Abstract
Lipoxygenases are found in animals, plants, and fungi, where they are involved in a wide range of cell-to-cell signaling processes. The presence of lipoxygenases in a number of bacteria and protozoa has been also established, but their biological significance remains poorly understood. Several hypothetical functions of lipoxygenases in bacteria and protozoa have been suggested without experimental validation. The objective of our study was evaluating the functions of bacterial and protozoan lipoxygenases by evolutionary and taxonomic analysis using bioinformatics tools. Lipoxygenase sequences were identified and examined using BLAST, followed by analysis of constructed phylogenetic trees and networks. Our results support the theory on the involvement of lipoxygenases in the formation of multicellular structures by microorganisms and their possible evolutionary significance in the emergence of multicellularity. Furthermore, we observed association of lipoxygenases with the suppression of host immune response by parasitic and symbiotic bacteria including dangerous opportunistic pathogens.










Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 October 2020
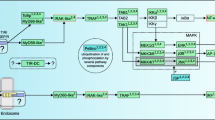
On p. 1051, Fig. 2, legend: instead of “nor” should read “not”.
On p. 1053, Fig. 4, legend: instead of “initial” should read “original”.
On p. 1059, Fig. 7, legend: instead of “initial” should read “original”.
References
Boldyrev, A. A., Kyaivyaryainen, E. I., and Ilyukha, V. A. (2017) Biomembranologiya: Uchebnoe Posobie (Biological Membranes: Manual) INFRA-M, Moscow.
Garreta, A., Val-Moraes, S. P., García-Fernández, Q., Busquets, M., Juan, C., Oliver, A., Ortiz, A., Gaffney, B. J., Fita, I., Manresa, A., and Carpena, X. (2013) Structure and interaction with phospholipids of a prokaryotic lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, FASEB J., 27, 4811-4821, doi: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.13-235952 .
Brash, A. R. (1999) Lipoxygenases: occurrence, functions, catalysis, and acquisition of substrate, J. Biol. Chem., 274, 23679-23682, doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.34.23679 .
Mashima, R., and Okuyama, T. (2015) The role of lipoxygenases in pathophysiology; new insights and future perspectives, Redox Biol., 6, 297-310, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.006 .
Yokomizo, T. (2014) Two distinct leukotriene B4 receptors, BLT1 and BLT2, J. Biochem., 157, 65-71, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvu078 .
Kanaoka, Y., and Boyce, J. A. (2004) Cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors: cellular distribution and function in immune and inflammatory responses, J. Immunol., 173, 1503-1510, doi: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.173.3.1503 .
Powell, W. S., and Rokach, J. (2015) Biosynthesis, biological effects, and receptors of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) and oxoeicosatetraenoic acids (oxo-ETEs) derived from arachidonic acid, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1851, 340-355, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.10.008 .
Kieran, N. E., Maderna, P., and Godson, C. (2004) Lipoxins: potential anti-inflammatory, proresolution, and antifibrotic mediators in renal disease, Kidney Int., 65, 1145-1154, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00487.x .
Brodhun, F., and Feussner, I. (2011) Oxylipins in fungi, FEBS J., 278, 1047-1063, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08027.x .
Heldt, H.-W. (2011) Plant Biochemistry, Academic Press, London.
Wasternack, C. (2007) Jasmonates: an update on biosynthesis, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development, Ann. Bot., 100, 681-697, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm079 .
Andreou, A., Brodhun, F., and Feussner, I. (2009) Biosynthesis of oxylipins in non-mammals, Prog. Lipid Res., 48, 148-170, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2009.02.002 .
De León, I. P., Hamberg, M., and Castresana, C. (2015) Oxylipins in moss development and defense, Front. Plant. Sci., 6, 483, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00483 .
