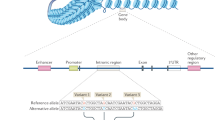
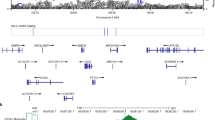
Abstract—Currently only a small fraction of the proteins encoded in the human genome serve as pharmaceutical targets. Genome-wide association studies are a powerful tool to uncover new genetic loci responsible for predisposition to complex diseases, such as autoimmune disorders. However, further work is still required to identify causative single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which directly mediate the disease risk at these loci, and to determine their target genes. These genes can be located millions base pairs away from the regulatory SNPs. Here, by using bioinformatic tools and databases, we identified five intergenic autoimmunity-associated polymorphisms with high probability of being causative, for which the target genes are still unknown. We tested their ability to influence gene expression using luciferase reporter system. The polymorphism rs6832151 affected the reporter expression in the CEM human T-cell line upon the highest enhancer activity. Target genes of this SNP could be further identified by introducing point mutations to the genome and comparison of transcriptomes of the derivative cell sublines carrying alternative alleles of rs6832151.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Gutierrez-Arcelus M., Rich S.S., Raychaudhuri S. 2016. Autoimmune diseases: Connecting risk alleles with molecular traits of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Genet. 17 (3), 160.
Theofilopoulos A.N., Kono D.H., Baccala R. 2017. The multiple pathways to autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol.18 (7), 716.
Costenbade K.H., Gay S., Alarcón-Riquelme M.E., Iaccarino L., Doria A. 2012. Genes, epigenetic regulation and environmental factors: which is the most relevant in developing autoimmune diseases? Autoimmun. Rev.11 (8), 604–609.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Australo-Anglo-American Spondylitis Consortium (TASC), Burton P.R., Clayton D.G., Cardon L.R., Craddock N., Deloukas P., Duncanson A., Kwiatkowski D.P., McCarthy M.I., Ouwehand W.H., Samani N.J., Todd J.A., Donnelly P., et al. 2007. Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat. Genet.39 (11), 1329.
Farh K.K.H., Marson A., Zhu J., Kleinewietfeld M., Housley W.J., Beik S., Shoresh N., Whitton H., Ryan R.J.H., Shishkin A.A., Hatan M., Carrasco-Alfonso M.J., Mayer D., Luckey C.J., Patsopoulos N.A., et al. 2015. Genetic and epigenetic fine mapping of causal autoimmune disease variants. Nature. 518 (7539), 337–343.
Zhu Y., Tazearslan C., Suh Y. 2017. Challenges and progress in interpretation of non-coding genetic variants associated with human disease. Exp. Biol. Med.242 (13), 1325–1334.
Gallagher M.D., Chen-Plotkin A.S. 2018. The post-GWAS era: From association to function. Am. J. Hum. Genet.102 (5), 717–730.
Murphy A., Chu J.H., Xu M., Carey V.J., Lazarus R., Liu A., Szefler S.J., Strunk R., Demuth K., Castro M., Hansel N.N., Diette G.B., Vonakis B.M., Adkin-son N.F.J., Klanderman B.J., et al. 2010. Mapping of numerous disease-associated expression polymorphisms in primary peripheral blood CD4+ lymphocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet.19 (23), 4745–4757.
Spain S.L., Barrett J.C. 2015. Strategies for fine-mapping complex traits. Hum. Mol. Genet.24 (R1), R111–R119.
ENCODE Project Consortium. 2012. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature. 489 (7414), 57–74.
Gorbacheva A.M., Korneev K.V., Kuprash D.V., Mitkin N.A. 2018. The risk G allele of the single-nucleotide polymorphism rs928413 creates a CREB1-binding site that activates IL33 Promoter in lung epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19 (10), 2911.
Bernstein B.E., Stamatoyannopoulos J.A., Costello J.F., Ren B., Milosavljevic A., Meissner A., Kellis M., Marra M.A., Beaudet A.L., Ecker J.R., Farnham P.J., Hirst M., Lander E.S., Mikkelsen T.S., Thomson J.A. 2010. The NIH roadmap epigenomics mapping consortium. Nat. Biotechnol.28 (10), 1045–1048.
Vorontsov I.E., Kulakovskiy I.V., Khimulya G., Nikolaeva D.D., Makeev V.J. 2015. PERFECTOS-APE ‒ Predicting regulatory functional effect of SNPs by approximate P-value estimation. In International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms, vol. 2. SCITEPRESS, pp. 102–108.
