Abstract
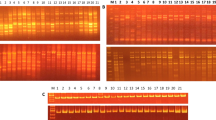
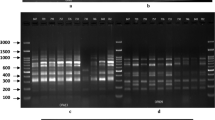
Greengram [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek], also known as mung bean, widely cultivated in a large number of countries, is an important pulse crop of Asia and is considered one of the ancestral species of the genus Vigna. Since yields of greengram have remained low across subtropical and tropical Asia, it is important to estimate genetic diversity in existing cultivars in order to see if the lack of genetic variability might be a constraining factor. In this study, 32 Indian cultivars of greengram were subjected to random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis using 21 decamer primers. A total of 267 amplification products were formed at an average of 12.71 per primer with an overall polymorphism of 64%. The extent of polymorphism was moderate to low. Jaccard similarity coefficient values ranged from 0.65 to 0.92. The cluster analysis resulted in mainly three clusters revealing greater homology between cultivars released from the same source. The results of principal components analysis also substantiated this conclusion. The close genetic similarity between the cultivars could be explained due to the high degree of commonness in their pedigrees. The narrow genetic base of the greengram cultivars revealed in the present analysis emphasises the need to exploit the large germplasm collections having diverse morphoagronomic traits in cultivar improvement programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, F., 1999. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA analysis reveals genetic relationships among annual Cicer species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98: 657–663.
Asemota, H.N., J. Ramser, C. Lopez-Perolta, K. Weising & G. Kohl, 1996. Genetic variation and cultivar identification of Jamaican yam germplasm by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. Euphytica 92: 341–351.
Asthana, A.N. & S.K. Chaturvedi, 1999. A little impetus needed, pp. 61–66 in The Hindu-Survey of Indian Agriculture 1999, edited by N. Ravi. Chennai, India.
Bhat, K.V., S. Chadha & S. Lakhanpaul, 1999. Study of genetic diversity in Indian and exotic seasme (Sesamum indicum L.) germplasm using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Euphytica 110: 21–33.
Bhat, K.V. & R.L Jarret, 1995. Random amplified polymorphic DNA and genetic diversity in Indian Musa germplasm. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 42: 107–118.
Bisht, I.S., R.K. Mahajan & T.G Kawalkar, 1998. Diversity in greengram (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) germplasm collection and its potential use in crop improvement. Ann. Appl. Biol. 132: 301–312.
Bisht, I.S., R.K. Mahajan & D.P Patel, 1998. The use of characterization data establish the Indian mung bean core collection and assessment of genetic diversity. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 45: 127–133.
Brunk, C.F., K.C. Jones & T.W. James, 1979. Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal. Biochem. 92: 497–500.
Cao, W., P. Huel, G. Scoles & R.N. Chibbar, 1998. Genetic diversity between spelta and macha wheats based on RAPD analysis. Euphytica 104: 181–189.
de Condolle A., 1886. Origin of Cultivated Plants. Hafner Publishing, New York.
Dana, S., 1966. The cross between Phaseolus aureus Roxb. and P. mungo L. Genetica 37: 259–274.
Davila, J.A., Y. Loarce & E. Ferrer, 1999. Molecular characterization and genetic mapping of random amplified microsatellite polymorphism in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98: 265–273.
Demeke, T., R.P. Adams & R.N. Chibbar, 1992. Potential use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD): A case study with Brassica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 990–994.
Fahima, T., G.L Sun, A. Behrav, T. Kuigma, A. Beiles & E. Nevo, 1999. RAPD polymorphism of wild emmer wheat populations. Triticum dicoccoides in Israel. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98: 434–447.
Horejsi, T. & J.E. Staub, 1999. Genetic variation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) as assessed by RAPD. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 46: 337–350.
Hu, J. & C.F. Quiros, 1991. Identification of broccoli and cauliflower cultivars with RAPD markers. Plant cell Rep. 10: 505–511.
Isabel, N., J. Beaulieu & J. Bousquet, 1995. Complete congruence between gene diversity estimates derived from genotypic data at enzyme and random amplified polymorphic DNA loci in black spruce. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 6369–6373.
Jaccard, P., 1908. Nouvelles recherché sur la distribution florale. Bull. Soc. Vaud. Sci. Natl. 44: 223–270.
Jain, H.K., 1994. Pulses–The wonder plants of world agriculture, pp. 1–4 in Twenty Five Years of Pulses Research in India, edited by M. Ali, A.N. Asthana and S.L. Mehta. Indian Institute of Pulses Research, Kanpur, India.
Jain, H.K. & K.L. Mehra, 1978. Evolution, adaptation, relationships and uses of the species Vigna cultivated in India, pp. 459–468 in Advances in Legume Sciences, edited by R.J. Summerfield and A.H. Bunting. Proceedings of International Legume Conference, Royal Botanic Garden, Kew.
Joshi, C.P. & H.T. Nguyen, 1993. Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers analyses based on intervarietal genetic relationships among hexaploid wheats. Plant Sci. 93: 95–103.
Koller, B., B. Lehman, J.M. McDermott & C. Cessler, 1993. Identification of apple cultivars using RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 85: 901–904.
Manivannan, N., E. Murugan, P.L. Viswanathan & C.V Dhankodi, 1998. Genetic divergence in greengram. Legume Res. 21: 131–133.
Saghai-Maroof, M.A., K.M. Soliman, R.A. Jorgenson & A.W. Allard, 1984. Ribosomal spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 8014–8018.
Sambrook, J., E.F. Fritsch & T. Maniatis, 1989. Molecular Cloning–A Laboratory Manual. 2nd edn., Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA.
Skrotch, P. & J. Nienhuis, 1995. Qualitative and quantitative characterization of RAPD variation among snap bean (Phaseolus lanatus L.) genotypes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 91: 1086–1091.
Steiner, J.J., E. Piccioni, M. Falcinelli & A. Liston, 1998. Germplasm diversity among cultivars and the NPGS Crimson Clover collection. Crop Sci. 38: 263–271.
Tickoo, J.L. & H.K. Jain, 1988. Mung bean, pp. 161–188 in Pulse Crops, edited by B. Baldev, S. Ramanujan and H.K. Jain. Oxford & IBH Publishing, New Delhi.
Tivang, J., P.W. Skrotch, J. Nienhuis & N. De Vos, 1996. RAPD variation among and within Artichoke (Cynara scolymos L.) cultivars and breeding populations. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 121:783–788.
Vavilov, N.I., 1926. The Origin, Variation, Immunity and Breeding of Cultivated Plants (Translated by K. Starr, Chester), Chronica Botanica 13. Waltham, Mass, USA.
Vierling, R.A. & H.T. Nguyen, 1992. Use of RAPD markers to determine the genetic diversity of diploid wheat genotype. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 835–838.
Yang, W., A.C. Oliviera, I. Godwin, K. Schertz & J.L. Bennetzen, 1996. Comparison of DNA marker technologies in characterizing plant genome diversity: Variability in Chinese sorghums. Crop Sci. 36: 1669–1676.
Zhang, L.H., P. Ozias-Akins, G. Kochert, S. Kresovich, R. Dean & W. Hanna, 1999. Differentiation of bermudagrass (Cyanodon spp.) genotypes by AFLP analyses. Theor. Appl. Genet. 98: 895–902.
Zukovskij, P.M., 1962. Cultivated Plants and their Wild Relatives. Commonwealth Agriculture Bureau, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakhanpaul, S., Chadha, S. & Bhat, K. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis in Indian mung bean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) cultivars. Genetica 109, 227–234 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017511918528
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017511918528