Horn, T., Adel, S., Schumann, R., Sur, S., Kakularam, K. R., Polamarasetty, A., Redanna, P., Kuhn, H., and Heydeck, D. (2015) Evolutionary aspects of lipoxygenases and genetic diversity of human leukotriene signaling, Prog. Lipid Res., 57, 13-39, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2014.11.001 .
Andreou, A. Z., Vanko, M., Bezakova, L., and Feussner, I. (2008) Properties of a mini 9R-lipoxygenase from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120 and its mutant forms, Phytochemistry, 69, 1832-1837, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.03.002 .
Lang, I., Göbel, C., Porzel, A., Heilmann, I., and Feussner, I. (2008) A lipoxygenase with linoleate diol synthase activity from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120, Biochem. J., 410, 347-357, doi: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20071277 .
Wang, X., Lu, F., Zhang, C., Lu, Y., Bie, X., Ren, D., and Lu, Z. (2014) Peroxidation radical formation and regiospecificity of recombinated Anabaena sp. lipoxygenase and its effect on modifying wheat proteins, J. Agric. Food. Chem., 62, 1713-1719, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jf405425c .
An, J. U., Hong, S. H., and Oh, D. K. (2018) Regiospecificity of a novel bacterial lipoxygenase from Myxococcus xanthus for polyunsaturated fatty acids, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids, 1863, 823-833, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.04.014 .
Vance, R. E., Hong, S., Gronert, K., Serhan, C. N., and Mekalanos, J. J. (2004) The opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa carries a secretable arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 2135-2139, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0307308101 .
Banthiya, S., Kalms, J., Yoga, E. G., Ivanov, I., Carpena, X., Hamberg, M., Kuhn, H., and Scheerer, P. (2016) Structural and functional basis of phospholipid oxygenase activity of bacterial lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1861, 1681-1692, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.08.002 .
Porta, H., and Rocha-Sosa, M. (2001) Lipoxygenase in bacteria: a horizontal transfer event? Microbiology, 147, 3199-3200, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-147-12-3199 .
Koeduka, T., Kajiwara, T., and Matsui, K. (2007) Cloning of lipoxygenase genes from a cyanobacterium, Nostoc punctiforme, and its expression in Eschelichia coli, Curr. Microbiol., 54, 315-319, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-006-0512-9 .
Dar, H. H., Tyurina, Y. Y., Mikulska-Ruminska, K., Shrivastava, I., Ting, H. C., et al. (2019) Pseudomonas aeruginosa utilizes host polyunsaturated phosphatidylethanolamines to trigger theft-ferroptosis in bronchial epithelium, J. Clin. Invest., 128, 4639-4653, doi: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI99490 .
Goloshchapova, K., Stehling, S., Heydeck, D., Blum, M., and Kuhn, H. (2019) Functional characterization of a novel arachidonic acid 12S-lipoxygenase in the halotolerant bacterium Myxococcus fulvus exhibiting complex social living patterns, MicrobiologyOpen, 8, e00775, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.775 .
Hansen, J., Garreta, A., Benincasa, M., Fusté, M. C., Busquets, M., and Manresa, A. (2013) Bacterial lipoxygenases, a new subfamily of enzymes? A phylogenetic approach, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 97, 4737-4747, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4887-9 .
Altschul, S. F., Madden, T. L., Schäffer, A. A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., and Lipman, D. J. (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs, Nucleic Acids Res., 25, 3389-3402, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389 .
UniProt Consortium (2018) UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase, Nucleic Acids Res., 46, 2699, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky092 .
Yoshimoto, T., Yamamoto, Y., Arakawa, T., Suzuki, H., Yamamoto, S., Yokoyama, C., Tanabe, T., and Toh, H. (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of human arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 172, 1230-1235, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(90)91580-l .
Hörnsten, L., Su, C., Osbourn, A. E., Hellman, U., and Oliw, E. H. (2002) Cloning of the manganese lipoxygenase gene reveals homology with the lipoxygenase gene family, Eur. J. Biochem., 269, 2690-2697, doi: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02936.x .