Kulakovskiy I.V., Vorontsov I.E., Yevshin I.S., Sharipov R.N., Fedorova A.D., Rumynskiy E.I., Medvedeva Y.A., Magana-Mora A., Bajic V.B., Papatsenko D.A., Kolpakov F.A., Makeev V.J. 2018. HOCOMOCO: Towards a complete collection of transcription factor binding models for human and mouse via large-scale ChIP-Seq analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.46 (D1), D252–D259.
Sandelin A., Alkema W., Engström P., Wasserman W.W., Lenhard B. 2004. JASPAR: An open-access database for eukaryotic transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res.32 (Suppl. 1), D91–D94.
Jolma A., Kivioja T., Toivonen J., Cheng L., Wei G., Enge M., Taipale M., Vaquerizas J.M., Yan J., Sillanpää M.J., Bonke M., Palin K., Talukder S., Hughes T.R., Luscombe N.M., et al. 2010. Multiplexed massively parallel SELEX for characterization of human transcription factor binding specificities. Genome Res.20 (6), 861–873.
Pogulis R.J., Vallejo A.N., Pease L.R. 1996. In vitro recombination and mutagenesis by overlap extension PCR. In: In Vitro Mutagenesis Protocols. Humana Press, pp. 167–176
Ustiugova A.S., Korneev K.V., Kuprash D.V., Afanasyeva M.A. 2019. Functional SNPs in the human autoimmunity-associated locus 17q12-21. Genes (Basel). 10 (2), 77.
Korneev K.V., Sviriaeva E.N., Mitkin N.A., Gorbacheva A.M., Uvarova A.N., Ustiugova A.S., Polanovsky O.L., Kulakovskiy I.V., Afanasyeva M.A., Schwartz A.M., Kuprash D.V. 2020. Minor C allele of the SNP rs7873784 associated with rheumatoid arthritis and type-2 diabetes mellitus binds PU.1 and enhances TLR4 expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta: Mol. Basis Dis.1866 (3), 165626.
Mitkin N.A., Muratova A.M., Korneev K.V., Pavshintsev V.V., Rumyantsev K.A., Vagida M.S., Uvarova A.N., Afanasyeva M.A., Schwartz A.M., Kuprash D.V. 2018. Protective C allele of the single-nucleotide polymorphism rs1335532 is associated with strong binding of Ascl2 transcription factor and elevated CD58 expression in B-cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta: Mol. Basis Dis.1864 (10), 3211–3220.
Buckley M., Gjyshi A., Mendoza-Fandiño G., Baskin R., Carvalho R.S., Carvalho M.A., Woods N.T., Monteiro A.N. 2016. Enhancer scanning to locate regulatory regions in genomic loci. Nat. Protoc.11 (1), 46.
Kotelnikova E., Kiani N.A., Messinis D., Pertsovskaya I., Pliaka V., Bernardo-Faura M., Rinas M., Vila G., Zubizarreta I., Pulido-Valdeolivas I., Sakellaropoulos T., Faigle W., Silberberg G., Masso M., Stridh P., et al. 2019. MAPK pathway and B cells overactivation in multiple sclerosis revealed by phosphoproteomics and genomic analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.116 (19), 9671–9676.
Schmiedel B.J., Singh D., Madrigal A., Valdovino-Gonzalez A.G., White B.M., Zapardiel-Gonzalo J., Ha B., Altay G., Greenbaum J.A., McVicker G., Seumois G., Rao A., Kronenberg M., Peters B., Vijayanand P. 2018. Impact of genetic polymorphisms on human immune cell gene expression. Cell. 175 (6), 1701–1715.
GTEx Consortium. 2013. The genotype-tissue expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet.45 (6), 580.
Yevshin I., Sharipov R., Kolmykov S., Kondrakhin Y., Kolpakov F. 2019. GTRD: A database on gene transcription regulation—2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res.47 (D1), D100–D105.
Chandra J., Kuo P.T., Hahn A.M., Belz G.T., Frazer I.H. 2017. Batf3 selectively determines acquisition of CD8+ dendritic cell phenotype and function. Immunol. Cell Biol.95 (2), 215–223.
Almuttaqi H., Udalova I.A. 2019. Advances and challenges in targeting IRF5, a key regulator of inflammation. FEBS J.286 (9), 1624–1637.
Cortes A., Brown M.A. 2011. Promise and pitfalls of the Immunochip. Arthritis Res. Ther.13 (1), 101.
Corradin O., Saiakhova A., Akhtar-Zaidi B., Myeroff L., Willis J., Cowper-Sal R., Lupien M., Markowitz S., Scacheri P.C. 2014. Combinatorial effects of multiple enhancer variants in linkage disequilibrium dictate levels of gene expression to confer susceptibility to common traits. Genome Res.24 (1), 1–13.
