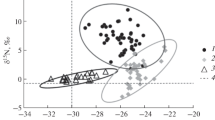
The natural abundance variations in carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios in a population of the earthworm Aporrectodea longa, a species known to feed on both soil and plant litter, is reported in this paper. Worms were collected from a small land area of an old white clover field and body tissue and mucus were analyzed separately. The range of isotopic values was small, but patterns of variation were not random. Tissue carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios were significantly higher in adult than in juvenile A. longa and tissue nitrogen isotope ratios tended to increase with increasing biomass of individuals. Further, carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios were positively correlated in both tissue and mucus. Possible causes of the observed patterns, including physiological effects, body composition and assimilation of C and N from different plant, soil and microbial sources are discussed. It is concluded that the causes of natural variability in isotopic composition must be understood and validated experimentally before natural abundance stable isotope methods can be used for the analysis of trophic relations among detritivorous soil invertebrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arthur D. R. (1965) Form and function in the interpretation of feeding in lumbricid worms. In: Viewpoints in Biology 4 (eds J. D. Carthy & C. L. Duddington) pp. 204–251. Butterworths, London.
Atlavinyte O. & Pociene C. (1973) The effect of earthworms and their activity on the amount of algae in the soil. Pedobiologia 13: 445–455.
Balesdent J. & Mariotti A. (1996) Measurement of soil organic matter turnover using 13C natural abundance. In: Mass Spectrometry of Soils (eds T. W. Boutton & S. Yamasaki) pp. 83–111. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Bernier N. (1998) Earthworm feeding activity and development of the humus profile. Biology and Fertility of Soils 26: 215–223.
Blair J. M., Parmelee R. W., Lavelle P. (1995) Influences of earthworms on biogeochemistry. In: Earthworm Ecology and Biogeography in North America (eds P. F. Hendrix) pp. 127–158. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton.
Bolton P. J. & Phillipson J. (1976) Burrowing, feeding, egestion and energy budgets of Allolobophora rosea (Savigny) (Lumbricidae). Oecologia 23: 225–245.
Bonkowski M. & Schaefer M. (1997) Interactions between earthworms and soil protozoa: a trophic component in the soil food web. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 29: 499–502.
Bouché M. B. (1972). Lombriciens de France: Écologie et Systématique. Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique, Paris (in French).
Bouché M. B., Rafidison Z., Toutain F. (1983) Étude de l’alimentation et du brassage pédo-intestinal du lombricien Nicodrilus velox (Annelida, Lumbricidae) par l’analyse élémentaire. Revue d’Écologie et de Biologie Du Sol 20: 49–75 (in French with English summary).
Bruulsema T. W. & Duxbury J. M. (1996) Simultaneous measurement of soil microbial nitrogen, carbon, and carbon isotope ratio. Soil Science Society of America Journal 60: 1787–1791.
Créach V., Schricke M. T., Bertru G., Mariotti A. (1997) Stable isotopes and gut analyses to determine feeding relationships in saltmarsh macroconsumers. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 44: 599–611.
Dalby P. R., Baker G. H., Smith S. E. (1998) Competition and cocoon consumption by the earthworm Aporrectodea longa. Applied Soil Ecology 10: 127–136.
Edwards C. A. & Fletcher K. E. (1988) Interactions between earthworms and microorganisms in organic-matter breakdown. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 24: 235–247.
Evans A. C. & Guild W. J. McL. (1948) Studies on the relationships between earthworms and soil fertility. IV. On the life cycles of some British Lumbricidae. Annals of Applied Biology 35: 471–484.
Ferrière G. (1980) Fonctions des lombriciens. VII. Une méthode d’analyse de la matière organique végétale ingérée. Pedobiologia 20: 263–273.
France R. (1996) Ontogenetic shift in crayfish δ13C as a measure of land–water ecotonal coupling. Oecologia 107: 239–242.
Fry B. & Parker P. L. (1979) Animal diet in Texas seagrass meadows: δ13C evidence for the importance of benthic plants. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 8: 499–509.
Gannes L. Z., del Rio C. M., Koch P. (1998) Natural abundance variations in stable isotopes and their potential uses in animal physiological ecology [review]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A: Molecular and Integrative Physiology 119: 725–737.
Gates G. E. (1972) Burmese earthworms: An introduction to the systematics and biology of megadrile oligochaetes with special reference to Southeast Asia. Transactions of the American Philosophical Society (New Series) 62(7): 1–326.
Gearing J. N. (1991) The study of diet and trophic relationships through natural abundance 13C. In: Carbon Isotope Techniques (eds D. C. Coleman & B. Fry) pp. 201–218. Academic Press, San Diego.
Gearing J. N., Gearing P. J., Rudnick D. T., Requejo A. G., Hutchins M. J. (1984) Isotopic variability of organic carbon in a phytoplankton-based, temperate estuary. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 48: 1089–1098.
Gerard B. M. (1967) Factors affecting earthworms in pastures. Journal of Animal Ecology 36: 235–252.