Vidal-Mas, J., Busquets, M., and Manresa, A. (2005) Cloning and expression of a lipoxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa 42A2, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 87, 245-251, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-004-4021-1 .
Marchler-Bauer, A., and Bryant, S. H. (2004) CD-Search: protein domain annotations on the fly, Nucleic Acids Res., 32 (suppl. 2), W327-W331, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh454 .
Marchler-Bauer, A., Bo, Y., Han, L., He, J., Lanczycki, C. J., et al. (2017) CDD/SPARCLE: functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures, Nucleic Acids Res., 45, D200-D203, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1129 .
Katoh, K., Rozewicki, J., and Yamada, K. D. (2019) MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization, Brief. Bioinform., 20, 1160-1166, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx108 .
Kuraku, S., Zmasek, C. M., Nishimura, O., and Katoh, K. (2013) aLeaves facilitates on-demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity, Nucleic Acids Res., 41, W22-W28, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt389 .
Katoh, K., Misawa, K., Kuma, K. I., and Miyata, T. (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform, Nucleic Acids Res., 30, 3059-3066, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf436 .
Gouveia-Oliveira, R., Sackett, P. W., and Pedersen, A. G. (2007) MaxAlign: maximizing usable data in an alignment, BMC Bioinformatics, 8, 312, doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-8-312 .
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., and Tamura, K. (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms, Mol. Biol. Evol., 35, 1547-1549, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096 .
Letunic, I., and Bork, P. (2016) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees, Nucleic Acids Res., 44, W242-W245, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw290 .
Huson, D. H., and Bryant, D. (2006) Application of phylogenetic networks in evolutionary studies, Mol. Biol. Evol., 23, 254-267, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msj030 .
Schirrmeister, B. E., Antonelli, A., and Bagheri, H. C. (2011) The origin of multicellularity in cyanobacteria, BMC Evol. Biol., 11, 45, doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-45 .
Elhai, J., and Khudyakov, I. (2018) Ancient association of cyanobacterial multicellularity with the regulator HetR and an RGSGR pentapeptide‐containing protein (PatX), Mol. Microbiol., 110, 931-954, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14003 .
Martínez, E., Cosnahan, R. K., Wu, M., Gadila, S. K., Quick, E. B., Mobley, J. A., and Campos-Gómez, J. (2019) Oxylipins mediate cell-to-cell communication in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Commun. Biol., 2, 1-10, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0310-0 .
An, J. U., and Oh, D. K. (2018) Stabilization and improved activity of arachidonate 11S-lipoxygenase from proteobacterium Myxococcus xanthus, J. Lipid Res., 59, 2153-2163, doi: https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M088823 .
Basu, S., Fey, P., Pandit, Y., Dodson, R., Kibbe, W. A., and Chisholm, R. L. (2012) DictyBase 2013: integrating multiple Dictyostelid species, Nucleic Acids Res., 41, D676-D683, doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1064 .
Levinson, W. (2008) Medical Microbiology and Immunology, 8th Edn., McGraw-Hill/Appleton & Lange, New York.
Boitsov, A. G., and Vasil’ev, O. D. (2013) Klinicheskaya Laboratornaya Diagnostika: Natsional’noe Rukovodstvo (Dolgov, V. V., and Menshikov, V. V., eds.) GEOTAR-Media, Moscow, pp. 380-388.
Kaftyreva, L. A., Boitsov, A. G., and Makarova M. A. (2013) Klinicheskaya Laboratornaya Diagnostika: Natsional’noe Rukovodstvo (Dolgov, V. V., and Menshikov, V. V., eds.) GEOTAR-Media, Moscow, pp. 342-365.
Totolyan, A. A., Burova, L. A., Dmitriev, A. V., and Suvorov, A. N. (2013) Klinicheskaya Laboratornaya Diagnostika: Natsional’noe Rukovodstvo (Dolgov, V. V., and Menshikov, V. V., eds.) GEOTAR-Media, Moscow, pp. 417-435.
