Abstract
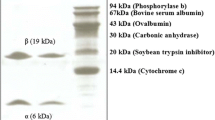
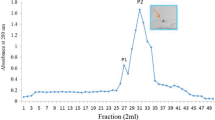
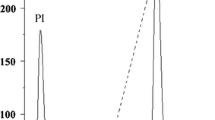
A homodimeric lectin adsorbed on Affi-gel blue gel and CM-Sepharose and possessing a molecular weight of 67 kDa was isolated from red kidney beans. The hemagglutinating activity of this lectin was inhibited by glycoproteins but not by simple sugars. The lectin manifested inhibitory activity on human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase and α-glucosidase. The N-terminal sequence of the lectin exhibited some differences from previously reported lectins from Phaseolus vulgaris but showed some similarity to chitinases. It exerted a suppressive effect on growth of the fungal species Fusarium oxysporum, Coprinus comatus, and Rhizoctonia solani. The lectin had low ribonuclease and negligible translation-inhibitory activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Balzarini, J., Neytes, J., Schols, D., Hosoya, M., Van Damme, E., Peumans, W., and de Clercq, E. (1992). Antiviral Res. 18, 191–207.
Benhamou, N., Broglie, K., Broglie, R., and Chet, I. (1993). Can.J. Microbiol. 39, 318–328.
Broekaert, W. F., Van Parijs, J., Leyns, F., Joos, H., and Peumans, W. (1989). Science 245, 1100–1102.
Collins, R. A., Ng, T. B., Fong, W. P., Wan, C. C., and Yeung, H. W. (1997a). Life Sci. 61, 933–949.
Collins, R. A., Ng, T. B., Fong, W. P., Wan, C. C., and Yeung, H. W. (1997b). Biochem.Mol.Biol.Int. 42, 1163–1169.
Del Campillo, E. and Lewis, L. N. (1992). Plant Physiol. 98, 955–961.
Dong, T. X., Ng, T. B., Wong, R. N. S., Yeung, H. W., and Xu, G. J. (1993). Int.J.Biochem. 25, 415–419.
Eden, L., Heslinga, L., Klok, R., Ledeboer, A. M., Maat, J., Tooene, M. Y., Visser, C., and Verrips, C. (1982). Gene 18, 1–2.
Endo, Y. and Tsurugi, K. (1987). J.Biol.Chem. 262, 8128–8130.
Fabre, C., Causse, H., Mourey, L., Konin, K. J., Riviere, M., Hendriks, H., Puzo, G., Samama, J. P., and Rouge, P. (1998). Biochem.J. 329, 551–560.
Goossens, A., Geremia, R., Bauw, G., Van Montagu, M., and Angenon, G. (1994). Eur.J.Biochem. 225, 787–795.
Gozia, R., Ciopraga, O., Bentia, J., Lungu, T., Zamfirescu, M., Tudor, I., Roseanu, R., and Nitu, F. (1995). FEBS Lett. 370, 245–249.
Graham, J. S., Burkhart, W., Xiong, J., and Gillikin, J. W. (1992) Plant Physiol. 98, 163–165.
Hanselle, T. (1998). Thesis, Institute for Biochemistry and Biotechnology of Plants, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Germany.
Kamemura, K., Furuichi, Y., Umekawa, H., and Takahashi, H. C. (1993). Biochim.Biophys.Acta 1158, 181–188.
Laemmli, U. K. and Favre, M. (1973). J.Mol.Biol. 80, 575–599.
Lam, Y. H., Wong, Y. S., Wang, B., Wong, R. N. S., Yeung, H. W., and Shaw, P. C. (1986). Plant Science 114, 111–117.
Leah, R., Tommerup, H., Svendsen, I., and Mundy, J. (1991). J.Biol. Chem. 246, 1564–1573.
Le Berre-Anton, V., Bompard-Gilles, C., Payan, F., and Rouge, P. (1997). Biochim.Biophys.Acta 1343, 31–40.
Matsumoto, I. and Osawa, T. (1972). Biochem.Biophys.Res.Commun. 46, 1810–1815.
McGrath, M. S., Hwang, K. M., Caldwell, S. E., Gaston, I., Luk, K. C., Wu, P., Ng, V. L., Crowe, S., Daniels, J., Marsh, J., Deinhart, T., Cekas, P. V., Uemari, J. C., Yeung, H. W., and Lifson, J. F. (1989). Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA 86, 2844–2848.
Mock, J. W. Y., Ng, T. B., Wong, R. N. S., Yao, Q. Z., Yeung, H. W., and Fong, W. P. (1996). Life Sci. 59, 1855–1859.
Nakaguchi, T., Arakawa, T., Philo, J. S., Wen, J., Ishimoto, M., and Yamaguchi, H. (1997). J.Biochem. 121, 350–354.
Ng, T. B., Chan, W. Y., and Yeung, H. W. (1992). Gen.Pharmacol. 23, 575–590.
Pelham, R. B. and Jackson, R. J. (1976). Eur.J.Biochem. 67, 247–256.
Sela, B. A., Lis, H., Shason, N., and Sachs, L. (1973). Biochim.Biophys. Acta 310, 273–277.
She, Q. B., Ng, T. B., and Liu, W. K. (1998). Biochem.Biophys.Res. Commun. 247, 106–111.
Tsao, S. W., Ng, T. B., and Yeung, H. W. (1990). Toxicon 28, 1183–1192.
Verheyden, R., Pletinckx, P., Maes, J., Pepermans, D., Wyns, H. A. M., Willem, L., and Martins, J. C. (1993). C.R.Acad.Sci.Ser.III 316, 788–792.
Vogelsang, R. and Barz, W. (1993). Planta 189, 60–69.
Wang, H. X., Ng, T. B., Liu, W. K., Ooi, V. E. C., and Chang, S. T. (1995). Int.J.Peptide Protein Res. 46, 508–513.
Ye, X. Y., Wang, H. X., and Ng, T. B. (1999). Biochem.Biophys.Res. Commun. 263, 130–134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, X.Y., Ng, T.B., Tsang, P.W.K. et al. Isolation of a Homodimeric Lectin with Antifungal and Antiviral Activities from Red Kidney Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) Seeds. J Protein Chem 20, 367–375 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012276619686
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012276619686