cannabinoid receptor expression is regulated by glucose and feeding in rat pancreatic islets. Regul Pept 2010;163(1–3):81–7.
Hayakawa K, Mishima K, Nozako M, Hazekawa M, Aoyama Y, Ogata A, et al. High-cholesterol feding aggravates cerebral infarction via decreasing the CB1 receptor. Neurosci Lett 2007;414(2):183–7.
Quintanilla-García C, Zúñiga-Guajardo S. The incretin effect and type 2 diabetes. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc 2010;48(5):509–20.
Tahrani AA, Piya MK, Barnett AH. Saxagliptin: a new DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adv Ther 2009;26(3):249–62.
Birnbaum Y, Castillo AC, Qian J, Ling S, Ye H, Perez-Polo JR, et al. Phosphodiesterase III inhibition increases cAMP levels and augments the infarct size limiting effect of a DPP-4 inhibitor in mice with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2012;26(6):445–56.
de Ranitz-Greven WL, Beulens JW, Hoeks LB, Belle-van Meerkerk G, Biesma DH, de Valk HW. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus failing on oral agents and starting once daily insulin regimen; a small randomized study investigating effects of adding vildagliptin. BMC Res Notes 2014;7:579.
Lehrke M, Marx N, Patel S, Seck T, Crowe S, Cheng K, et al. Safety and tolerability of linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive pooled analysis of 22 placebo-controlled studies. Clin Ther 2014;36(8): 1130–46.
Itou M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Sata M. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4: a key player in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19(15):2298–306.
Scheen AJ. Safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for treating type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2015; 14(4):505–24.
Arase Y, Kawamura Y, Seko Y, Kobayashi M, Suzuki F, Suzuki Y, et al. Efficacy and safety in sitagliptin therapy for diabetes complicated by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Res 2013;43(11):1163–8.
Karabulut S, Coskun ZM, Bolkent S. Immunohistochemical, apoptotic and biochemical changes by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor-sitagliptin in type-2 diabetic rats. Pharmacol Rep 2015;67(5):846–53.
Desmet VJ, Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, Chen TS, Craig R, Kaplowitz N, et al. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. J Hepatol 2003;38(4)382–6 [Hepatology. 1981. 1, 431-435].
Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001;29(9):e45.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951;193(1):265–75.
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM. Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 1963;61:882–8.
Ledwozyw A, Michalak J, Stepień A, Kadziołka A. The relationship between plasma triglycerides, cholesterol, total lipids and lipid peroxidation products during human atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta 1986;155(3): 275–83.
Reznick AZ, Packer L. Oxidative damage to proteins: spectrophotometric method for carbonyl assay. Methods Enzymol 1994;233:357–63.
Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 1984;105:121–6.
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 1971;44(1):276–87.
Grover JK, Vats V, Yadav S. Effect of feeding aqueous extract of Pterocarpus marsupium on glycogen content of tissues and the key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. Mol Cell Biochem 2002;241(1–2):53–9.
Lee SJ, Zhang GF, Sung NJ. Hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effects of Orostachys japonicus A. Berger extracts in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Nutr Res Pract 2011;5(4):301–7.
Koyuturk M, Sacan O, Karabulut S, Turk N, Bolkent S, Yanardag R, et al. The role of ghrelin on apoptosis, cell proliferation and oxidant-antioxidant system in the liver of neonatal diabetic rats. Cell Biol Int 2015;39(7):834–41.
Turk N, Dagistanli FK, Sacan O, Yanardag R, Bolkent S. Obestatin and insulin in pancreas of newborn diabetic rats treated with exogenous ghrelin. Acta Histochem 2012;114(4):349–57.
Chandran R, Parimelazhagan T, Shanmugam S, Thankarajan S. Antidiabetic activity of Syzygium calophyllifolium in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced type-2 diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 2016;82:547–54.
Smits MM, Tonneijck L, Muskiet MH, Kramer MH, Cahen DL, van Raalte DH. Gastrointestinal actions of glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies: glycaemic control beyond the pancreas. Diabetes Obes Metab 2016; 18(3):224–35.