Van’t Wout, E. F., van Schadewijk, A., van Boxtel, R., Dalton, L. E., Clarke, H. J., Tommassen, J., Marciniak, S. J., and Hiemstra, P. S. (2015) Virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa induce both the unfolded protein and integrated stress responses in airway epithelial cells, PLoS Pathog., 11, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004946 .
Stoyanova, M., Pavlina, I., Moncheva, P., and Bogatzevska, N. (2007) Biodiversity and incidence of Burkholderia species, Biotechnology and Biotechnological Equipment, 21, 306-310, doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2007.10817465 .
Antunes, L., Visca, P., and Towner, K. J. (2014) Acinetobacter baumannii: evolution of a global pathogen, Pathog. Dis., 71, 292-301, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/2049-632X.12125 .
Davin-Regli, A. (2015) Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae; versatile bacterial pathogens confronting antibiotic treatment, Front. Microbiol., 6, 392, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00392 .
Lebeaux, D., Lanternier, F., Degand, N., Catherinot, E., Podglajen, I., Rubio, M. T., Suarez, F., Lecuit, M., Mainardi, J.-L., and Lortholary, O. (2010) Nocardia pseudobrasiliensis as an emerging cause of opportunistic infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, J. Clin. Microbiol., 48, 656-659, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01244-09 .
Baba, H., Nada, T., Ohkusu, K., Ezaki, T., Hasegawa, Y., and Paterson, D. L. (2009) First case of bloodstream infection caused by Rhodococcus erythropolis, J. Clin. Microbiol., 47, 2667-2669, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00294-09 .
Hong, S. K., Lee, J. S., and Kim, E. C. (2015) First Korean case of Cedecea lapagei pneumonia in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Ann. Lab. Med., 35, 266-268, doi: https://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.2.266 .
Herrera, V. R. C., De Silva, M. F. R., Alcaraz, H. O., Espiritu, G. C., Peña, K. C., and Melnikov, V. (2018) Death related to Cedecea lapagei in a soft tissue bullae infection: a case report, J. Med. Case Rep., 12, 328, doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1866-x .
Vandamme, P., Peeters, C., De Smet, B., Price, E. P., Sarovich, D. S., Henry, D. A., Hird, T. J., Zlosnik, J. E. A., Mayo, M., Warner, J., Baker, A., Currie, B. J., and Carlier, A. (2017) Comparative genomics of Burkholderia singularis sp. nov., a low G+C content, free-living bacterium that defies taxonomic dissection of the genus Burkholderia, Front. Microbiol., 8, 1679, doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01679 .
De Smet, B., Mayo, M., Peeters, C., Zlosnik, J. E., Spilker, T., Hird, T. J., LiPuma, J. J., Kidd, T. J., Kaestli, M., Ginther, J. L., Wagner, D. M., Keim, P., Bell, S. C., Jacobs, J. A., Currie, B. J., and Vandamme, P. (2015) Burkholderia stagnalis sp. nov. and Burkholderia territorii sp. nov., two novel Burkholderia cepacia complex species from environmental and human sources, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 65, 2265-2271, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.000251 .
Segonds, C., Clavel-Batut, P., Thouverez, M., Grenet, D., Le Coustumier, A., Plésiat, P., and Chabanon, G. (2009) Microbiological and epidemiological features of clinical respiratory isolates of Burkholderia gladioli, J. Clin. Microbiol., 47, 1510-1516, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02489-08 .
Quon, B. S., Reid, J. D., Wong, P., Wilcox, P. G., Javer, A., Wilson, J. M., and Levy, R. D. (2011) Burkholderia gladioli – a sessorictor of poor outcome in cystic fibrosis patients who receive lung transplants? A case of locally invasive rhinosinusitis and persistent bacteremia in a 36-year-old lung transplant recipient with cystic fibrosis, Can. Respir. J., 18, e64-e65, doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/304179 .