Gleixner G., Danier H-J., Werner R. A., Schmidt H-L. (1993) Correlations between the 13C content of primary and secondary plant products in different cell compartments and that in decomposing Basidiomycetes. Plant Physiology 102: 1287–1290.
Goericke R., Montoya J. P., Fry B. (1994) Physiology of isotopic fractionation in algae and cyanobacteria. In: Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science (eds K. Lajtha & R. H. Michener) pp. 187–221. Blackwell Science, Oxford.
Guild W. J. McL. (1955) Earthworms and soil structure. In: Soil Zoology (ed. D. K. McE. Kevan) pp. 83–98. Butterworths, London.
Gunn A. & Cherrett J. M. (1993) The exploitation of food resources by soil meso- and macro-invertebrates. Pedobiologia 37: 303–320.
Haines E. B. & Montague C. L. (1979) Food sources of estuarine invertebrates analyzed using 13C/12C ratios. Ecology 60: 48–56.
Handley L. L. & Scrimgeour C. M. (1997) Terrestrial plant ecology and 15N natural abundance: the present limits to interpretation for uncultivated systems with original data from a Scottish old field. Advances in Ecological Research 27: 133–212.
Havelange S., Lepoint G., Dauby P., Bouquegneau J.-M. (1997) Feeding of the sparid fish Sarpa salpa in a seagrass ecosystem: Diet and carbon flux. Marine Ecology: Pubblicazioni Della Stazione Zoologica Di Napoli I 18: 289–297.
Hendrix P. F. (1996) Nearctic earthworm fauna in the southern USA: Biodiversity and effects on ecosystem processes. Biodiversity and Conservation 5: 223–234.
Hentschel B. T. (1998) Intraspecific variations in δ13C indicate ontogenetic diet changes in deposit-feeding polychaetes. Ecology 79: 1357–1370.
Hoch M. P., Snyder R. A., Cifuentes L. A., Coffin R. B. (1996) Stable isotope dynamics of nitrogen recycled during interactions among marine bacteria and protists. Marine Ecology Progress Series 132: 229–239.
Högberg P., Högbom L., Schinkel H., Högberg M., Johannisson C., Wallmark H. (1996) 15N abundance of surface soils, roots and mycorrhizas in profiles of European forest soils. Oecologia 108: 207–214.
Hyvönen R., Andersson S., Clarholm M., Persson T. (1994) Effects of lumbricids and enchytraeids on nematodes in limed and unlimed coniferous mor humus. Biology and Fertility of Soils 17: 201–205.
Jackson D. & Harkness D. D. (1987) The use and interpretation of δ13C values as a means of establishing dietary composition. Oikos 48: 258–264.
van Kessel C., Farrell R. E., Pennock D. J. (1994) Carbon-13 and nitrogen-15 natural abundance in crop residues and soil organic matter. Soil Science Society of America Journal 58: 382–389.
Kretzschmar A. (1983) Soil transport as a homeostatic mechanism for stabilizing the earthworm environment. In: Earthworm Ecology: From Darwin to Vermiculture (ed. J. E. Satchell) pp. 59–66. Chapman & Hall, London.
Larney F. J. A. (1985) Effects of soil physical conditions, deep loosening and seedbed cultivations on growth and yield of sugar beet. PhD thesis, National University of Ireland, Dublin.
Lavelle P., Lattaud C., Trigo D., Barois I. (1995) Mutualism and biodiversity in soils. Plant and Soil 170: 23–33.
Lavelle P., Pashanasi B., Charpentier F. et al. (1998) Large-scale effects of earthworms on soil organic matter and nutrient dynamics. In: Earthworm Ecology (ed. C. A. Edwards) pp. 103–122. Soil and Water Conservation Society, St. Lucie Press, Boca Raton.
Lindsay D. J., Minagawa M., Mitani I., Kawaguchi K. (1998) Trophic shift in the Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus in its early life history stages as detected by stable isotope ratios in Sagami Bay, Central Japan. Fisheries Science 64: 403–410.
Macko S. A., Lee W. Y., Parker P. L. (1982) Nitrogen and carbon isotope fractionation by two species of marine amphipods: laboratory and field studies. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 63: 145–149.
Marriott C. A., Hudson G., Hamilton D. et al. (1997) Spatial variability of soil total C and N and their stable isotopes in an upland Scottish grassland. Plant and Soil 196: 151–162.
Martin A., Balesdent J., Mariotti A. (1992a) Earthworm diet related to soil organic matter dynamics through 13C measurements. Oecologia 91: 23–29.
Martin A., Mariotti A., Baldesdent J., Lavelle P. (1992b) Soil organic matter assimilation by a geophagous tropical earthworm based on δ13C measurements. Ecology 73: 118–128.
Mary B., Mariotti A., Morel J. L. (1992) Use of 13C variations at natural abundance for studying the biodegradation of root mucilage, roots and glucose in soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 24: 1065–1072.
Miller R. F., Orr G. L., Fritz P., Downer R. G. H., Morgan A. V. (1985) Stable carbon isotope ratios in Periplaneta americana L., the American cockroach. Canadian Journal of Zoology 63: 584–589.
