Abstract
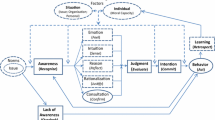
This study attempts to extend the literature in ethics research by developing and testing a model of an individual's ethical system which identifies the sources of influence on the decision process. The model is developed from an interdisciplinary literature review and includes six subsystems or spheres that exert influence on an individual: the workplace, family, religion, legal system, community, and profession. The study also examines the role of materiality in the decision-making process.
Using this model, empirical tests identify the spheres that exert the most influence on the decision-maker facing an ethical dilemma. In addition, the relative importance of the spheres and the interaction among the spheres is examined. Findings show that: (1) individuals rate variables at different levels of importance as the materiality of the breach changes and (2) the spheres that are considered most important for minor ethical breaches are different than the spheres considered most influential in a major ethical situation.
Exploratory factor analysis suggests that the variables representing the spheres can be summarized by three factors. Further, it indicates that these factors change with materiality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackoff, R. L.: 1962, Scientific Method(John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York).
Andolsen, B. H.: 1997, ‘Roman Catholic Tradition and Ritual and Business Ethics: A Feminist Perspective’, Business Ethics Quarterly 7(March), 71-82.
Armstrong, M. B.: 1987, ‘Moral Development and Accounting Education’, Journal of Accounting Education 5, 27-43.
Backoff, J. F. and C. L. Martin Jr.: 1991, ‘Historical Perspectives: Development of the Codes of Ethics in the Legal, Medical, and Accounting Professions’, Journal of Business Ethics 10(2), 99-110.
Ball, G. A., L. K. Trevino and H. P. Sims Jr.: 1994, ‘Just and Unjust Punishment: Influences on Subordinate Performance and Citizenship’, Academy of Management Journal 37(2), 299-316.
Bart, V., L. K. Trevino and D. L. Shapiro: 1993, ‘Peer Reporting of Unethical Behavior: The Influence of Justice Evaluations and Social Context Factors’, Journal of Business Ethics 12(4), 253-263.
Bommer, M., C. Gratta, J. Gravendir and M. Tuttle: 1987, ‘A Behavioral Model of Ethical and Unethical Decision Making,' Journal of Business Ethics 6(4), 265-280.
Brady, F. N.: 1988, ‘Practical Formalism: A New Methodological Proposal for Business Ethics’, Journal of Business Ethics 7(3), 163-170.
Cohen, J. R., L. W. Pant and D. J. Sharp: 1998, ‘The Effect of Gender and Academic Discipline Diversity on the Ethical Evaluations, Ethical Intentions and Ethical Orientation of Potential Public Accounting Recruits’, Accounting Horizons 12(3), 250-270.
Donaldson, T. and L. E. Preston: 1995, ‘The Stakeholder Theory of the Corporation: Concepts, Evidence, and Implications’, Academy of Management Review 20, 65-91.
Dubinsky, A. J. and B. Loken: 1989, ‘Analyzing Ethical Decision Making in Marketing’, Journal of Business Research 19(2), 83-107.
Fama, E.: 1980, ‘Agency Problems and the Theory of the Firm’, Journal of Political Economy 88(2), 288.
Ferrell, O. C. and L. G. Gresham: 1985, ‘A Contingency Framework for Understanding Ethical Decision Making in Marketing’, Journal of Marketing 49(3), 87-89.
Fox, R. L. and R. A. Schuhmann: 1999, ‘Gender and Local Government: A Comparison of Women and Men City Managers’, Public Administration Review 59(3), 231.
Gharajedaghi, J.: 1985, Toward a Systems Theory of Organization. The Systems Inquiry Series (Intersystems Publications, Seaside, CA).
Gilligan, C.: 1982, In a Different Voice(Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA).
Hair, J. F., R. E. Anderson, R. L. Tatham and W. C. Black: 1998, Multivariate Data Analysis, 5th Edition (Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ).
Horvath, C. M.: 1995, ‘Excellence v Effectiveness: Mac Intyre's Critique of Business’, Business Ethics Quarterly 5(3), 499-532.
Hopwood, A.: 1976, Accounting and Human Behavior(Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ).
Hunt, S. D. and S. Vitell: 1986, ‘A General Theory of Marketing Ethics’, Journal of Macromarketing 6(1), 5-16.
Jensen, M. and W. Meckling: 1976, ‘The Theory of the Firm: Managerial Behavior, Agency Costs, and Ownership Structure’, Journal of Financial Economics.