Imataki, O., Kita, N., Nakayama-Imaohji, H., Kida, J. I., Kuwahara, T., and Uemura, M. (2014) Bronchiolitis and bacteraemia caused by Burkholderia gladioli in a non-lung transplantation patient, New Microbes New Infect., 2, 175, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/nmi2.64 .
Haraga, A., West, T. E., Brittnacher, M. J., Skerrett, S. J., and Miller, S. I. (2008) Burkholderia thailandensis as a model system for the study of the virulence-associated type III secretion system of Burkholderia pseudomallei, Infect. Immun., 76, 5402-5411, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00626-08 .
Thatcher, L. F., Myers, C. A., O’Sullivan, C. A., and Roper, M. M. (2017) Draft genome sequence of Rhodococcus sp. strain 66b, Genome Announc., 5, e00229-17, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00229-17 .
Han, J. I., Spain, J. C., Leadbetter, J. R., Ovchinnikova, G., Goodwin, L. A., Han, C. S., Woyke, T., Davenport, K. W., and Orwin, P. M. (2013) Genome of the root-associated plant growth-promoting bacterium Variovorax paradoxus strain EPS, Genome Announc., 1, e00843-13, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00843-13 .
Han, J. I., Choi, H. K., Lee, S. W., Orwin, P. M., Kim, J., LaRoe, S. L., Kim, T.-G., O’Neil, J., Leadbetter, J. R., Lee, S. Y., Hur, C.-G., Spain, J. C., Ovchinnikova, G., Goodwin, L., and Han, C. (2011) Complete genome sequence of the metabolically versatile plant growth-promoting endophyte Variovorax paradoxus S110, J. Bacteriol., 193, 1183-1190, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00925-10 .
Chung, E. J., Park, J. A., Jeon, C. O., and Chung, Y. R. (2015) Gynuella sunshinyii gen. nov., sp. nov., an antifungal rhizobacterium isolated from a halophyte, Carex scabrifolia Steud, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 65, 1038-1043, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.000060 .
Gibb, A. P., Martin, K. M., Davidson, G. A., Walker, B., and Murphy, W. G. (1995) Rate of growth of Pseudomonas fluorescens in donated blood, J. Clin. Pathol., 48, 717-718, doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.48.8.717 .
Gershman, M. D., Kennedy, D. J., Noble-Wang, J., Kim, C., Gullion, J., Kacica, M., Jensen, B., Pascoe, N., Saiman, L., McHale, J., Wilkins, M., Schoonmaker-Bopp, D., Clayton, J., Arduino, M., Srinivasan, A., and Pseudomonas fluorescens Investigation Team (2008) Multistate outbreak of Pseudomonas fluorescens bloodstream infection after exposure to contaminated heparinized saline flush prepared by a compounding pharmacy, Clin. Infect. Dis., 47, 1372-1379, doi: https://doi.org/10.1086/592968 .
Walker, T. S., Bais, H. P., Déziel, E., Schweizer, H. P., Rahme, L. G., Fall, R., and Vivanco, J. M. (2004) Pseudomonas aeruginosa-plant root interactions. Pathogenicity, biofilm formation, and root exudation, Plant Physiol., 134, 320-331, doi: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.027888 .
Rahme, L. G., Ausubel, F. M., Cao, H., Drenkard, E., Goumnerov, B. C., Lau, G. W., Mahajan-Miklos, S., Plotnikova, J., Tan, M. W., Tsongalis, J., Walendziewicz, C. L., and Tompkins, R. G. (2000) Plants and animals share functionally common bacterial virulence factors, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 8815-8821, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.16.8815 .
Van Baarlen, P., Van Belkum, A., Summerbell, R. C., Crous, P. W., and Thomma, B. P. (2007) Molecular mechanisms of pathogenicity: how do pathogenic microorganisms develop cross-kingdom host jumps?, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 31, 239-277, doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00065.x .