Moody S. A., Briones M. J. I., Piearce T. G., Dighton J. (1995) Selective consumption of decomposing wheat straw by earthworms. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 27: 1209–1213.
Morgan A. J. & Winters C. (1991) Diapause in the earthworm, Aporrectodea longa: morphological and quantitative X-ray microanalysis of cryosectioned chloragogenous tissue. Scanning Microscopy 5: 219–227.
Neilson R., Hamilton D., Wishart J. et al. (1998) Stable isotope natural abundances of soil, plants and soil invertebrates in an upland pasture. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 30: 1773–1782.
Owens N. J. P. (1987) Natural variations in 15N in the marine environment. Advances in Marine Biology 24: 389–451.
Parkinson D. & McLean M. A. (1998) Impacts of earthworms on the community structure of other biota in forest soils. In: Earthworm Ecology (ed. C. A. Edwards) pp. 213–226. Soil and Water Conservation Society, St. Lucie Press, Boca Raton.
Peterson B. J. & Fry B. (1987) Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 18: 293–320.
Piearce T. G. (1978) Gut contents of some lumbricid earthworms. Pedobiologia 18: 153–157.
van Rhee J. A. (1963) Earthworm activities and the breakdown of organic matter in agricultural soils. In: Soil Organisms: Proceedings of the Colloquium on Soil Fauna, Soil Microflora and Their Relationships (eds J. Doeksen & J. van der Drift) pp. 55–59. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam.
Satchell J. E. (1980) r worms and K worms: A basis for classifying lumbricid earthworm strategies. In: Soil Biology as Related to Land Use Practices: Proceedings of the VII International Soil Zoology Colloquium (ed. D. L. Dindal) pp. 848–863. EPA, Washington DC.
Schmidt O. & Ostle N. J. (1999) Tracing nitrogen derived from slurry in earthworms using 15N/14N stable isotope ratios at natural abundances. Applied Soil Ecology 12: 7–13.
Schmidt O., Scrimgeour C. M., Curry J. P. (1999) Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios in body tissue and mucus of feeding and fasting earthworms (Lumbricus festivus). Oecologia 118: 9–15.
Schmidt O., Scrimgeour C. M., Handley L. L. (1997) Natural abundance of 15N and 13C in earthworms from a wheat and a wheat-clover field. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 29: 1301–1308.
Scrimgeour C. M., Gordon S. C., Handley L. L., Woodford J. A. T. (1995) Trophic levels and anomalous δ15N of insects on raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.). Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies 31: 107–115.
Sims R. W. & Gerard B. M. (1985). Earthworms: Keys and Notes for the Identification and Study of the Species. Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series) no. 31. The Linnean Society of London, London.
Slim F. J., Hemminga M. A., Ochieng C., Jannink N. T., de la Morinière E. C., van der Velde G. (1997) Leaf litter removal by the snail Terebralia palustris (Linnaeus) and sesarmid crabs in an East African mangrove forest (Gazi Bay, Kenya). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 215: 35–48.
Sokal R. R. & Rohlf F. J. (1995). Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, 3rd edn. W. H. Freeman, New York.
Spain A. & Le Feuvre R. (1997) Stable C and N isotope values of selected components of a tropical Australian sugarcane ecosystem. Biology and Fertility of Soils 24: 118–122.
Sutoh M., Koyama T., Yoneyama T. (1987) Variations of natural 15N abundances in the tissues and digesta of domestic animals. Radioisotopes 36: 74–77.
Tayasu I. (1998) The use of carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios in termite research. Ecological Research 13: 377–387.
Thielemann U. (1989) Untersuchungen zur Lumbricidenfauna mit neu entwickelten Methoden in erosionsgefährdeten Gebieten des Kraichgaus. PhD thesis, University of Heidelberg, Germany.
Webb S. C., Hedges R. E. M., Simpson S. J. (1998) Diet quality influences the δ13C and δ15N of locusts and their biochemical components. Journal of Experimental Biology 201: 2903–2911.
Wedin D. A., Tieszen L. L., Dewey B., Pastor J. (1995) Carbon isotope dynamics during grass decomposition and soil organic matter formation. Ecology 76: 1383–1392.
Yoneyama T. (1996) Characterization of natural 15N abundance of soils. In: Mass Spectrometry of Soils (eds T. W. Boutton & S. Yamasaki) pp. 205–223. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Yoneyama T., Fujita K., Yoshida T., Matsumoto T., Kambayashi I., Yazaki J. (1986) Variation in natural abundance of 15N among plant parts and in 15N/14N fractionation during N2 fixation in the legume-rhizobia symbiotic system. Plant and Cell Physiology 27: 791–799.
vander Zanden M. J., Hulshof M., Ridgway M. S., Rasmussen J. B. (1998) Application of stable isotope techniques to trophic studies of age-0 smallmouth bass. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 127: 729–739.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, O. Intrapopulation variation in carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios in the earthworm Aporrectodea longa. Ecol Res 14, 317–328 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1703.1999.00310.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1703.1999.00310.x