Jones, T. M.: 1991, ‘Ethical Decision-Making by Individuals in Organizations: An Issue Contingent Model’, Academy of Management Review 16(2), 366-395.
Jones, S. J. and K. M. Hiltebeitel: 1995, ‘Organizational Influence in a Model of the Moral Decision Process of Accountants’, Journal of Business Ethics 14(6), 417-431.
Kohlberg, L.: 1971, Indoctrination Versus Relativity in Value Education. In Zygon 6 (Zygon and the University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL).
Kohlberg, l.: 1976, ‘Moral Stages and Moralization: The Cognitive Developmental Approach’, in T. Lechona (ed.), Moral Development and Behavior: Theory Research and Social Issues(Holt Rinehart, and Winston, New York).
Kohut, G. F. and S. E. Corriher: 1994, ‘The Relationship of Age, Gender, Experience and Awareness of Written Ethics Policies to Business Decision-Making’, SAM Advanced Management Journal 59(Winter), 32-39.
Mc Coy, B. H.: 1983, ‘Applying the Acts of Action Oriented Decision Making to the Knotty Issues of Everyday Life’, Management Review 72, 20-24.
Moser, M. R.: 1988, ‘Ethical Conflict at Work: A Critique of the Literature and Recommendations for Future Research’, Journal of Business Ethics 7(5), 381-387.
Nesteruk, J.: 1996, ‘Law Virtue, and the Corporation’, American Business Law Journal 33(3), 473-487.
Nodoushani, O.: 1987, Social Systems Sciences and Politics. Dissertation, University of Pennsylvania.
Noreen, E.: 1988, ‘The Economics of Ethics: A New Perspective on Agency Theory’, Accounting Organizations and Society 13(4), 359-369.
Peters, T. J. and N. Austin.: 1985, A Passion for Excellence(Random House, New York).
Peters, T. J. and T. H. Waterman: 1982, In Search of Excellence(Harper and Row, New York).
Reiss, M. C. and K. Mitra: 1998, ‘The Effects of Individual Difference Factors on the Acceptability of Ethical and Unethical Workplace Behaviors’, Journal of Business Ethics 17(14), 1581-1593.
Rest, J.: 1979, Development in Judging Moral Issues(University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis).
Robin, D. P., E. W. King and R. E. Reidenbach: 1996 ‘The Effects of Attorney's Perceived Duty to Client on their Ethical Decision making Process’, American Business Law Journal 34(2), 277-300.
Schlacter, P. J.: 1990, ‘Organizational Influences on Individual Ethical Behavior in Public Accounting’, Journal of Business Ethics 9(11), 839-853.
Sheidahl, T. K.: 1986, ‘Ethical Dilemmas in Managerial Accounting’, Management Accounting 64, 34-41.
SPSS, Inc.: SPSS for Windows 10.0(SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL.).
Thorne, L.: 2000, ‘The Development of Two Measures to Assess Accountant's Prescriptive and Deliberative Moral Reasoning’, Behavioral Research in Accounting 12, 139-169.
Trevino, L. K.: 1986, ‘Ethical Decision-Making in Organizations: A Person-Situation Interactionist Model’, Academy of Management Review 11(3), 601-617.
Trevino, L. K., K. D. Butterfield and D. L. McCabe: 1998, ‘The Ethical Context in Organizations: Influences on Employee Attitudes and Behaviors’, Business Ethics Quarterly 8(3), 447-476.
Waters, J. A. and P. D. Chant: 1982, ‘Internal Control of Managerial Integrity: Beyond Accounting Systems’, California Management Review 24(3), 60-67.
Weaver, G. R., L. K. Trevino and P. L. Cochran: 1999, ‘Corporate Ethics Practices in the Mid-1990's: An Empirical Study of the Fortune 1000’, Journal of Business Ethics 18(3), 283-294.
Wolfinger, N. H., J. Rabow, and M. D. Newcomb: 1999, ‘The Different Voices of Helping: Gender Differences in Recounting Dilemmas’, Gender Issues 17(13), 70.
Wright, M.: 1995, ‘Can Moral Judgement and Ethical Behavior Be Learned: A Review of the Literature’, Management Decision 33(9), 17-29.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mc Devitt, R., Van Hise, J. Influences in Ethical Dilemmas of Increasing Intensity. Journal of Business Ethics 40, 261–274 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020543929684
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020543929684