Relman, D. A., and Falkow, S. (2015) A molecular perspective of microbial pathogenicity, in Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Eighth Edition (Bennett, J. E., Dolin, R., and Blaser, M. J., eds.) Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, pp. 1-10.
Singh, A., Vaidya, B., Khatri, I., Srinivas, T. N. R., Subramanian, S., Korpole, S., and Pinnaka, A. K. (2014) Grimontia indica AK16T, sp. nov., isolated from a seawater sample reports the presence of pathogenic genes similar to Vibrio genus, PLoS One, 9, e85590, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085590 .
Nakai, R., Fujisawa, T., Nakamura, Y., Baba, T., Nishijima, M., Karray, F., Sami Sayadi, S., Isoda, N., Naganuma, T., and Niki, H. (2016) Genome sequence and overview of Oligoflexus tunisiensis Shr3 T in the eighth class Oligoflexia of the phylum Proteobacteria, Stand. Genomic. Sci., 11, 90, doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40793-016-0210-6 .
Nishijima, M., Adachi, K., Katsuta, A., Shizuri, Y., and Yamasato, K. (2013) Endozoicomonas numazuensis sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from marine sponges, and emended description of the genus Endozoicomonas Kurahashi and Yokota 2007, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 63, 709-714, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.042077-0 .
Schmidt, E. W., Obraztsova, A. Y., Davidson, S. K., Faulkner, D. J., and Haygood, M. G. (2000) Identification of the antifungal peptide-containing symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei as a novel δ-proteobacterium,“Candidatus Entotheonella palauensis”, Marine Biol., 136, 969-977, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270000273 .
McCauley, E. P., Haltli, B., and Kerr, R. G. (2015) Description of Pseudobacteriovorax antillogorgiicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from the gorgonian octocoral Antillogorgia elisabethae, belonging to the family Pseudobacteriovoracaceae fam. nov., within the order Bdellovibrionales, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 65, 522-530, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.066266-0 .
Thompson, F. L., Thompson, C. C., Naser, S., Hoste, B., Vandemeulebroecke, K., Munn, C., Bourne, D., and Swings, J. (2005) Photobacterium rosenbergii sp. nov. and Enterovibrio coralii sp. nov., vibrios associated with coral bleaching, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 55, 913-917, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63370-0 .
Pascual, J., Macian, M. C., Arahal, D. R., Garay, E., and Pujalte, M. J. (2009) Description of Enterovibrio nigricans sp. nov., reclassification of Vibrio calviensis as Enterovibrio calviensis comb. nov. and emended description of the genus Enterovibrio Thompson et al. 2002, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 59, 698-704, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.001990-0 .
Thompson, F. L., Hoste, B., Thompson, C. C., Goris, J., Gomez-Gil, B., Huys, L., De Los, P., and Swings, J. (2002) Enterovibrio norvegicus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the gut of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) larvae: a new member of the family Vibrionaceae, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 52, 2015-2022, doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-6-2015 .
URL: https://thefishsite.com/articles/nocardia-seriolae-a-chronic-problem.
Hurst, S., Rowedder, H., Michaels, B., Bullock, H., Jackobeck, R., Abebe-Akele, F., Durakovic, U., Gately, J., Janicki, E., and Tisa, L. S. (2015) Elucidation of the Photorhabdus temperata genome and generation of a transposon mutant library to identify motility mutants altered in pathogenesis, J. Bacteriol., 197, 2201-2216, doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00197-15 .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest in financial or any other sphere. This article does not contain any studies with animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurakin, G.F., Samoukina, A.M. & Potapova, N.A. Bacterial and Protozoan Lipoxygenases Could be Involved in Cell-to-Cell Signaling and Immune Response Suppression. Biochemistry Moscow 85, 1048–1063 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920090059
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297920090059