Abstract
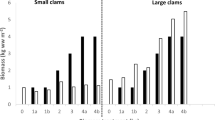
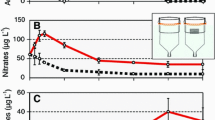
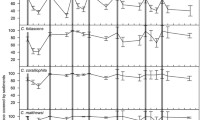
The remarkable biodiversity of the littoral zone of Lake Tanganyika appears to be at risk through increasing sediment input caused by anthropogenic pressures. An in-situ field experiment was done to investigate the effects of increased sediment loads on the size-structure of gastropod communities on a rocky shore site in the lake. Gastropods were removed prior to the addition of sediment, and subsequent further removals were done after seven days and six months. Relative to controls, mean size of individuals of both Lavigeria grandis (Smith) and Lavigeria sp. Q decreased following the addition of sediment, while that of Lavigeria sp. P increased. A subsequent laboratory experiment found that survivorship of larger individuals of Lavigeria grandis was less than smaller individuals in the sediment-impacted treatment. It is hypothesised that decreased algal availability on sediment-impacted rock surface increased starvation of larger snails. Alterations to the size-structure of Lavigeria sp. P populations appear related to intraspecific differences in competitive ability. These results highlight the complex and unpredictable effects of increases in sediment loads on aquatic ecosystems and have implications for the conservation of littoral communities in sediment-impacted areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge, D. W., B. S. Payne & A. C. Miller, 1987. The effects of intermittent exposure to suspended solids and turbulence on three species of freshwater mussels. Environmental Pollution 45: 17–28.
Alin, S. R., A. S. Cohen, R. Bills, M. M. Gashagaza, E. Michel, J. J. Tiercelin, K. Martens, P. Coveliers, S. K. Mboko, K. West, M. Soreghan, S. Kimbadi & G. Ntakimazi, 1999. Effects of landscape disturbance on animal communities in Lake Tanganyika, East Africa. Conservation Biology 13: 1017–1033.
Boles, G. R., 1981. Macroinvertebrate colonization of replacement substrate below a hypolimnial release reservoir. Hydrobiologia 78: 133–146.
Bruton, M. N., 1985. The effects of suspensoids on fish. Hydrobiologia 125: 221–241.
Chutter, F. M., 1969. The effects of sand and silt on the invertebrate fauna of streams and rivers. Hydrobiologia 34: 57–76.
Cohen, A. S., R. Bills, C. Z. Cocquyt & A. G. Caljon, 1993a. The impact of sediment pollution on biodiversity in Lake Tanganyika. Conservation Biology 7: 667–677.
Cohen, A. S., M. J. Soreghan & C. A. Scholz, 1993b. Estimating the age of formation of lakes-an example from Lake Tanganyika, East African Rift system. Geology 21: 511–514.
Cohen, A. S., 1994. Extinction in ancient lakes: biodiversity crises and conservation 40 years after J.L. Brooks. In Martens, K., B. Goddeeris & G. W. Coulter (eds), Speciation in ancient lakes. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Ergebnisse der Limnologie 44, Stuttgart: 451–479.
Cohen, A. S., 1995. Paleoecological approaches to the conservation biology of benthos in ancient lakes: a case study from Lake Tanganyika. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 14: 654–668.
Commito, J. A., S. F. Thrush, R. D. Pridmore, J. E. Hewitt & V. J. Cummings, 1995. Dispersal dynamics in a wind-driven benthic system. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 1513–1518.
Coulter, G.W., 1991. Composition of the flora and fauna. In Coulter, G. W. (ed), Lake Tanganyika and its life. Oxford University Press London: 200–274.
Coulter, G. W., 1994. Lake Tanganyika. In Martens, K., B. Goddeeris & G. W. Coulter (eds), Speciation in ancient lakes. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Ergebnisse der Limnologie 44, Stuttgart: 13–18.
Davies-Colley, R. J., C. W. Hickey, J. M. Quinn & P. A. Ryan, 1992. Effects of clay discharges on streams. 1. Optical properties and epilithon. Hydrobiologia 248: 215–234.
De Roos, A. M., L. Persson & E. McCauley, 2003. The influence of size-dependent life-history traits on the structure and dynamics of populations and communities. Ecology Letters 6: 473–487.
Diggle, P. J., K.-Y. Liang & S. L. Zeger, 1994. Analysis of Longitudinal Data. Oxford Science Publications, Oxford, 253 pp.
Dokulil, M. T., 1994. Environmental control of phytoplankton productivity in turbulent turbid systems. Hydrobiologia 289: 65–72.
Donohue, I. & K. Irvine, 2003. Effects of sediment particle size composition on survivorship of benthic invertebrates from Lake Tanganyika, Africa. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 157: 131–144.
Donohue, I., E. Verheyen & K. Irvine, 2003. In situ experiments on the effects of increased sediment loads on littoral rocky shore communities in Lake Tanganyika, East Africa. Freshwater Biology 48: 1603–1616.
