Abstract
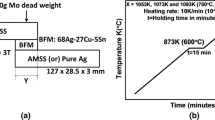
Both Ti-6Al-4V and 304 stainless steels (304SS) are good engineering alloys and widely used in industry due to their excellent mechanical properties as well as corrosion resistance. Well-developed joining process can not only promote the application of these alloys, but also can provide designers versatile choices of alloys. Brazing is one of the most popular methods in joining dissimilar alloys. In this study, three-selected silver base filler alloys, including Braze 580, BAg-8 and Ticusil®, are used in vacuum brazing of 304SS and Ti-6Al-4V. Based upon dynamic sessile drop test, Braze 580 has the lowest brazing temperature of 840°C, in contrast to 870°C for BAg-8 and 900°C for Ticusil® braze alloy. No phase separation is observed for all brazes on 304SS substrate. However, phase separation is observed for all specimens brazed above 860°C on Ti-6Al-4V substrate. The continuous reaction layer between Braze 580 and 304SS is mainly comprised of Ti, Fe and Cu. The thickness of reaction layer at Braze 580/Ti-6Al-4V interface is much larger than that at Braze 580/304SS interface. Meanwhile, a continuous Cu-Sn-Ti ternary intermetallic compound is found at the Braze 580/Ti-6Al-4V interface. Both Ticusil® and BAg-8 brazed joint have similar interfacial microstructures. Different from the Braze 580 specimen, there is a thick Cu-Ti-Fe reaction layer in both BAg-8/304SS and Ticusil®/304SS interfaces. The formation of Cu-Ti-Fe interfacial layer can prohibit wetting of BAg-8 and Ticusil® molten brazes on 304SS substrate. Meanwhile, continuous Ti2Cu and TiCu layers are observed in Ti-6Al-4V/BAg-8 and Ti-6Al-4V/Ticusil® interfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. M. SCHWARTZ, in “Ceramic Joining” (ASM International, Ohio, 1990).
G. HUMPSTON and D. M. JACOBSON, in “Principles of Soldering and Brazing” (ASM International, Ohio, 1993) p. 164.
R. ROGER, E. W. COLLINGS and G. WELSCH, in“Material Properties Handbook: Titanium” (ASM International, Ohio, 1993).
W. F. SMITH, in “Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys,” 2nd ed. (McGraw Hill Inc., New York, 1993).
J. R. DAVIS et al., in “ASM Handbook, Vol. 2: Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special Purpose Materials” (ASM International, Ohio, 1990).
M. M. SCHWARTZ, in “Brazing” (ASM International, Ohio, 1987).
D. L. OLSON et al., in “ASM Handbook, Vol. 6: Welding, Brazing and Soldering” (ASM International, Ohio, 1993).
N. A. DECECCO and J. N. PARKS, Welding J. 32 (1953) 1071.
N. A. TINER,ibid. 34 (1955) 846.
W. T. KAARLELA and W. S. MARGOLIS, ibid. 53 (1974) 629.
T. WANTANABE, Y. HIGO, T. MIKI and A. YANAGISAWA, Quarterly J. the Japan Welding Society 12 (1994) 502.
W. F. SMITH, in “Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys” (McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, 1993) p. 288.
D. A. PORTER and K. E. EASTERLING, in “Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys” (Chapman & Hall Inc., New York, 1992).
O. OKADA, K. NAKATA and S. KASAHARA, J. Nuclear Materials 265 (1999) 232.
I. AMATO, P. G. CAPPELLI and G. FENOGLIO, Welding Research International 7 (1977) 434.
M. SCHWARTZ, in “Brazing: For the Engineering Technologist” (Chapman & Hall, New York, 1995) p. 8.
R. E. LEE, in “Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis” (Prentice Hall, New York, 1993) p. 130.
T. B. MASSALSKI, in “Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams” (ASM International, Ohio, 1990) p. 1494.
C. C. LIN, R. B. CHEN and R. K. SHIUE, J. Mater. Sci. 36 (2001) 2145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C.C., Ou, C.L. & Shiue, R.K. The microstructural observation and wettability study of brazing Ti-6Al-4V and 304 stainless steel using three braze alloys. Journal of Materials Science 37, 2225–2235 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015356930476
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015356930476