Sanyal A., Lajoie B.R., Jain G., Dekker J. 2012. The long-range interaction landscape of gene promoters. Nature. 489 (7414), 109–113.
Szymański K., Bednarczuk T., Krajewski P., Płoski R. 2012. The replication of the association of the rs6832151 within chromosomal band 4p14 with Graves’ disease in a Polish Caucasian population. Tissue Antigens. 79 (5), 380–383.
Chu X., Pan C.M., Zhao S.X., Liang J., Gao G.Q., Zhang X.M., Yuan G.Y., Li C.G., Xue L.Q., Shen M., Liu W., Xie F., Yang S.Y., Wang H.F., Shi J.Y., et al. 2011. A genome-wide association study identifies two new risk loci for Graves’ disease. Nat. Genet.43 (9), 897.
Cooper J.D., Simmonds M.J., Walker N.M., Burren O., Brand O.J., Guo H., Wallace C., Stevens H., Coleman G., Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Franklyn J.A., Todd J.A., Gough S.C.L. 2012. Seven newly identified loci for autoimmune thyroid disease. Hum. Mol. Genet.21 (23), 5202–5208.
Van der Meer L.T., Jansen J.H., Van Der Reijden B.A. 2010. Gfi1 and Gfi1b: Key regulators of hematopoiesis. Leukemia. 24 (11), 1834.
Ghandi M., Huang F.W., Jané-Valbuena J., Kryukov G.V., Lo C.C., McDonald E.R., Barretina J., Gelfand E.T., Bielski C.M., Li H., Hu K., Andreev-Drakhlin A.Y., Kim J., Hess J.M., Haas B.J., et al. 2019. Next-generation characterization of the cancer cell line encyclopedia. Nature. 569 (7757), 503–508.
Foley G.E., Lazarus H., Farber S., Uzman B.G., Boone B.A., McCarthy R.E. 1965. Continuous culture of human lymphoblasts from peripheral blood of a child with acute leukemia. Cancer. 18 (4), 522–529.
Schneider U., Schwenk H.U., Bornkamm G. 1977. Characterization of EBV-genome negative “null” and “T” cell lines derived from children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and leukemic transformed non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer. 19 (5), 621–626.
Hamano R., Wu X., Wang Y., Oppenheim J.J., Chen X. 2015. Characterization of MT-2 cells as a human regulatory T cell-like cell line. Cell. Mol. Immunol.12 (6), 780–782.
Matsuo Y., Drexler H.G. 1998. Establishment and characterization of human B cell precursor-leukemia cell lines. Leuk. Res. 22 (7), 567–579.
Pistillo M.P., Tanigaki N., Mazzoleni O., Ciccone E., Hämmerling U., Park M., Terasaki P.I., Ferrara, G.B. 1987. Human lymphoblastoid cell lines secreting antibodies with restricted HLA specificity. Immunogenetics. 25 (3), 145–151.
Karpova M.B., Schoumans J., Ernberg I., Henter J.I., Nordenskjöld M., Fadeel B. 2005. Raji revisited: cytogenetics of the original Burkitt’s lymphoma cell line. Leukemia. 19 (1), 159–161.
Klein G., Lindahl T., Jondal M., Leibold W., Menézes J., Nilsson K., Sundström C. 1974. Continuous lymphoid cell lines with characteristics of B cells (bone-marrow-derived), lacking the Epstein–Barr virus genome and derived from three human lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.71 (8), 3283–3286.
Sundström C., Nilsson K. 1976. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int. J. Cancer.17 (5), 565–577.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are especially grateful to I.E. Vorontsov for help in editing and designing this acticle.
Funding
The study was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 18-75-00072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
This study does not contain any research involving humans or animals as research objects.
Conflict of interest. The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary materials are available for this article at https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320040160 and are accessible for authorized users.
Additional information
Abbreviations: TF, transcription factor; eQTL, expression quantitative trait loci; GWAS, Genome-wide association studies; GFI1, Growth Factor Independent 1 Transcriptional Repressor; PICS, Probabilistic Identification of Causal SNPs; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; H3K27Ac, acetylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 protein subunit; ENCODE, Encyclopedia of DNA Elements.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ustiugova, A.S., Afanasyeva, M.A. Noncoding Polymorphism rs6832151 Is an Attractive Candidate for Genome Editing Aimed at Finding New Molecular Mechanisms of Autoimmune Diseases. Mol Biol 54, 730–738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320040160
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893320040160