Donohue, I. & K. Irvine, 2004. Seasonal patterns of sediment loading and benthic invertebrate community dynamics in Lake Tanganyika, Africa. Freshwater Biology: 000: 000–000.
Ellis, M. M., 1936. Erosion silt as a factor in aquatic environments. Ecology 17: 29–42.
Emerson, C. W. & J. Grant, 1991. The control of soft-shell clam (Mya arenaria) recruitment on intertidal sandflats by bedload sediment transport. Limnology and Oceanography 36: 1288–1300.
Emson, R. H. & R. J. Faller-Fritsch, 1976. An experimental investigation into the effect of crevice availability on abundance and size-structure in a population of Littorina rudis (Maton): Gastropoda: Prosobranchia. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 23: 285–297.
Gillespie, G. R., 2002. Impacts of sediment loads, tadpole density, and food type on the growth and development of tadpoles of the spotted tree frog Litoria spenceri: an in-stream experiment. Biological Conservation 106: 141–150.
Graham, A. A., 1990. Siltation of stone-surface periphyton in rivers by clay-sized particles from low concentrations in suspension. Hydrobiologia 199: 107–115.
Hart, R. C., 1986. Zooplankton abundance, community structure and dynamics in relation to inorganic turbidity, and their implications for a potential fishery in Lake le Roux, South Africa. Freshwater Biology 16: 351–371.
Hart, R. C., 1988. Zooplankton feeding rates in relation to suspended sediment content: potential influences on community structure in a turbid reservoir. Freshwater Biology 19: 123–139.
Herbert, W. M., J. S. Alabaster, M. C. Dart & R. Lloyd, 1961. The effect of china-clay wastes on trout streams. International Journal of Air and Water Pollution 5: 56–74.
Herbert, W. M. & J. C. Merkens, 1961. The effect of suspended mineral solids on the survival of trout. International Journal of Air and Water Pollution 5: 46–55.
Herbert, W. M. & J. M. Richards, 1963. The growth and survival of fish in some suspensions of solids of industrial origin. International Journal of Air and Water Pollution 7: 297–302.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1970. The Ecology of Running Waters. Liverpool University Press, Liverpool, 555 pp.
Lezzar, K. E., J. J. Tiercelin, M. De Batist, A. S. Cohen, T. Bandora, P. Van Rensbergen, C. Le Turdu, W. Mifundu & J. Klerkx, 1996. New seismic stratigraphy and late Tertiary history of the north Tanganyika Basin, East African rift system, deduced from multichannel and high-resolution reflection seismic data and piston core evidence. Basin Research 8: 1–28.
Lind, O. T., T. H. Chrzanowski & L. Dávalos-Lind, 1997. Clay turbidity and the relative production of bacterioplankton and phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 353: 1–18.
Manirakiza, P., A. Covaci, L. Nizigiymana, G. Ntakimazi & P. Schepens, 2002. Persistent chlorinated pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in selected fish species from Lake Tanganyika, Burundi, Africa. Environmental Pollution 117: 447–455.
Martin, P., B. Goddeeris & K. Martens, 1993. Oxygen concentration profiles in soft-sediment of Lake Baikal (Russia) near the Selenga Delta. Freshwater Biology 29: 343–349.
Martin, P., L. Granina, K. Martens & B. Goddeeris, 1998. Oxygen concentration profiles in sediments of two ancient lakes: Lake Baikal (Siberia, Russia) and Lake Malawi (East Africa). Hydrobiologia 367: 163–174.
McCann, K. S., 2000. The diversity-stability debate. Nature 405: 228–233.
Quinn, J. M., R. J. Davies-Colley, C. W. Hickey, M. L. Vickers & P. A. Ryan, 1992. Effects of clay discharges on streams. 2. Benthic invertebrates. Hydrobiologia 248: 235–247.
Raffaelli, D. G. & R. N. Hughes, 1978. The effects of crevice size and availability on populations of Littorina rudis and Littorina neritoides. Journal of Animal Ecology 47: 71–83.
Richardson, J. & I. G. Jowett, 2002. Effects of sediment on fish communities in East Cape streams, North Island, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 36: 431–442.
Roegner, C., C. Andre, M. Lindegarth, J. E. Eckman & J. Grant, 1995. Transport of recently settled soft-shell clams (Mya arenaria L.) in laboratory flume flow. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 187: 13–26.
Vandelannoote, A., H. Robberecht, H. Deelstra, F. Vyumvuhore, L. Bitetera & F. Ollevier, 1996. The impact of the River Ntahangwa, the most polluted Burundian affluent of Lake Tanganyika, on the water quality of the lake. Hydrobiologia 328: 161–171.
Worthington, E. B. & R. Lowe-McConnell, 1994. African lakes reviewed: creation and destruction of biodiversity. Environmental Conservation 21: 199–213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donohue, I., Irvine, K. Size-specific effects of increased sediment loads on gastropod communities in Lake Tanganyika, Africa. Hydrobiologia 522, 337–342 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000029969.44130.80
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000029969.44130.80