Holst JJ. The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev 2007;87 (4):1409–39.
Thyssen S, Arany E, Hill DJ. Ontogeny of regeneration of b-cells in the neonatal rat after treatment with streptozotocin. Endocrinology 2006;147(5):2346–56.
Bermúdez-Siva FJ, Serrano A, Diaz-Molina FJ, Sánchez Vera I, Juan-Pico P, Nadal A, et al. Activation of cannabinoid cb1 receptors induces glucose intolerance in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2006;531(1–3):282–4.
Pertwee RG. Pharmacology of cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Pharmacol Ther 1997;74(2): 129–80.
Zhuang S, Kittler J, Grigorenko EV, Kirby MT, Sim LJ, Hampson RE, et al. Effects of long-term exposure to delta9-THC on expression of cannabinoid receptor (CB1) mRNA in different rat brain regions. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 1998;62 (2):141–9.
Duarte JMN, Nogueira C, Mackie K, Oliveira CR, Cunha RA, Köfalvi A. Increase of cannabinoid CB1 receptor density in the hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Neurol 2007;204(1):479–84.
Zhang F, Challapalli SC, Smith PJ. Cannabinoid CB(1) receptor activation stimulates neurite outgrowth and inhibits capsaicin-induced Ca(2+) influx in an in vitro model of diabetic neuropathy. Neuropharmacology 2009;57(2):88–96.
Radziszewska E, Bojanowska E. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor stimulation and blockade on food consumption and body weight in rats treated with a cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2. Med Sci Monit Basic Res 2013;19:6–11.
Alhadeff AL, Rupprecht LE, Hayes MR. GLP-1 neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract project directly to the ventral tegmental area and nucleus accumbens to control for food intake. Endocrinology 2012;153(2):647–58.
González-Mariscal I, Krzysik-Walker SM, Kim W, Rouse M, Egan JM. Blockade of cannabinoid 1 receptor improves GLP-1R mediated insulin secretion in mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2016;423:1–10.
Silvestri C, Di Marzo V. The endocannabinoid system in energy homeostasis and the etiopathology of metabolic disorders. Cell Metab 2013;17(4):475–90.
Kopáni M, Celec P, Danisovic L, Michalka P, Biró C. Oxidative stress and electron spin resonance. Clin Chim Acta 2006;364(1–2):61–6.
Li YG, Ji DF, Lin TB, Zhong S, Hu GY, Chen S. Protective effect of sericin peptide against alcohol-induced gastric injury in mice. Chin Med J (Engl) 2008;121 (20):2083–7.
Nicotera P, Orrenius S. Role of thiols in protection against biological reactive intermediates. Adv Exp Med Biol 1986;197:41–51.
Tsikas D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem 2016;S0003-2697(16):30357–8.
Ávila Dde L, Araújo GR, Silva M, Miranda PH, Diniz MF, Pedrosa ML, et al. Vildagliptin ameliorates oxidative stress and pancreatic beta cell destruction in type 1 diabetic rats. Arch Med Res 2013;44(3):194–202.
Dalle-Donne I, Rossi R, Giustarini D, Milzani A, Colombo R. Protein carbonyl groups as biomarkers of oxidative stress. Clin Chim Acta 2003;329(1–2):23–38.
Sathiyapriya V, Selvaraj N, Bobby Z, Agrawal A. Perturbation of erythrocyte antioxidant barrier, lipid peroxidation and protein carbonylation in non-diabetic first degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007;78(2):171–5.
Shinde SN, Dhadke VN, Suryakar AN. Evaluation of oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus and follow-up along with vitamin E supplementation. Indian J Clin Biochem 2011;26(1):74–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coskun, Z.M., Koyuturk, M., Karabulut, S. et al. CB-1R and GLP-1R gene expressions and oxidative stress in the liver of diabetic rats treated with sitagliptin. Pharmacol. Rep 69, 822–829 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.03.013
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.03.013