Abstract
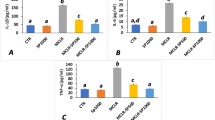
Microcystin-LR, a cyclic heptapeptide synthesized by the blue-green algae, Microcystis aeruginosa, is a potent hepatotoxin. Pathological examination of livers from mice and rats that received microcystin-LR revealed severe, peracute, diffuse, centrilobular hepatocellular necrosis, and hemorrhage. These changes were correlated with increased serum activities of sorbitol dehydrogenase, alanine aminotransferase, and lactate dehydrogenase. Pretreatment of either rats or mice with a single dose of silymarin, a flavonolignane isolated from the wild artichoke (Silybum marianum L. Gaertn), completely abolished the lethal effects, pathological changes, and significantly decreased the levels of serum enzymes induced by microcystin-LR intoxication.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. P. Botes, A. A. Tuinman, P. L. Wessels, C. C. Viljoen, H. Kruger, D. H. Williams, S. Santikarn, R. J. Smith, and S. J. Hammond. The structure of cyanoginosin-LA, a cyclic heptapeptide toxin from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1:2311–2318 (1984).
M. T. Runnegar and I. R. Falconer. Effect of toxin from the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa on ultrastructural morphology and actin polymerization in isolated hepatocytes. Toxicon 24:109–115 (1986).
D. N. Slatkin, R. D. Stoner, W. H. Adams, J. H. Kycia, and H. W. Siegelman. Atypical pulmonary thrombosis caused by a toxic peptide. Science 220:1383–1385 (1983).
G. A. Miura, N. A. Robinson, T. W. Geisbert, K. A. Bostian, J. D. White, and J. G. Pace. Comparison of in vivo and in vitro toxic effects of microcystin-LR in fasted rats. Toxicon 27:1229–1240 (1989).
W. H. Adams, R. D. Stoner, D. G. Adams, D. N. Slatkin, and H. W. Siegelman. Pathophysiologic effects of a toxic peptide from Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxicon 23:441–447 (1985).
A. Pelter and R. Hansel. The structure of silybin (silybim substance E6, the first flavonolignan. Tetrahedron Lett. 25:2911–2916 (1968).
G. Hahn, H. D. Lehmann, M. Kurten, H. Uebel, and G. Vogel. Pharmacology and toxicology of silymarin, the anti-hepatotoxic mechanism of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. Arzneim Forsch. 23:698–704 (1973).
K. A. Mereish and R. Solow. Effect of antihepatotoxic agents against microcystin-LR toxicity in cultured rat hepatocytes. Pharm. Res. 7:256–259 (1990).
G. W. Parker and D. G. Martin. Technique for cardiovascular monitoring in awake tethered rats. Lab. Anim. Sci. 39:463–467 (1989).
A. Valenzuela, C. Lagos, K. Schmidt, and L. A. Videla. Silymarin protection against hepatic lipid peroxidation induced by acute ethanol intoxication in the rat. Biochem. Pharmacol. 34:2209–2212 (1985).
J. Baumann, F. von Bruchhausen, and G. Wurm. Flavonoids and related compounds as inhibitors of arachidonic acid peroxidation. Prostaglandins 20:627–639 (1980).
A. Valenzuela and R. Guerra. Differential effect of silybin on the Fe+2-ADP and t-butylhydroperoxide-induced microsomal lipid peroxidation. Experientia 42:139–141 (1986).
A. Valenzuela, R. Guerra, and L. A. Videla. Antioxidant properties of the flavonoids silybin and (+)-cyanodanol-3: comparison with butylated hydroxyanisole and butylated hydroxytoluene. Planta Med. 6:438–440 (1986).
J. Sonnenbichler and I. Zetl. Biochemical effects of the flavonolignane silibinin on RNA, protein and DNA synthesis in rat livers. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 213:319–331 (1986).
I. R. Falconer and M. T. Runnegar. Effect of the peptide toxin from Microcystis aeruginosa on intracellular calcium, pH and membrane integrity in mammalian cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 63:215–225 (1987).
M. T. Runnegar, J. Andrews, R. G. Gerdes, and I. R. Falconer. Injury to hepatocytes induced by a peptide toxin from the cyanobactrium Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxicon 25:1235–1239 (1987).
S. M. Naseem, H. B. Hines, D. A. Creasia, and K. A. Mereish. Comparative effect of toxins on arachidonic acid release and metabolism in cultured rat hepatocytes and alveolar macrophages. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. J. 2:A1353 (1988).
W. H. Adams, J. P. Stone, B. Sylvester, R. D. Stoner, D. N. Slatkin, N. R. Tempel, and H. W. Siegelman. Pathophysiology of cyanoginosin-LR: In vivo and in vitro studies. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 96:248–257 (1988).
M. T. Runnegar, I. R. Falconer, and J. Silver. Deformation of isolated rat hepatocytes by a peptide hepatotoxin from the blue-green alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 317:268–272 (1981).
S. B. Hooser, V. R. Beasley, R. A. Lovell, W. W. Carmichael, and W. M. Haschek. Toxicity of microcystin-LR, a cyclic heptapeptide hepatotoxin from Microcystis aeruginosa to rats and mice. Vet. Pathol. 26:246–252 (1989).
F. Mirabelli, A. Salis, V. Marinoni, G. Finardi, G. Bellomo, H. Thor, and S. Orrenius. Menadione-induced bleb formation in hepatocytes is associated with the oxidation of thiol groups in actin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 264:261–269 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mereish, K.A., Bunner, D.L., Ragland, D.R. et al. Protection Against Microcystin-LR-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Silymarin: Biochemistry, Histopathology, and Lethality. Pharm Res 8, 273–277 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015868809990
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015868809990